A method for separating molybdenum in tungstate solution by ion exchange
An ion exchange method and tungstate technology, applied in the field of rare metal metallurgy, can solve problems such as adverse effects of the process, complex mineral raw materials, deterioration of the production environment, etc., and achieve the effects of good desorption separation effect, easy desorption process, and safe and convenient measurement.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
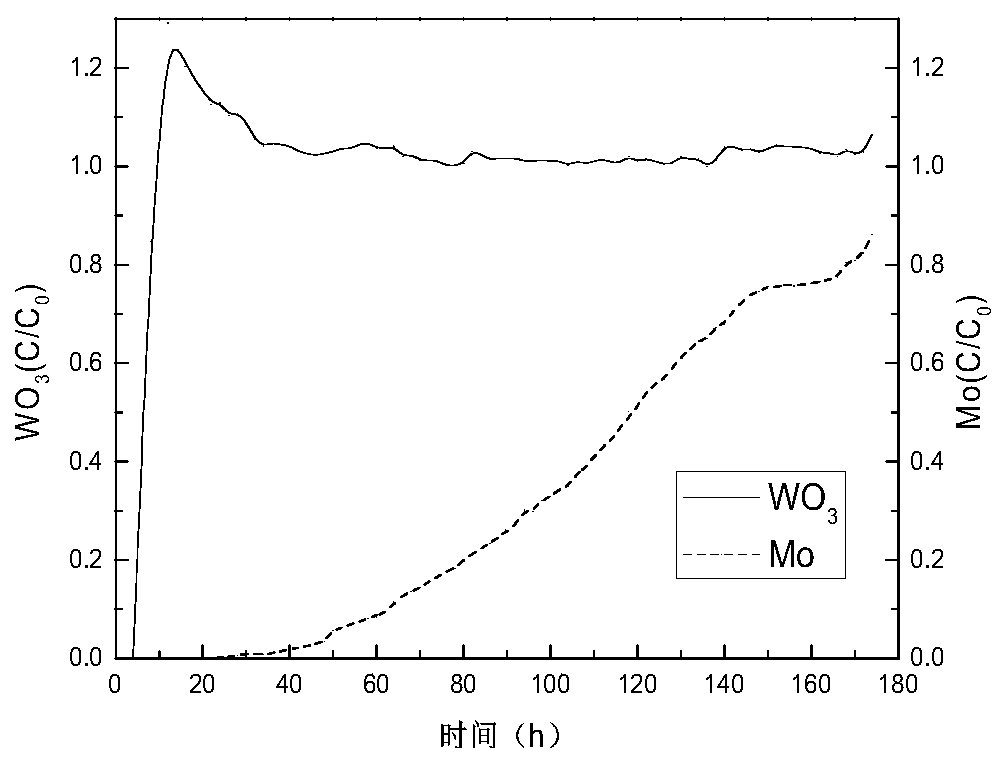
[0033]The feed liquid is a prepared ammonium molybdenum tungstate solution, which is vulcanized in advance with a vulcanizing agent. The vulcanization conditions are: prepare 5L containing WO 3 100g / L, Mo1g / L simulated feed liquid, add 148g trimeric thiocyanate as vulcanizing agent. The vulcanization temperature was 70°C, and the pH of the feed solution was adjusted to 9.5 after thiolation. The thiolation rate was 99.5% tested by extraction method. Take 20ml of feed solution each time, 5ml of HBDM-1 resin in a beaker, and adsorb at room temperature for 1 hour. From the adsorption results, it can be seen that the adsorption rate of tungsten and molybdenum varies greatly with pH. When the pH is 9.25 to 9.5, the adsorption of molybdenum The tungsten adsorption rate reached the maximum, reaching 78.79%, while the adsorption rate of tungsten increased with the decrease of pH. It can be known by calculation that the separation coefficient of tungsten and molybdenum can reach 3.28 ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] The feed liquid is the thiolated ammonium molybdenum tungstate solution prepared in Example 1. Each time, 20 ml of the feed liquid is taken, and 5 ml of HBDM-1 resin is adsorbed in a beaker for 1 hour, and the adsorption temperature is controlled to be normal temperature (25° C.)~ 60°C. It can be seen from the experimental results that the adsorption rate of tungsten and molybdenum keeps increasing with the increase of temperature, and the calculation shows that the separation coefficient is continuously increasing. At room temperature, the adsorption rates of tungsten and molybdenum are 27.19% and 60.63% respectively. According to the actual economic factors and experimental results, it can meet the requirements of tungsten and molybdenum separation at room temperature.
Embodiment 3
[0037] The feed solution is the thiolated ammonium molybdenum tungstate solution prepared in Example 1. 20ml feed solution and 5ml HBDM-1 resin are taken each time and adsorbed at room temperature. The adsorption time is 5min~2h respectively. It can be seen from the results It can be seen that with the extension of adsorption time, the adsorption rate of tungsten and molybdenum increases continuously, and the calculation shows that the separation coefficient increases continuously, indicating that the longer the adsorption time, the better the separation effect of tungsten and molybdenum. After 2 hours, the adsorption rate of tungsten and molybdenum tended to be stable and reached an equilibrium state.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| separation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com