A decoding method of motor imaginary EEG signals based on OA-WMNE brain source imaging
A technology of motor imagery and EEG signals, applied in the field of brain source space decoding of EEG signals, can solve problems affecting the accuracy of decoding, purpose conflicts, uneven estimation of cortical dipole sources, etc., to increase universal application performance, reducing the effect of noise interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
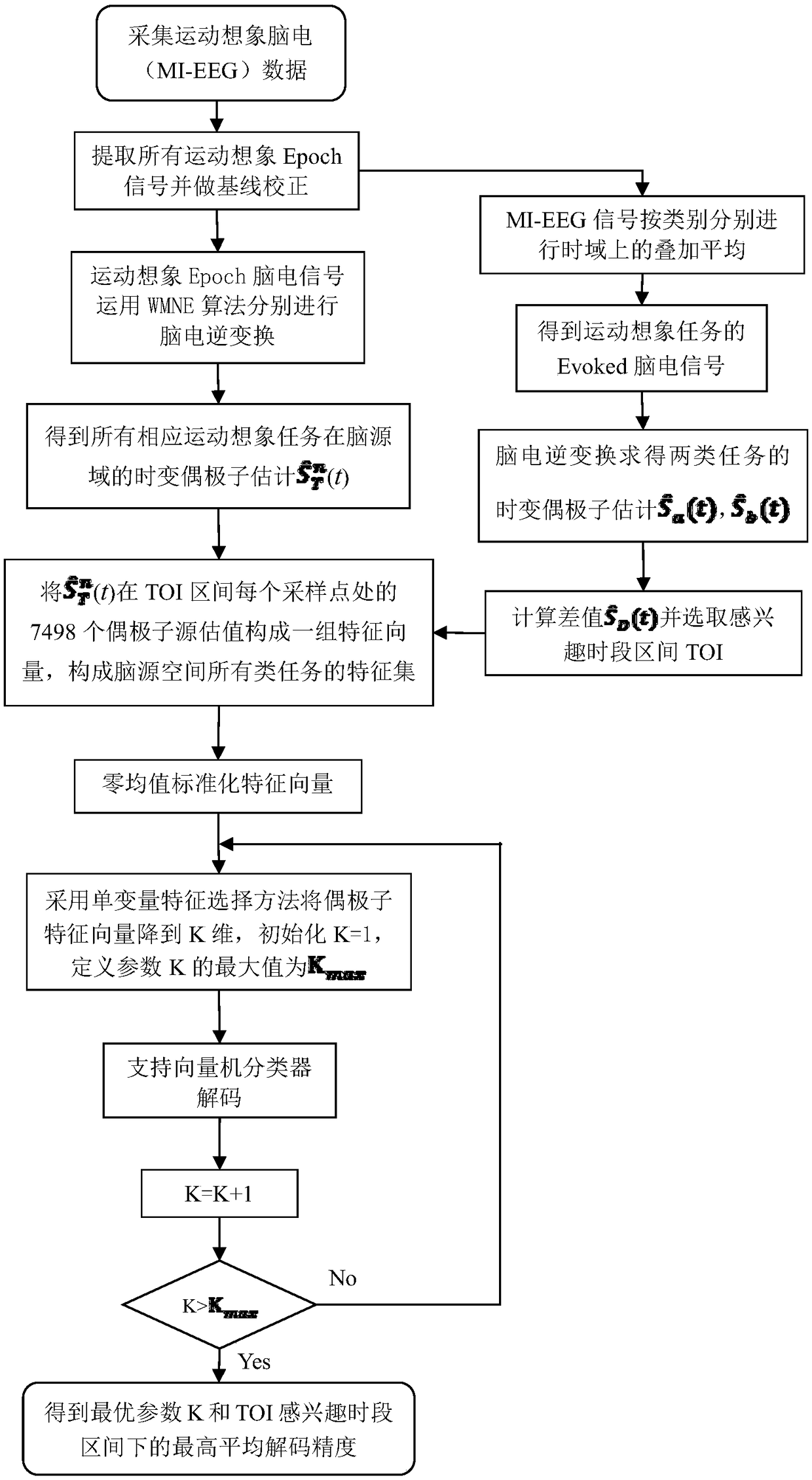
[0034] The concrete experiment of the present invention is carried out in the Python 2.7 emulation environment under Windows 10 (64 bits) operating system.
