A method for constructing a cross-linked structure model of graphene oxide and polycarbodiimide by computer simulation
A polycarbodiimide and cross-linked structure technology, applied in the field of cross-linked polymers, can solve problems such as uncontrollable reactivity, difficulty in building a cross-linked structure model, and long simulation time of the cross-linking reaction process, reaching a range of components Large, controllable responsiveness and short simulation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
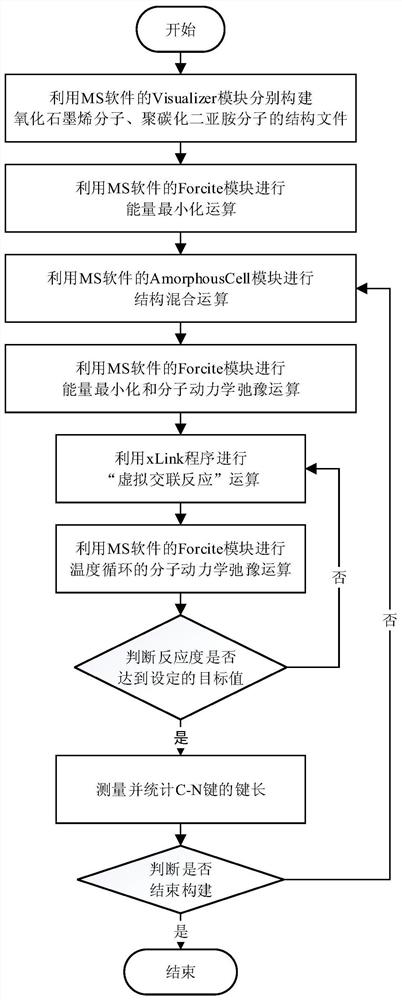
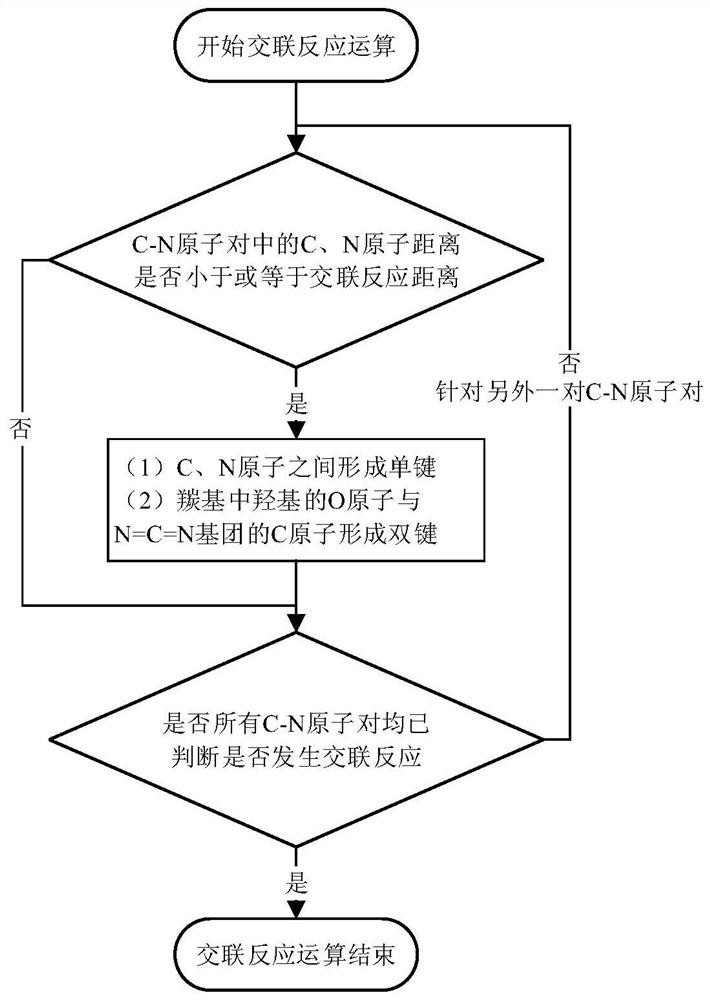
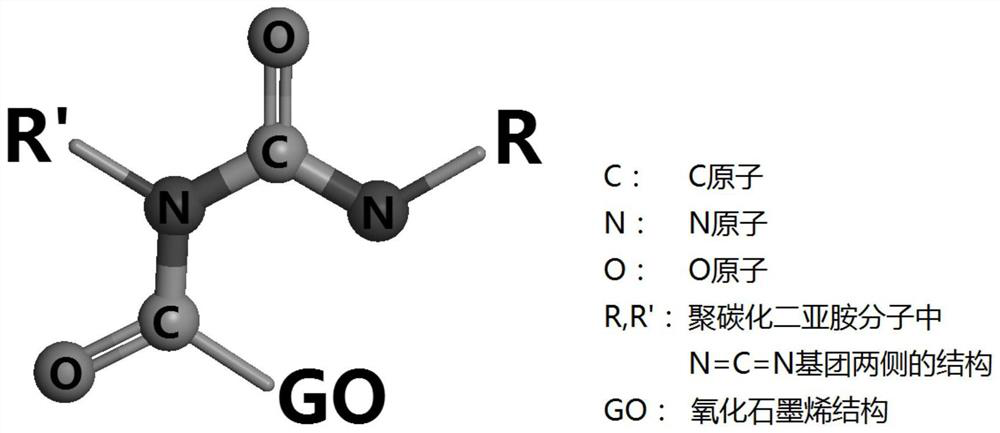
[0072] A method of using computer simulation to construct a crosslinked structure model of graphene oxide and polycarbodiimide, taking 2 graphene oxide molecules and 5 polycarbodiimide molecules to construct a crosslinked structure with a reactivity of 100% as an example , including the following steps:
[0073] (1) Use the Visualizer module in the MS software to construct the structures GO1 and NCN1 of graphene oxide molecules and polycarbodiimide molecules, respectively;
[0074] (2) Use the Forcite module in the MS software to perform energy minimization calculations on the two structure files GO1 and NCN1 obtained in step (1), respectively, and use the Smart Minimize method, the COMPASS molecular force field, and the Atom based non-bonding summation method , get the energy-optimal structures GO2 and NCN2 respectively;
[0075] (3), use the Amorphous Cell module in the MS software to carry out the structure mixing operation on the two structures GO2 and NCN2 obtained in st...
Embodiment 2
[0101] A method of using computer simulation to construct a crosslinked structure model of graphene oxide and polycarbodiimide, taking 5 graphene oxide molecules and 10 polycarbodiimide molecules to construct a crosslinked structure with a reactivity of 80% as an example , including the following steps:
