Novel mutations in anaplastic lymphoma kinase predicting response to ALK inhibitor therapy in lung cancer patients
A lymphoma kinase and inhibitor technology, applied in the field of mutation detection, can solve problems such as resistance mutation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Example 1. Detection of ALK mutations in lung cancer patients
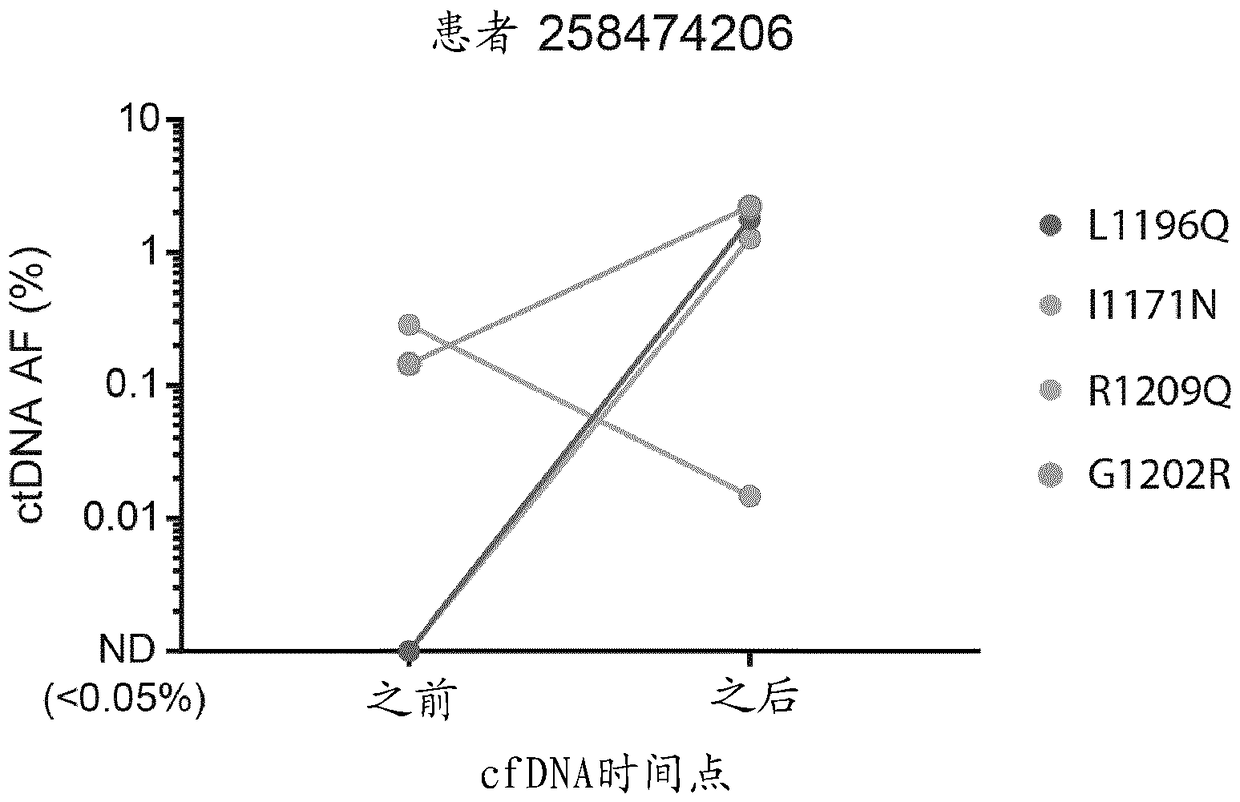
[0061] Cell-free DNA from patients was isolated before and after alectinib treatment. This cfDNA was subjected to next generation sequencing using standard Illumina HiSeq workflow and analysis as described in US20140296081. Single nucleotide variants (SNVs) in patients were identified using sequencing data, and SNVs that were present at only one of the two time points in a given patient were further examined. One variant, R1209Q, was identified in six patients. In 5 / 6 patients it was present only after alectinib therapy ( figure 1 ), providing evidence that it can confer resistance to alectinib. In the sixth patient, a known resistant variant to alectinib was detected, so a separate clone may have conferred alectinib resistance ( figure 2 ). The other variant, I1268V, was identified in one patient but only before alectinib treatment, suggesting that it may confer sensitivity to alectinib.
[0062]...
Embodiment 2
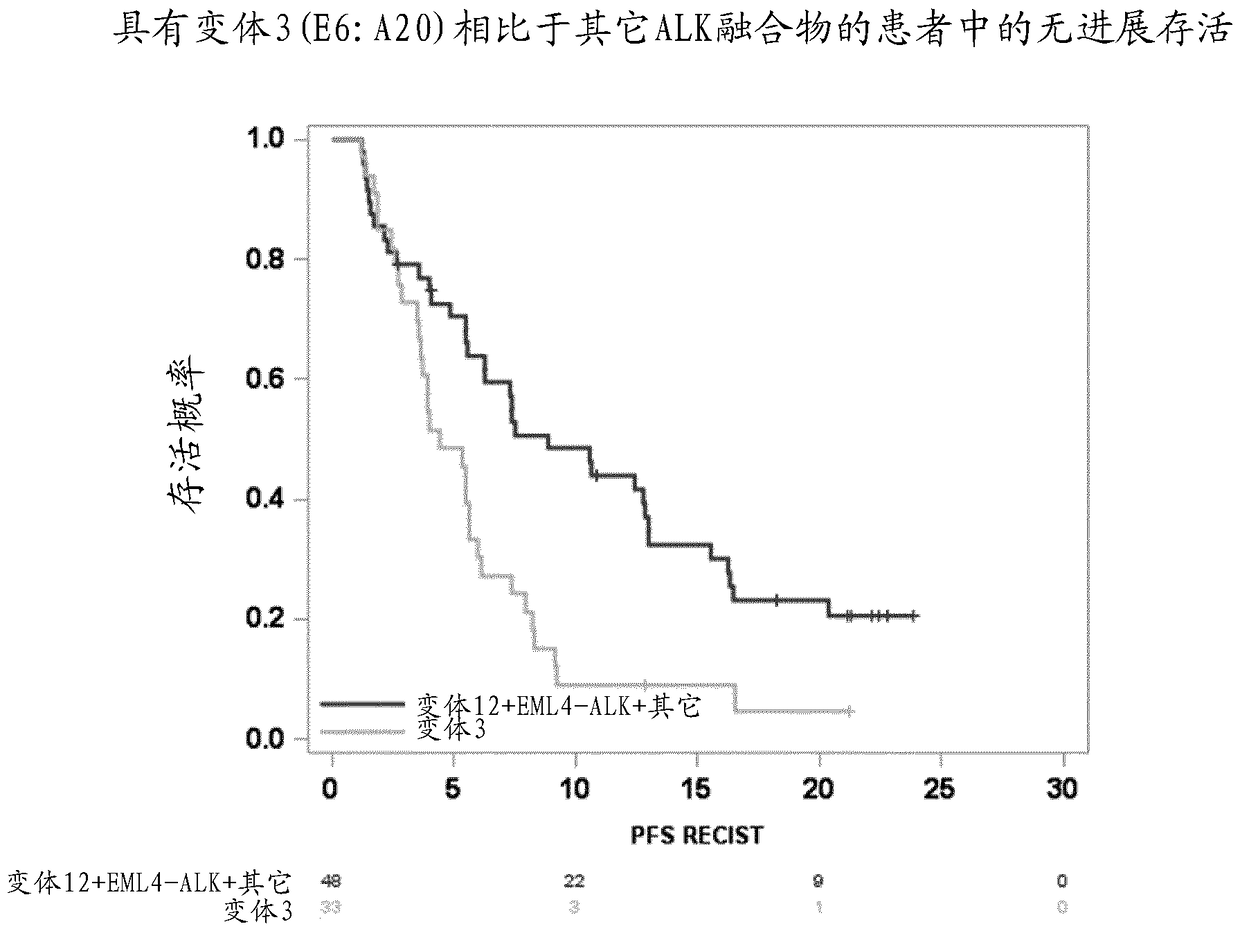
[0064] Example 2: Factors Affecting ALK Fusion Results
[0065] Table 1 shows that the hazard ratios for patients with ALK fusion variant 3 (EML4 exon 6 joined to ALK exon 20) were much higher than those for patients without ALK fusion variant 3. Figure 8 showed that patients with variant 3 fusions had significantly shorter progression-free survival (PFS) compared to patients with other ALK fusions. This was found to be true regardless of race and treatment status (ie, ALK inhibitor-treated individuals with ALK fusion variant 3 had worse outcomes than ALK inhibitor-treated individuals with a different ALK fusion). On average, individuals with variant 3 fusions were approximately 2.6 times more likely to progress (p-value 0.0012). This hazard ratio of 2.6 was derived from a Cox PH multivariate model performed on 72 patient plasma samples taken prior to treatment with alectinib. The model predicts progression-free survival (PFS) from the effect of the variant 3 fusion, adju...
