Absolute position coding and decoding method for optical grating of absolute position displacement sensor
A technology of displacement sensor and absolute position, which is applied in the direction of converting sensor output, instrument, measuring device, etc. It can solve the problems of limited installation space, increased encoder volume, and increased difficulty of circular grating manufacturing process, so as to reduce the amount of data, Prevents misreading of position signals and improves manufacturing accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
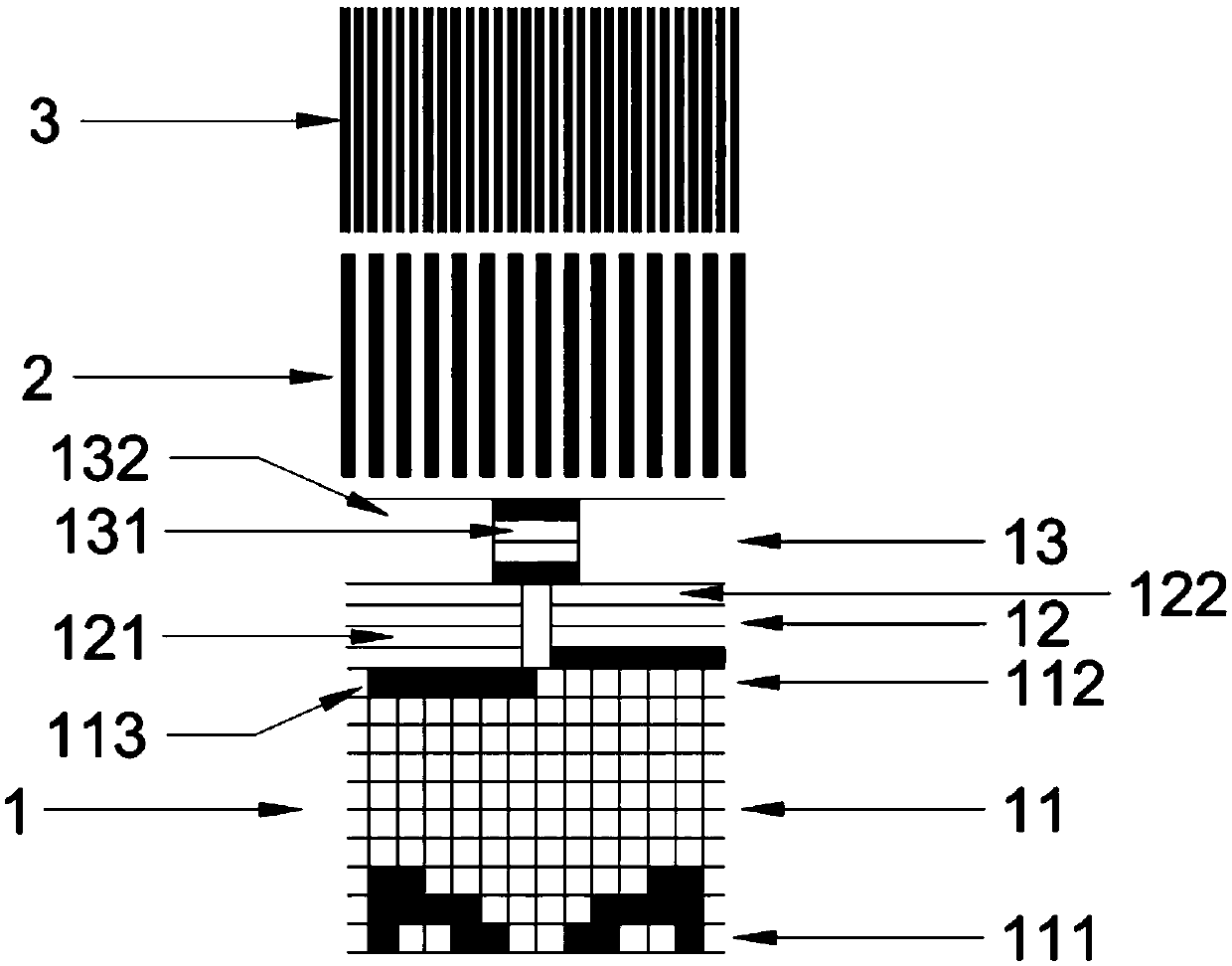
[0040] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment is an absolute position displacement sensor grating absolute position encoding and decoding method, the linear grating absolute position encoding is divided into 3 code tracks, the first is absolute code track 1, the second code track, and the third code track is an equidistant incremental code track. The absolute code track 1 is composed of a Gray code area 11 , an interval code area 12 and an inter-interval code area 13 . The second code track is the low-order equidistant incremental code track 2, the number of reticle lines in the low-order equidistant incremental code track 2 is equal to the number of Gray codes, and the width of each low-bit equidistant incremental code track 2 is equal to half the width of the Gray code. That is, each Gray code corresponds to a complete low-bit equidistant incremental code track 2 reticle cycle unit. The third code track is the high equidistant incremental code track 3, and the number o...
