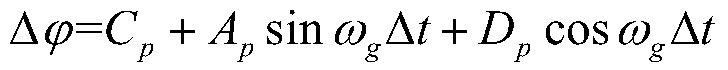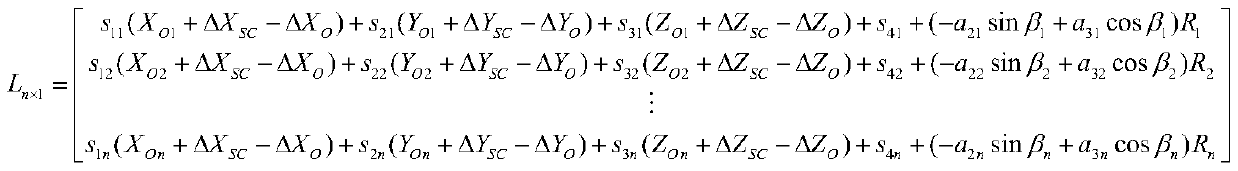In-orbit calibration method when pointing angle error of satellite-borne laser altimeter is nonconstant
A technology of laser altimeter and calibration method, which is applied in the field of laser remote sensing, and can solve problems such as pointing angle system error, angle system offset, and plane direction error of spaceborne laser altimeter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] The technical solutions of the present invention will be further specifically described below through the embodiments and in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
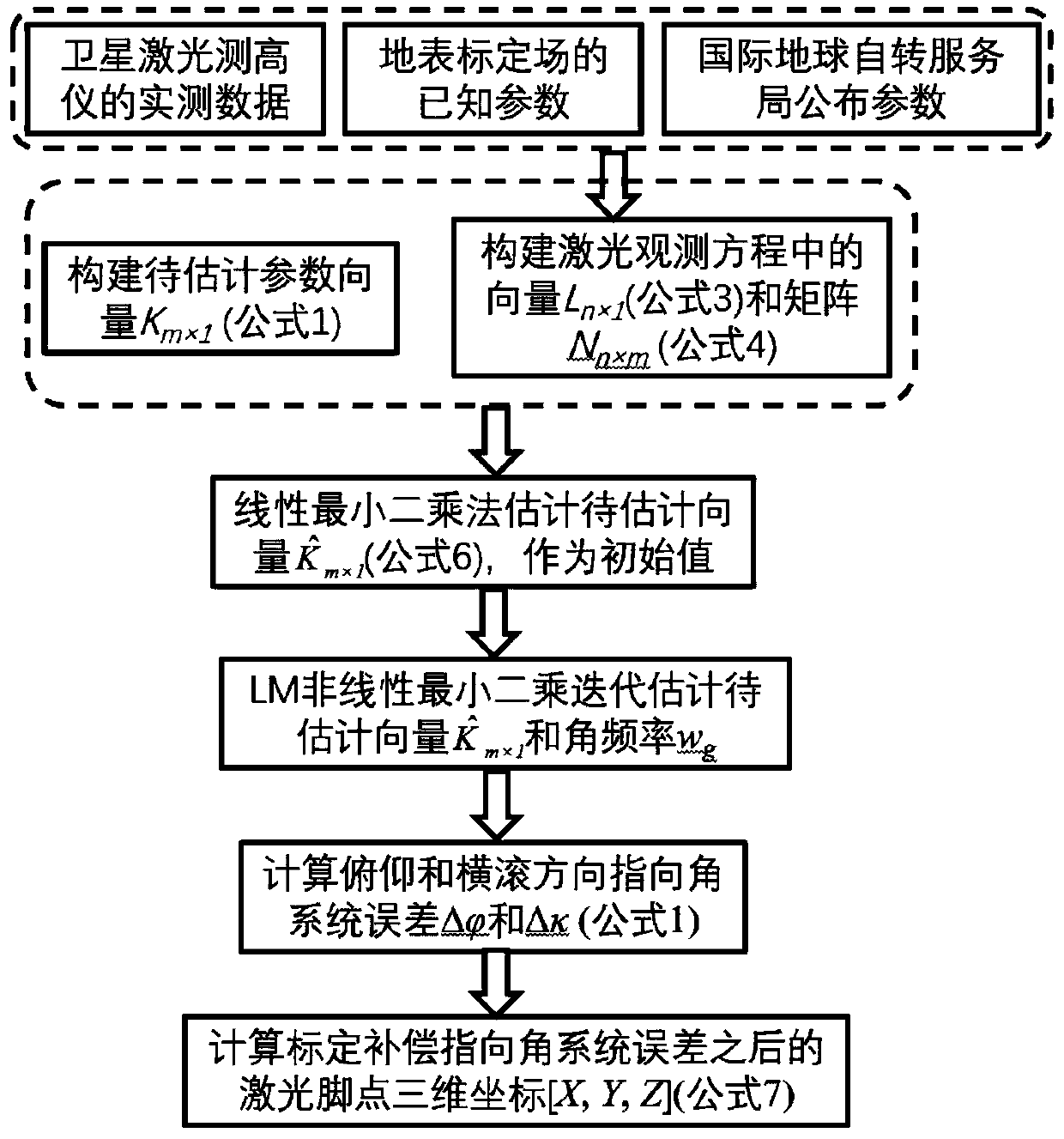
[0029] see figure 1 , the method for on-orbit calibration of non-constant pointing angle error proposed by the embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0030] Step 1. Determine the expression form of the laser pointing angle system error of the spaceborne laser altimeter in the pitch and roll directions, and construct the vector K to be estimated m×1 , the implementation includes expressing the pitch and roll direction angle errors as follows:
[0031]
[0032] In formula (1), and Δκ are angle errors in pitch and roll direction respectively; C p and C r are the constant term (bias) angle system error in the pitch and roll directions respectively; A p and D p are the amplitudes of the sine and cosine terms of the trigonometric function in the pitch direction, A r and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com