Embodiment 3
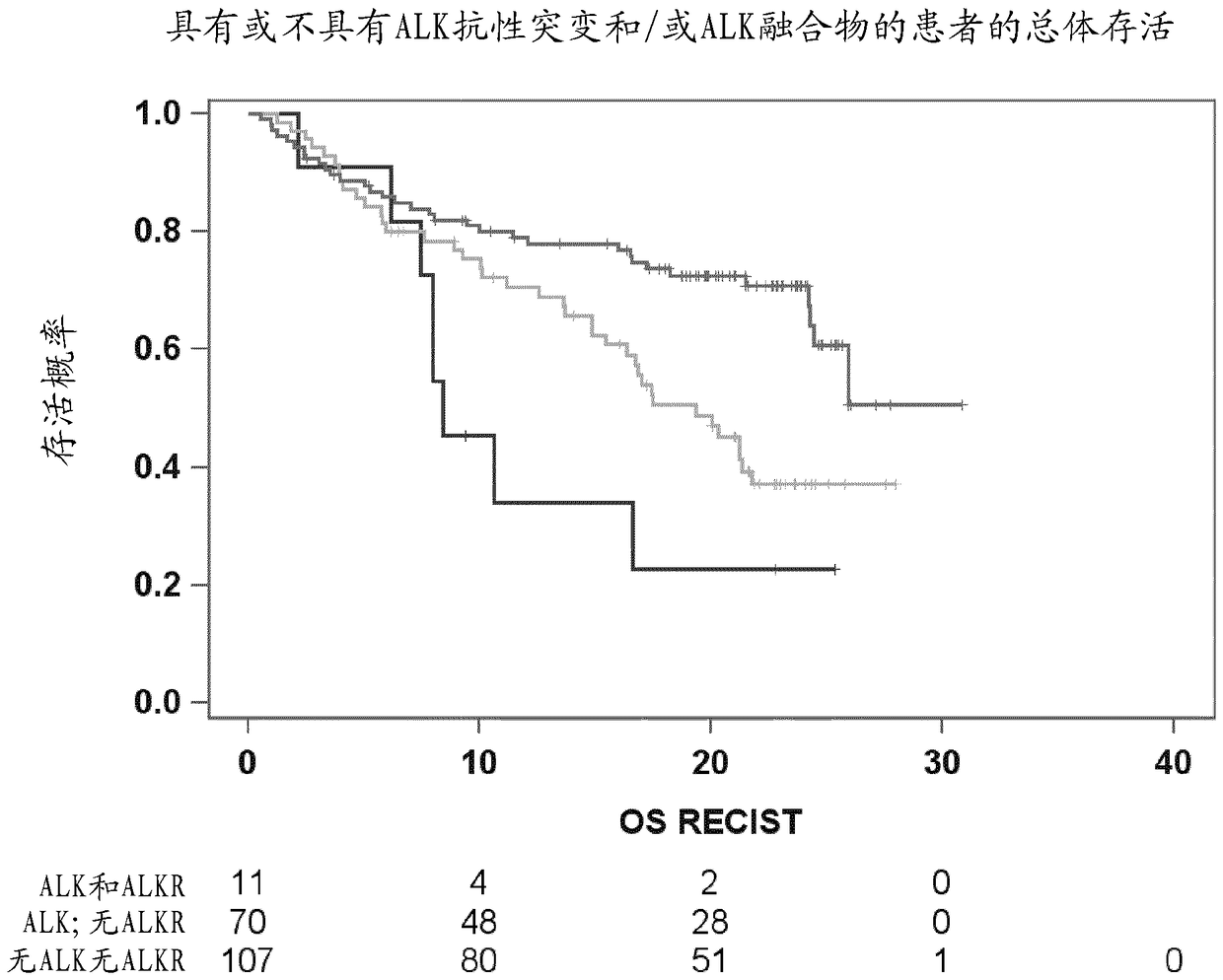
[0068] Example 3: Single Nucleotide Variation (SNV) and ALK Fusion Analysis
[0069] Plasma samples were collected from 188 stage IIIB-IV NSCLC (non-small cell lung cancer) patients who had progressed after crizotinib treatment (before second line therapy (eg treatment with alectinib)). These patients had previously been determined to be ALK-fusion positive by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). The presence or absence of the most common ALK fusions was detected using a circulating tumor DNA panel (Avenio ctDNA panel). Table 2 shows the frequency of detected fusions.
[0070] Table 2
[0071] fusion variant
EML4 exon 13-ALK exon 20
26
EML4 exon 13-ALK exon 24
1
EML4 exon 14-ALK exon 20
1
EML4 exon 18-ALK exon 20
3
EML4 exon 19-ALK exon 20
1
EML4 exon 20-ALK exon 20
4
EML4 exon 21-ALK exon 20
3
EML4 exon 6-ALK exon 20
33
none detected
107
other fusi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com