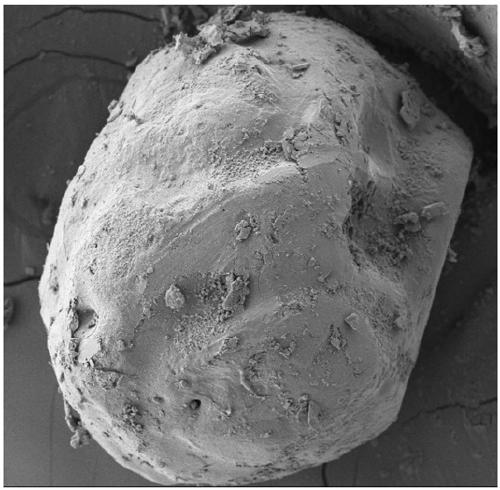
Method for preparing superhydrophobic oxidant based on lotus effect
A technology of lotus leaf effect and oxidant, which is applied in the field of anti-moisture absorption, which can solve the problems of few reports on energetic materials, affect the performance of use, reduce hygroscopicity, etc., and achieve the effects of small proportion, low thermal decomposition temperature and high product quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A method for preparing superhydrophobic oxidant based on the lotus leaf effect, comprising the following steps:
[0026] Step 1, dissolving 1g of myristic acid in ethyl acetate to form a solution with a mass concentration of 2%, adding 50g of ammonium perchlorate solid particles, stirring for 30 minutes, filtering and drying for later use;
[0027] Step 2: dissolving 0.5 g of copper chloride into ethyl acetate to form a solution with a concentration of 1%, adding the dried solid in step 1, stirring for 20 minutes, filtering and drying to obtain superhydrophobic oxidant particles.
Embodiment 2
[0029] A method for preparing superhydrophobic oxidant based on the lotus leaf effect, comprising the following steps:
[0030] Step 1, dissolving 1 g of heptadecanoic acid in ethyl acetate to form a solution with a mass concentration of 3%, adding 50 g of ammonium perchlorate solid particles, stirring for 30 minutes, filtering and drying for later use;
[0031] Step 2: dissolving 0.5 g of silver nitrate into ethyl acetate to form a solution with a concentration of 1%, adding the dried solid in step 1, stirring for 20 minutes, filtering and drying to obtain superhydrophobic oxidant particles.
Embodiment 3
[0033] A method for preparing superhydrophobic oxidant based on the lotus leaf effect, comprising the following steps:
[0034] Step 1, dissolving 1g of vinyltriethoxysilane in dichloroethane to prepare a solution with a mass concentration of 1%, adding 50g of ammonium dinitramide solid particles, stirring for 10 minutes, filtering and drying to obtain the finished product;
[0035] Step 2: dissolving 0.5 g of ferric nitrate into ethyl acetate to form a solution with a concentration of 1%, adding the dried solid in step 1, stirring for 20 minutes, filtering and drying to obtain superhydrophobic oxidant particles.
[0036] The hygroscopicity test (adopting GJB770A-97 standard) is carried out to the untreated ammonium dinitramide crystal and the superhydrophobic spherical ammonium dinitramide prepared, and the hygroscopic rate of the untreated ammonium dinitramide crystal is 68%; This embodiment obtains The moisture absorption rate of the superhydrophobic oxidant particles is 15...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com