A time-delay power system stability analysis method and controller for reducing conservatism
A technology of power system and analysis method, applied in the field of wide-area power system analysis, which can solve the problems of inaccurate model description and reduction of conservatism.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0276] Example 1: Consider an interval variable time delay system, where:
[0277]
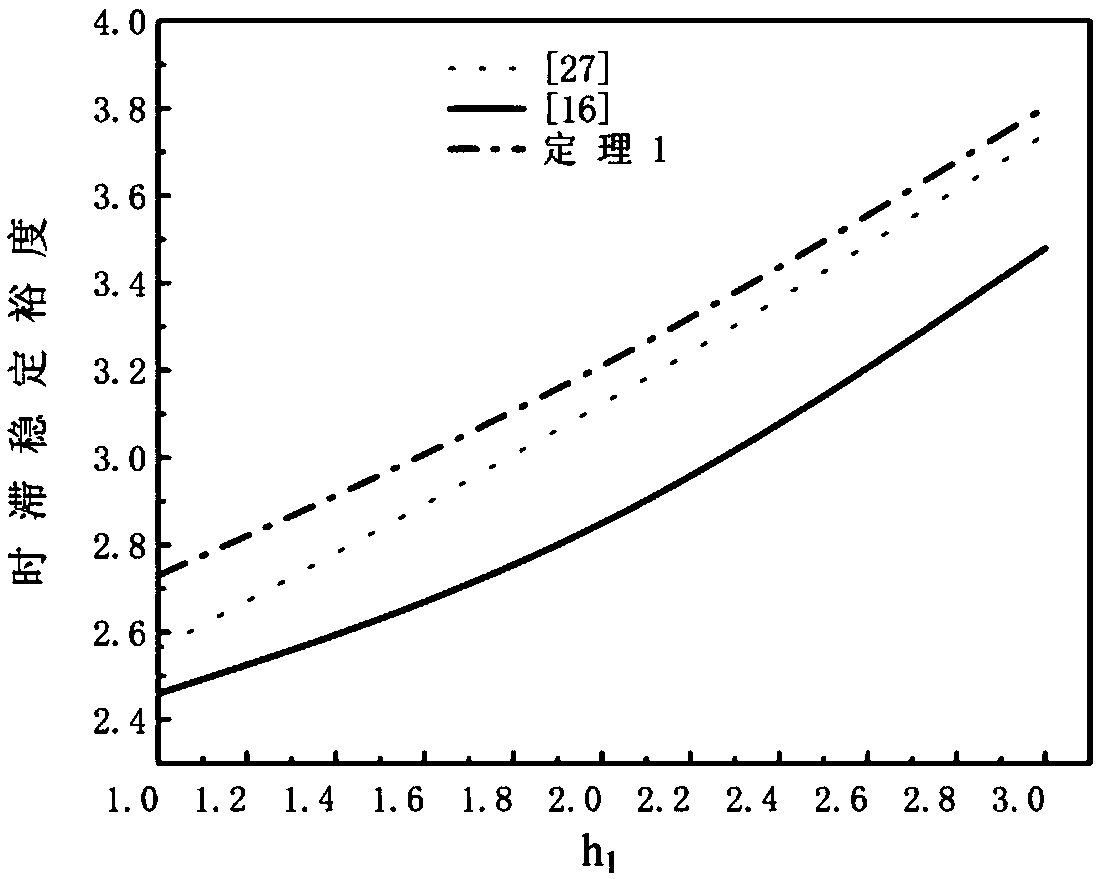
[0278] When μ=0.5 and μ=0.9, at the lower bound of the time lag h 1 Given a given situation, use Theorem 1 to find the upper bound of the maximum time delay that guarantees the stable operation of the system, and compare the results of this application with literature [16] and literature [27]. Table 1 gives different time delays. Lower bound h 1 The upper bound of time delay h obtained by different methods 2 . It can be seen from Table 1 that in h 1 When the values are 1, 2, and 3, the upper bound of the maximum allowable time delay obtained by Theorem 1 of this application is larger than the results obtained in [16] and [27], which is less conservative.
