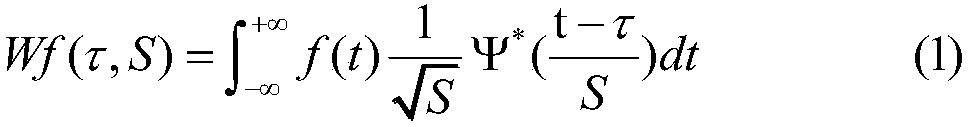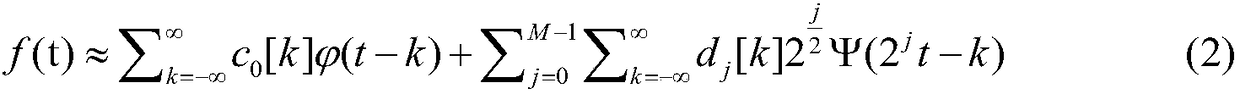Single-phase grounding fault judgment method for small-current grounding system
A single-phase ground fault, small current grounding technology, applied to the fault location, detecting faults according to the conductor type, measuring electricity and other directions, can solve problems such as the single-phase ground fault identification problem that cannot be solved well, and achieve the effect of accurate distinction and judgment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] The single-phase grounding fault judging method of the small current grounding system of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0017] The first step is to extract the transient current characteristic component W value .
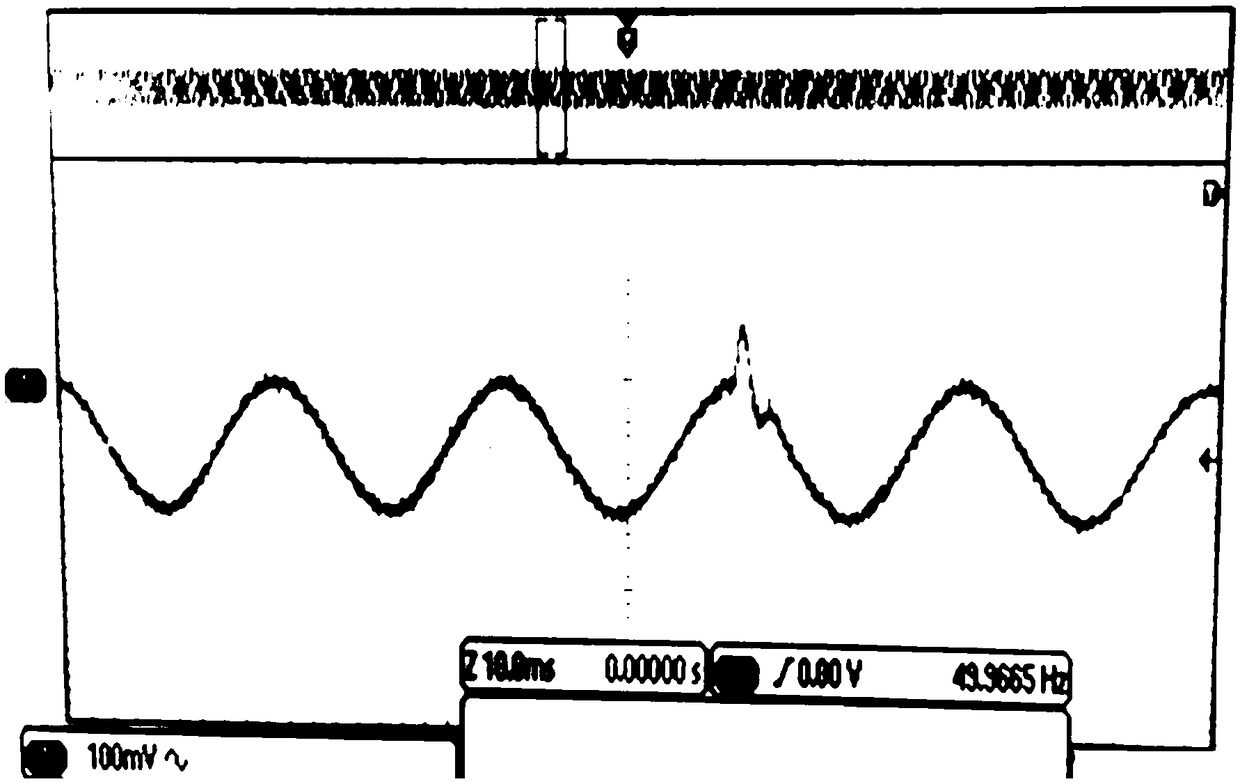
[0018] The maximum value of the current wavelet analysis mode coefficient when the small current grounding system works normally and the maximum value of the current wavelet analysis mode coefficient when the ground fault occurs are taken as the transient current characteristic component W value In this embodiment, the small current grounding system of 10KV overhead line is taken as an example.
[0019] Suppose the wavelet function Ψ(t) is compactly supported, in L 2 (R) The wavelet transform with a translation of τ and a scale of s in space can be defined as
[0020]
[0021] For the convenience of calculation, the scale and translation need to be discretized. Let the scale S=2 -j , translation τ=ks=2 -j , the high efficiency...
Embodiment 2
[0059] The difference between Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 1 is that the single-phase statistical vector ξ of the small-current grounding system constructed in the third step is different, because in practice, the data difference of the current and electric field measurements of each line is relatively large , the transient change of the current is also relatively large, and the maximum value of the wavelet analysis modulus coefficient is also different. Therefore, it is difficult to establish a single-phase-to-ground fault Fisher classification model with fixed parameters suitable for all line branches. In order to solve this problem, it is necessary to establish a generalized classifier so that the classifier has the ability of self-adaptive self-learning. The adaptive establishment of classifier parameters specifically includes the following steps.
[0060] Step 1: According to the statistical law of electric field drop when single-phase grounding occurs, set the ground fau...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com