Quantum Byzantine agreement method based on tripartite participation
A Byzantine and agreement technology, applied in the field of quantum Byzantine agreement based on the participation of three parties, can solve the problems of low detection efficiency, high cost of discrete variable quantum state preparation, and difficult realization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
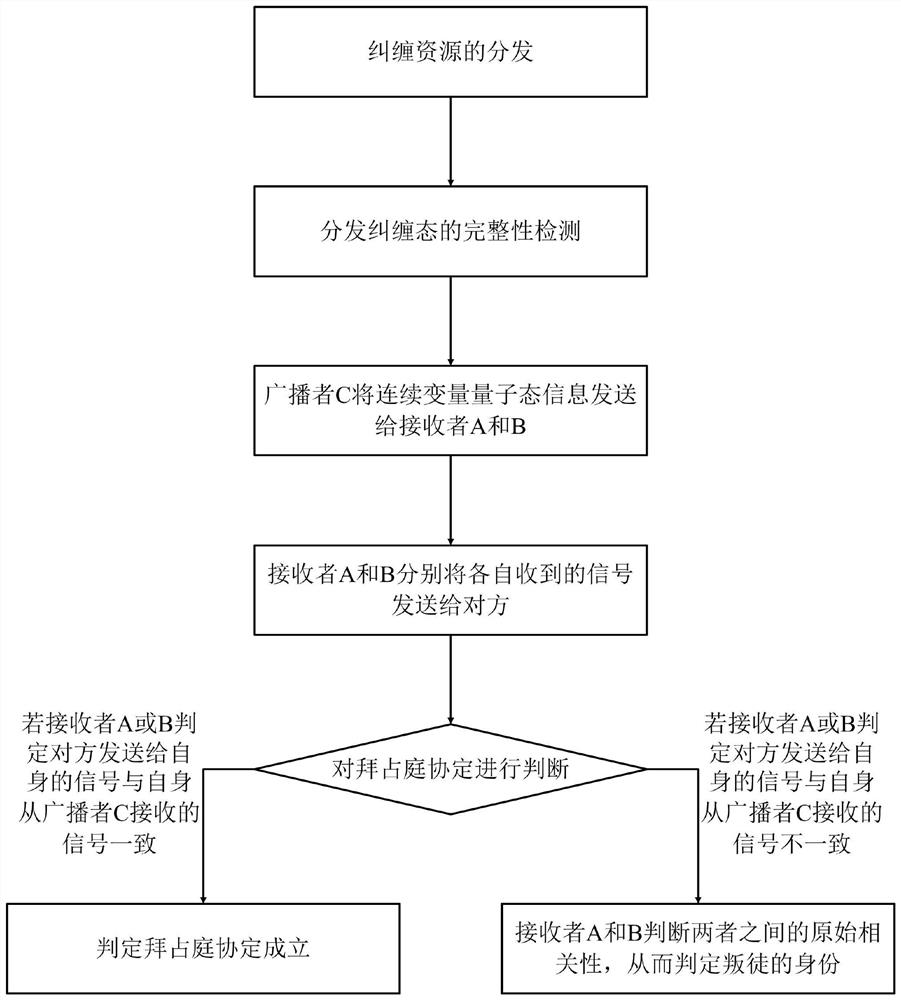