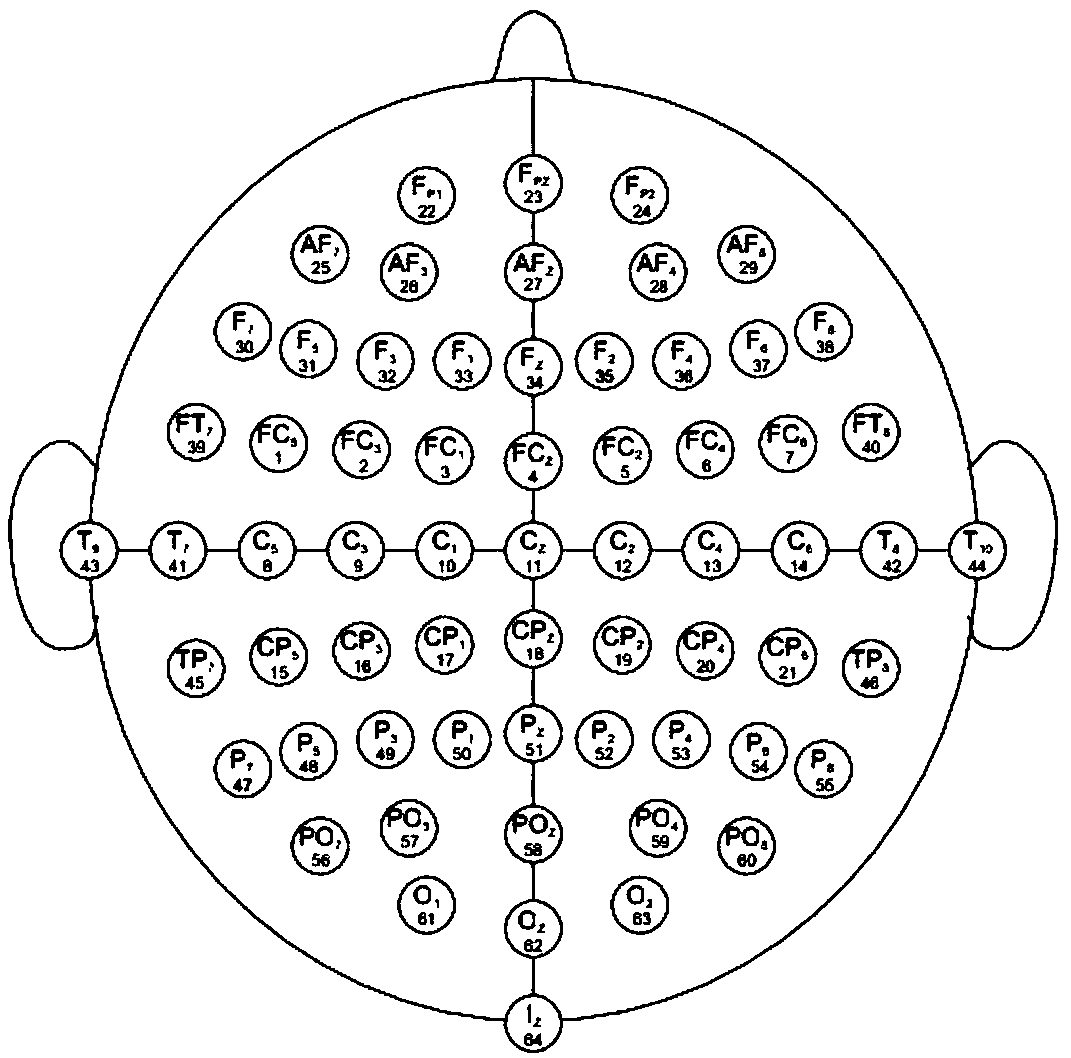
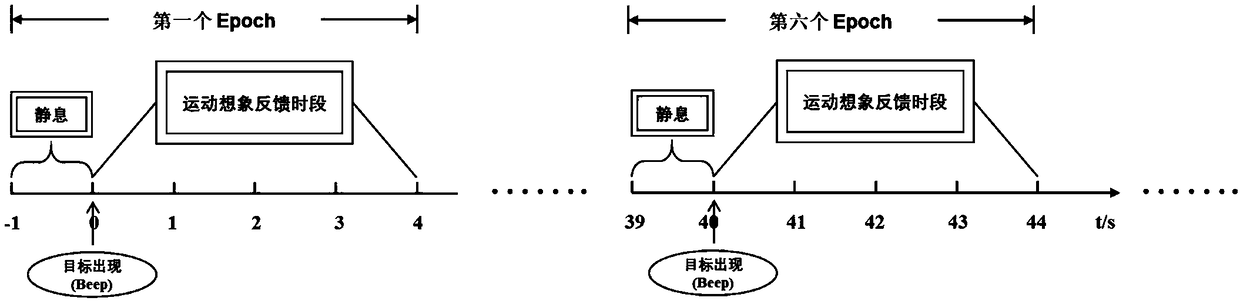
[0035] The MI-EEG data set used in the present invention comes from the public database of the "BCI2000Instrumentation" system, and is collected by the developer using the international standard 10-10 lead system. The EEG signal collected by the system is 64 leads, and the sampling frequency is 160Hz , the electrode positions are distributed as Figure 2.1 shown. A single motor imagery task lasts for 4s, and the specific acquisition experiment sequence is as follows: Figure 2.2 shown. When t = -1 ~ 0s, the subject is in a resting state; when t = 0s, the target on the screen appears and triggers a Beep sound at the same time, if the subject observes that the target is at the top of the screen, the subject is at 0 ~ 4s Imagine the opening and closing movement of the hands until the target disappears. If the target appea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com