Adenoassociated virus vectors for the treatment of mucopolysaccharidoses
A vector and variant technology, applied in the vector and nucleic acid sequence for the treatment of mucopolysaccharidosis type IIID or Sanfilippo syndrome D type, in the field of treatment of mucopolysaccharidosis, which can solve the problem of limiting the long-term efficacy of products, volume difficulties, and no Application of MPSⅢD and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0192] Example 1: Construction of pAAV-CAG-hGNS
[0193] The CDS of human glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase (NCBI reference sequence: NM_002076.3) was used as starting material and chemically synthesized for the stated purpose (GeneArt; Life Technologies). Acceptance CDS were cloned in plasmid pMA-RQ(AmpR) flanked by MluI and EcoRI restriction sites at 5' and 3', respectively.
[0194] The MluI / EcoRI human glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase CDS fragment was excised from the pMA-RQ plasmid and subsequently cloned into the MluI and EcoRI restriction sites of the AAV backbone plasmid pAAV-CAG between. The resulting plasmid was named pAAV-CAG-hGNS (accession number DSM 32342). see figure 1 A and SEQ ID NO:5 in.
[0195] The AAV backbone plasmid pAAV-CAG used here has been previously generated and contains the ITR from the AAV2 genome, the CAG promoter and the polyA signal from rabbit β-globin, and a multiple cloning site for cloning the CDS of interest. The CAG promoter is a...
Embodiment 2
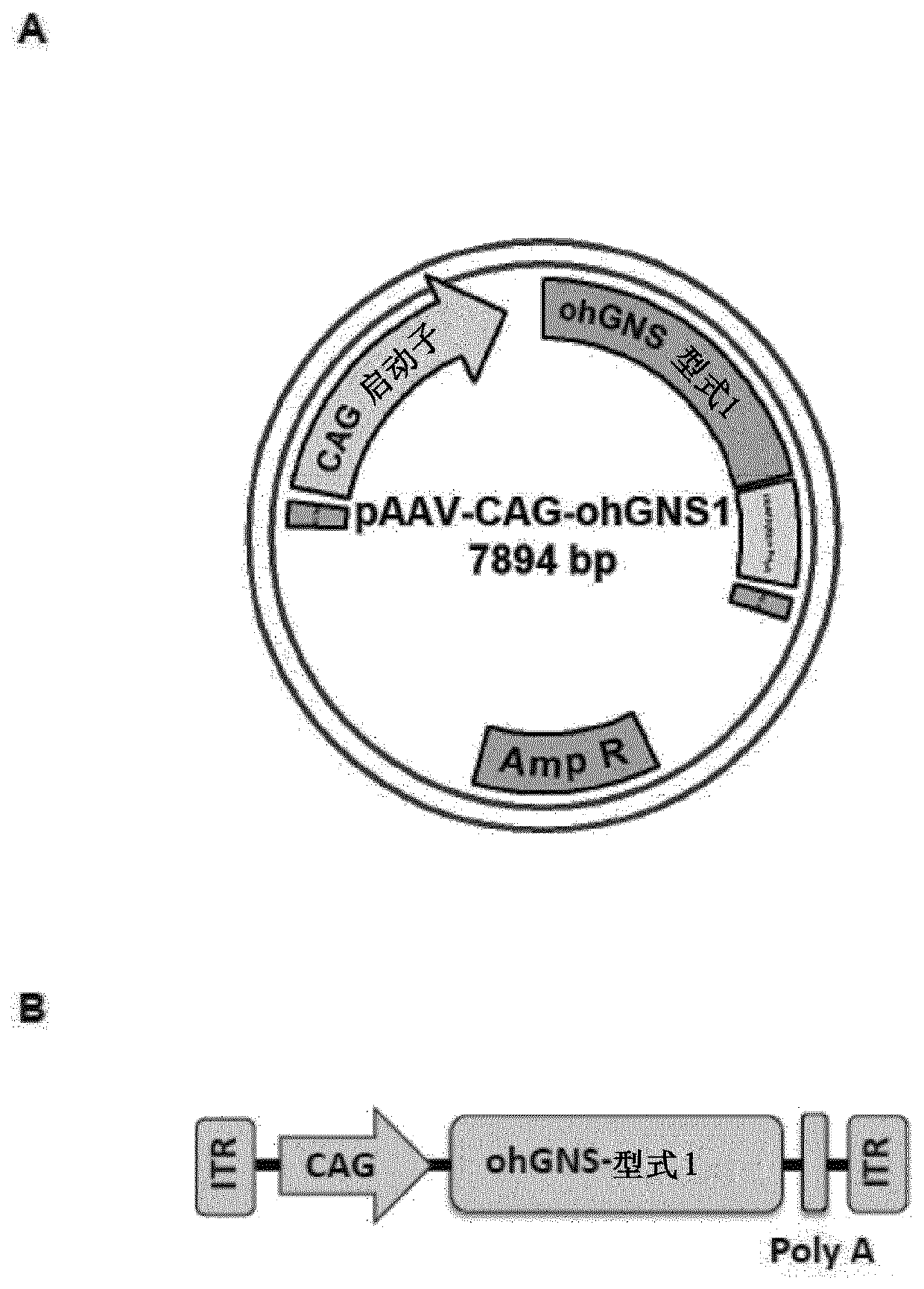
[0196] Example 2: Construction of pAAV-CAG-ohGNS-version 1
[0197] An expression cassette containing an optimized form of the glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase cDNA sequence (ohGNS) was designed and obtained. Sequence optimization to maximize the efficiency of N-acetylglucosamine 6-sulfatase protein production in humans to increase RNA stability by eliminating cryptic splice sites and RNA destabilizing sequence elements, adding RNA stabilizing sequence elements, Codon optimization and G / C content adaptation to avoid changes such as stable RNA secondary structure. The CDS of human glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase (NCBI reference sequence: NM_002076.3) was used as a starting point for sequence optimization.
[0198] The first optimized CDS (GeneArt; Life Technologies) was cloned in the plasmid pMA-T(AmpR) flanked by MluI and EcoRI restriction sites on the 5' and 3' sides, respectively.
[0199] The MluI / EcoRI optimized human glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase CDS fragment ...
Embodiment 3
[0200] Example 3: Construction of pAAV-CAG-ohGNS-version 2
[0201] Sequence optimization (DNA2.0 Inc) was performed on the CDS of human glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase (NCBI reference sequence: NM_002076.3). The optimized CDS was cloned in plasmid pJ204(AmpR) flanked 5' and 3' with MluI and EcoRI restriction sites, respectively.
[0202] The MluI / EcoRI optimized human glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase CDS fragment was excised from the pJ204 plasmid and subsequently cloned into the AAV backbone plasmid pAAV-CAG between the MluI and EcoRI restriction sites between. The resulting plasmid was named pAAV-CAG-ohGNS-version 2 (accession number DSM 32344). see image 3 A and SEQ ID NO:7 in.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com