[0036] Such as figure 2 Shown is the method flowchart of the method of the present invention: the quantum Byzantine agreement method based on the participation of three parties provided by the present invention specifically includes the following steps:
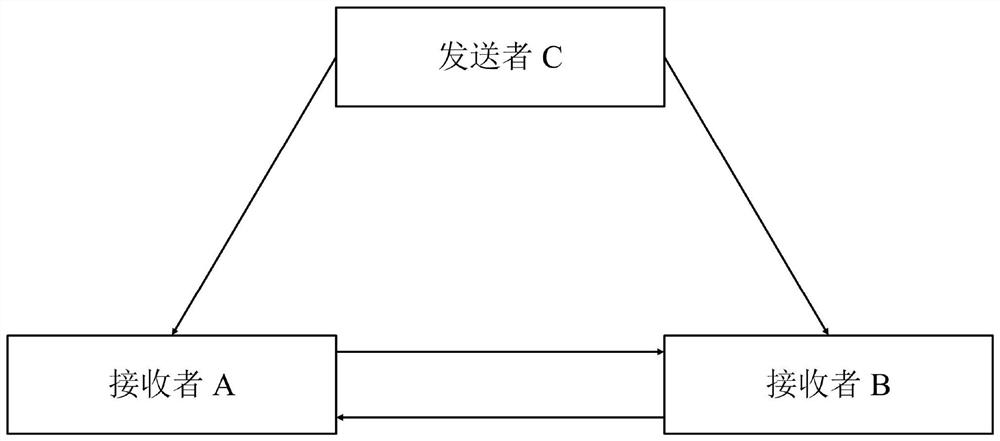
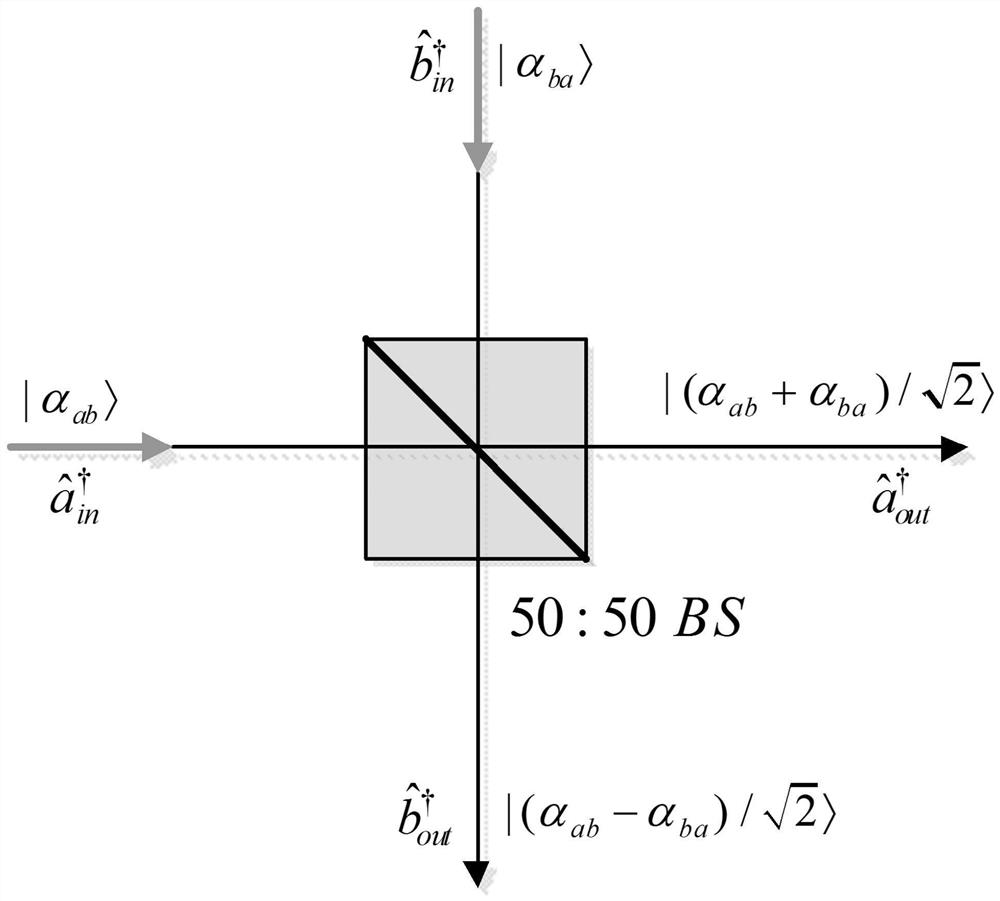
[0037] Such as figure 1 As shown, the three participants C (broadcaster), A and B (both receivers) share the three-mode continuous variable quantum unweighted graph state, and the broadcaster sends the information |α c > