Method for separating and enriching lithium from magnesium lithium
A magnesium-lithium, enrichment technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, lithium compounds, alkali metal compounds, etc., can solve the problem of increasing the pressure of magnesium removal and precipitation conversion process, increasing the cost of lithium carbonate products, and high lithium-rich concentrates. problems, to achieve the effect of reducing equipment investment, reducing energy consumption and production costs, and increasing the concentration of lithium ions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
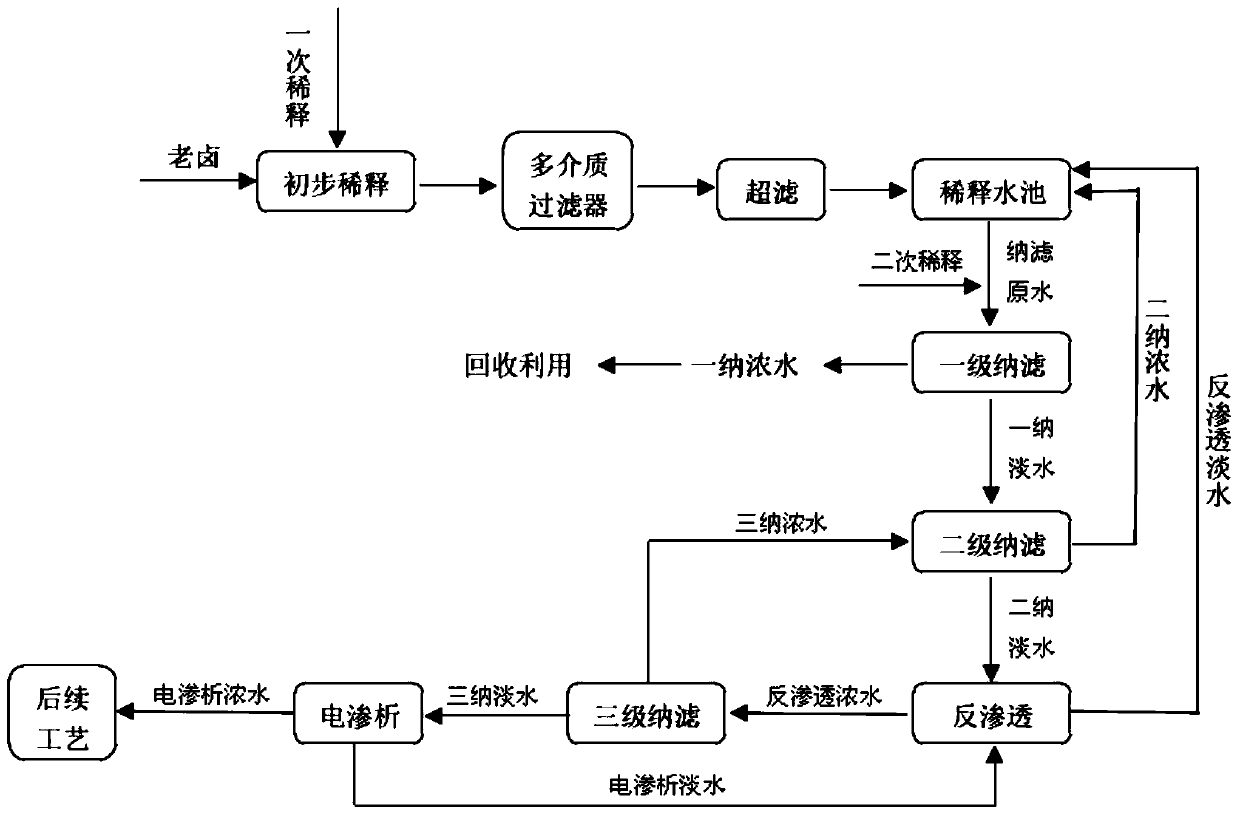
[0077] (1) The old brine used comes from a sulfate-type salt lake in Qinghai. The lithium ion content in the old brine is 2.5g / L, and the Mg / Li mass ratio is 50. The old brine is diluted once and enters the multi-media filter to remove impurities such as suspended solids and sediment in the brine, and then enters the organic ultrafiltration equipment for complete removal of impurities. The old brine after complete removal of impurities enters the separation unit through the twice-diluted nanofiltration raw water for magnesium and lithium separation. The old bittern is diluted 15 times in the whole process.
[0078] (2) The pretreated brine enters the separation unit for magnesium and lithium separation, and the magnesium ion content in the obtained nanofiltration fresh water is reduced to 0.12g / L; the lithium ion content is 0.95g / l, and the Mg / Li mass ratio is 0.125.
[0079] The magnesium-lithium separation unit is mainly composed of a monovalent ion-selective nanofiltration...
Embodiment 2
[0092] (1) The old brine used comes from a sulfate-type salt lake in Qinghai. The lithium ion content in the old brine is 2.5g / L, and the Mg / Li mass ratio is 50. The old brine is diluted once and enters the multi-media filter to remove impurities such as suspended solids and sediment in the brine, and then enters the organic ultrafiltration equipment for complete removal of impurities. The old brine after complete removal of impurities is diluted twice and enters the separation unit for separation of magnesium and lithium. The old brine was diluted 15 times in the whole process.
[0093] (2) The pretreated brine enters the separation unit for magnesium and lithium separation, and the magnesium ion content in the obtained nanofiltration fresh water is reduced to 0.23g / L; the lithium ion content is 0.65g / L, and the Mg / Li mass ratio is 0.30.
[0094] The magnesium-lithium separation unit is mainly composed of a monovalent ion-selective nanofiltration membrane with an operating p...
Embodiment 3
[0107] (1) The old brine used comes from a sulfate-type salt lake in Qinghai. The lithium ion content in the old brine is 0.2g / L, and the Mg / Li mass ratio is 180. The old brine is diluted once and enters the multi-media filter to remove impurities such as suspended solids and sediment in the brine, and then enters the organic ultrafiltration equipment for complete removal of impurities. The old brine after complete removal of impurities is diluted twice and enters the separation unit for separation of magnesium and lithium. During the whole process, the old brine was diluted 15 times.
[0108] (2) The pretreated brine enters the separation unit for magnesium and lithium separation, and the magnesium ion content in the obtained nanofiltration fresh water is reduced to 0.32g / L; the lithium ion content is 0.1g / L, and the Mg / Li mass ratio is 3.2.
[0109] The magnesium-lithium separation unit is mainly composed of a monovalent ion-selective nanofiltration membrane with an operati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com