Stability margin quick assessment method in asymmetrical fault condition
A stable margin and asymmetric technology, applied in the direction of AC network circuits, electrical components, circuit devices, etc., can solve problems such as huge amount of calculation, unsatisfactory control effect, poor pertinence of off-line decision-making analysis, etc., and achieve fast and accurate calculation good sex effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
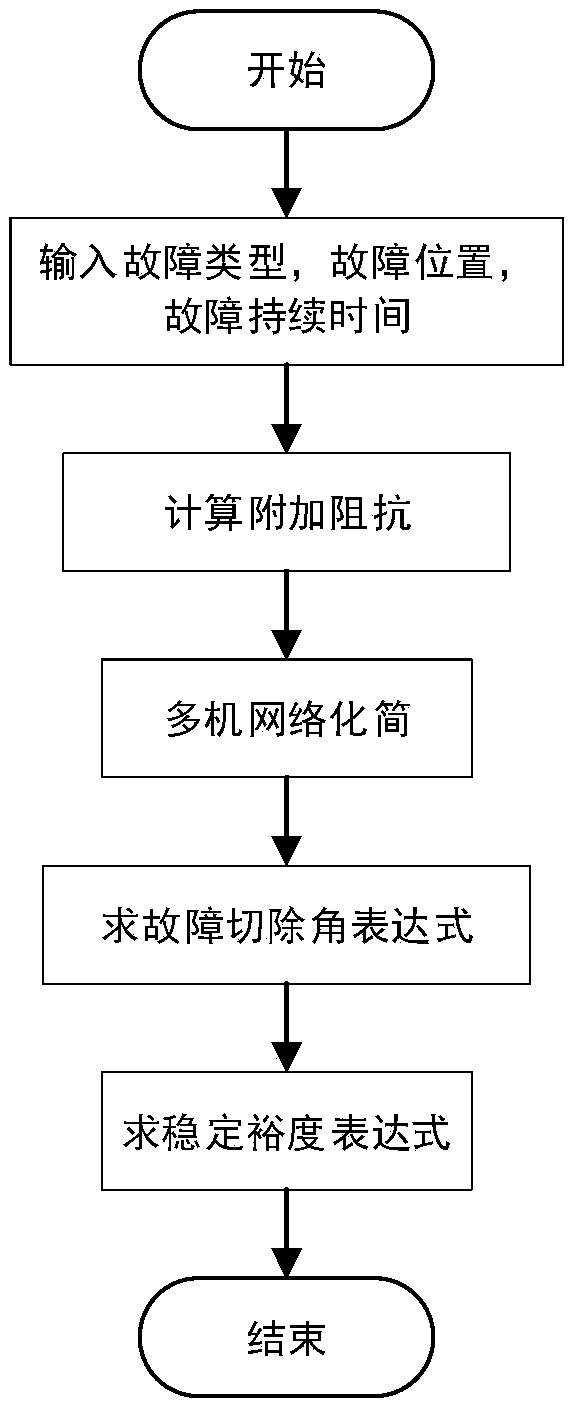
[0021] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
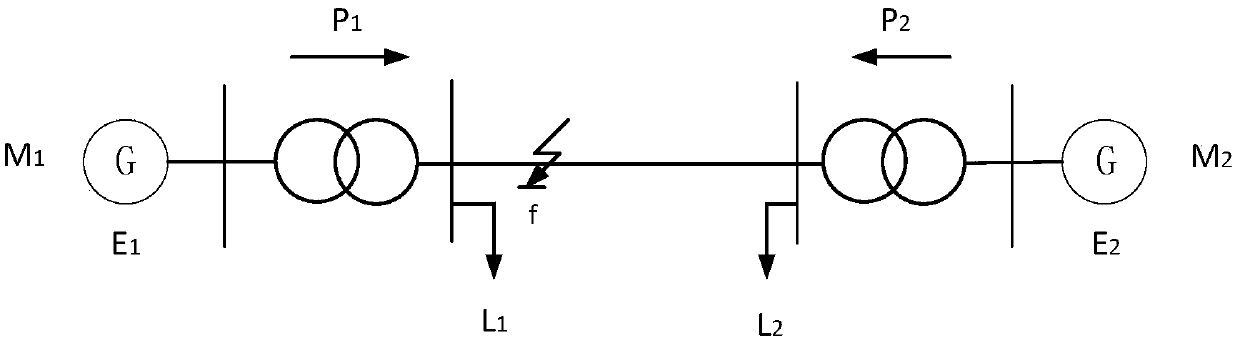
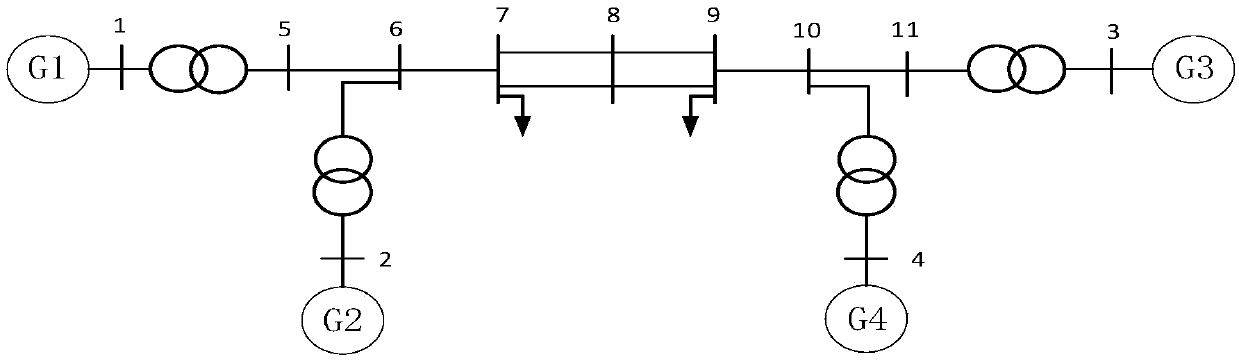
[0022] Depend on figure 1 The calculation flow chart shown is for calculation and analysis. Firstly, the additional impedance value in the case of asymmetrical short circuit is calculated according to the network structure. For a power system with N-buses, the m-buses are connected to loads only, and the n-buses are connected to generators. When a short-circuit fault occurs at point f on line r-j, line r-j is divided into two sections by fault point f, and the line impedance is as follows:
[0023] Z rf =α·z L (1),
[0024] Z fj =(1-α)·z L (2),
[0025] α represents the percentage of the distance from the fault location to the receiving end node to the total length of the line. z L Indicates the impedance of the line r-f. According to the line parameters, the node impedance matrix before the system fault is calculated as Z (s) , ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com