Embodiment 2
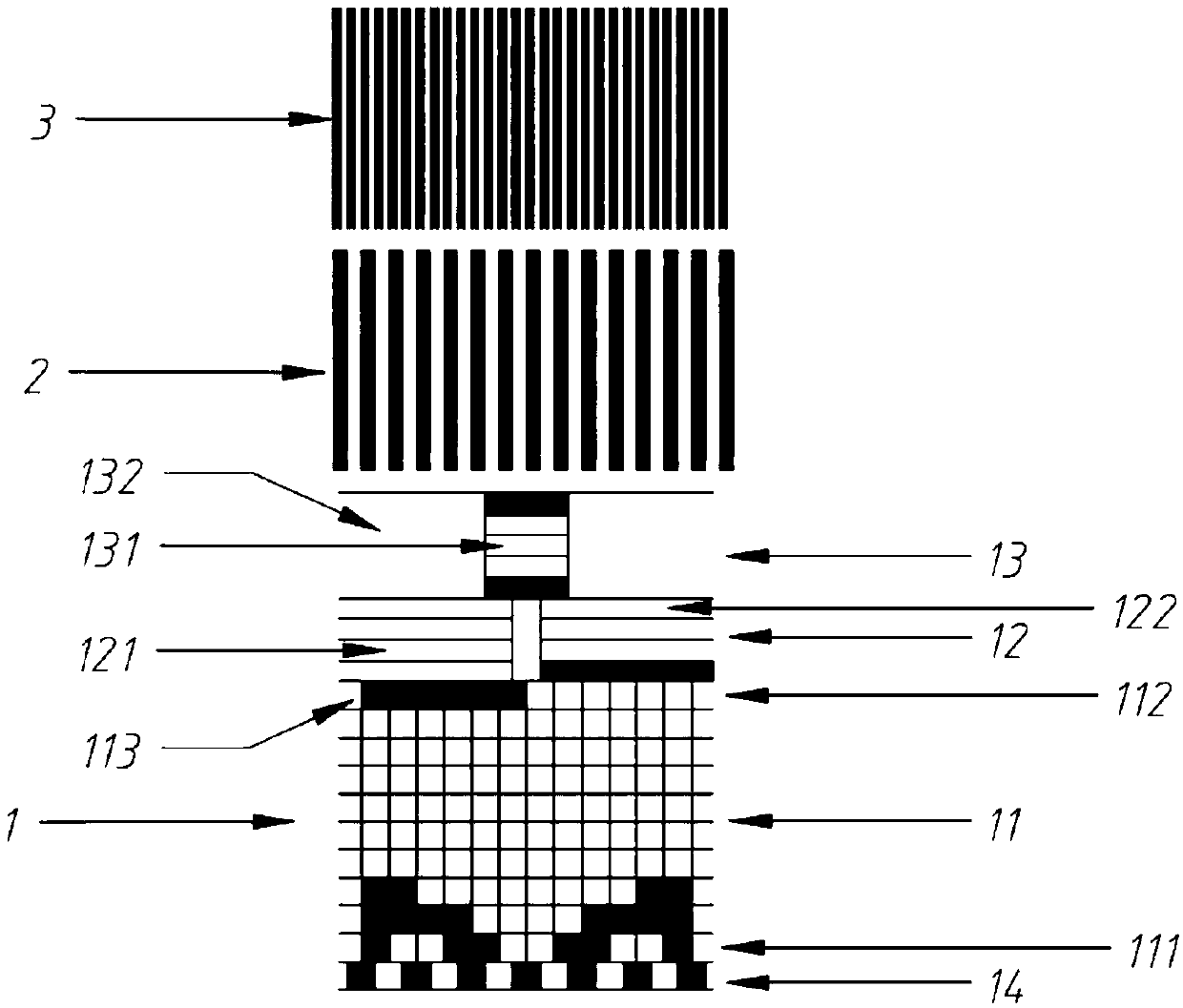
[0053] Such as image 3 As shown, in an absolute position displacement sensor grating absolute position encoding and decoding method in this embodiment, the absolute position encoding of the circular grating with a smaller diameter is divided into 3 code tracks, the first is absolute code track 1, and the second code track , The third code track is an equidistant incremental code track. The absolute code track 1 is composed of a gray code area 11 and a parity span identification code area 14 . The second code track is the low-bit equidistant incremental code track 2, the number of reticle lines in the low-bit equidistant incremental code track 2 is equal to the number of Gray codes, and the width of each low-bit equidistant incremental code track 2 is equal to half the width of a Gray code , that is, each Gray code corresponds to a complete low-bit equidistant incremental code track 2 reticle cycle unit. The third code track is the high equidistant incremental code track 3, ...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Such as figure 2 As shown, this embodiment is an absolute position displacement sensor grating absolute position encoding and decoding method, the linear grating absolute position encoding is divided into 3 code tracks, the first is absolute code track 1, the second code track, and the third code track is an equidistant incremental code track. The absolute code track 1 is composed of a parity span identification code area 14 , a Gray code area 11 , an interval code area 12 and a pass interval code area 13 . The second code track is the low-order equidistant incremental code track 2, the number of reticle lines in the low-order equidistant incremental code track 2 is equal to the number of Gray codes, and the width of each low-bit equidistant incremental code track 2 is equal to half the width of the Gray code. That is, each Gray code corresponds to a complete low-bit equidistant incremental code track 2 reticle cycle unit. The third code track is the high equidistant...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com