[0102] (1) Use the Visualizer module in the MS software to construct the structures GO1 and NCN1 of graphene oxide molecules and polycarbodiimide molecules, respectively;
[0103] (2) Use the Forcite module in the MS software to perform energy minimization calculations on the two structure files GO1 and NCN1 obtained in step (1), respectively, and use the Smart Minimize method, the COMPASS molecular force field, and the Atom based non-bonding summation method , get the energy-optimal structures GO2 and NCN2 respectively;
[0104] (3), use the Amorphous Cell module in the MS software to carry out the structure mixing operation on the two structures GO2 and NCN2 obtained in st...
Embodiment 3
[0129] A method of using computer simulation to construct a crosslinked structure model of graphene oxide and polycarbodiimide, taking 1 graphene oxide molecule and 10 polycarbodiimide molecules to construct a crosslinked structure with a reactivity of 100% as an example , including the following steps:
[0130] (1) Use the Visualizer module in the MS software to construct the structures GO1 and NCN1 of graphene oxide molecules and polycarbodiimide molecules, respectively;
[0131] (2) Use the Forcite module in the MS software to perform energy minimization calculations on the two structure files GO1 and NCN1 obtained in step (1), respectively, and use the Smart Minimize method, the COMPASS molecular force field, and the Atom based non-bonding summation method , get the energy-optimal structures GO2 and NCN2 respectively;
[0132] (3), use the Amorphous Cell module in the MS software to carry out the structure mixing operation on the two structures GO2 and NCN2 obtained in st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com