[0279] in figure 1 , figure 2 When μ=0.5 and μ=0.9, the stable operation area of the system of this application and literature [16] and [27] are respectively given. It can be seen that, compared with literature [16] and [27], the system ha...
example 2
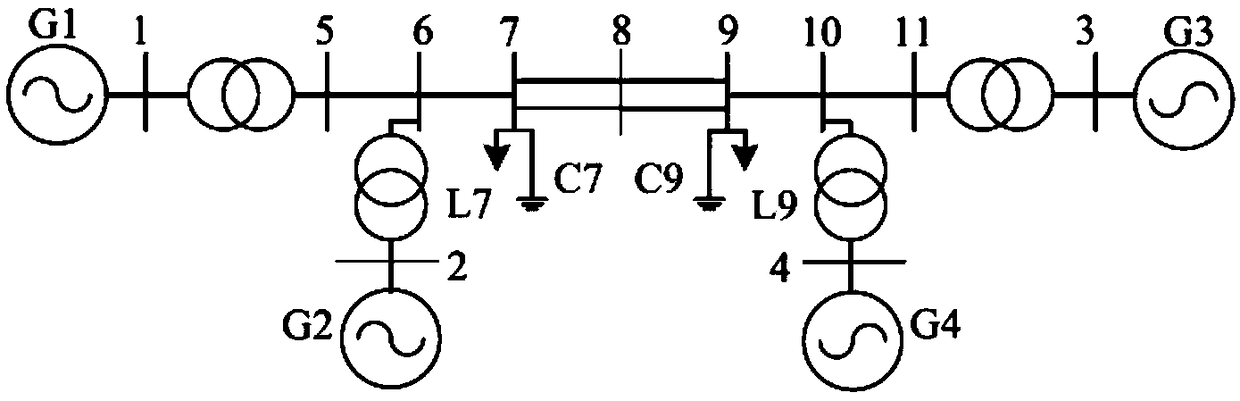
[0282] Example 2: Use as image 3 The shown 4-machine 11-node system further analyzes the effectiveness of the method adopted in this application in reducing the conservativeness of the conclusion on the stability of the wide-area time-varying time-delay power system.
[0283] According to the method of modal analysis in literature [29], the state matrix A, A of the four-machine power system is obtained 1 They are:
[0284]
[0285] Table 2 lists the upper bound of the time delay obtained by Theorem 1 of 0.571, which is compared with 0.195 in [6], 0.288 in [29], 0.328 in [30], and 0.440 in [18]. The upper bounds of lag are larger than other documents, which shows that the method proposed in this application is effective in reducing the stability of wide-area time-varying time-delay systems. It also proves that the method in this application is effective in multi-machine systems. Sex.
[0286] Table 2 Using different methods to obtain the maximum time lag
[0287] method
example 3
[0288] Example 3: Use as Figure 4 The single-machine infinite bus system shown here verifies the control effect of the controller designed in this application. Refer to the literature [31] for the values of specific parameters of the system.
[0289] Among them, the state matrix A, A of the single-machine infinite power system 1 They are:
[0290]
[0291]
[0292] For the single-machine infinite bus system, Table 3 shows the upper bound of the maximum time delay obtained by different methods. It can be seen that the upper bound of the maximum time delay of the system obtained by theorem 1 of this application is 69.74, which is greater than the literature [17] 65.4 in [15], 61.3 in [18], 65.4 in [18], 65.29 in [14], and 68.1 in [21], verifying that the proposed method reduces the conservativeness of the system stability criterion.
[0293] Table 3 Use different methods to obtain the maximum time lag
[0294] method
[17]
[15]
[18]
[14]
[21]
Theorem 1
h2
65.4
60.9
65.4
65.3
68.1
69.74
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com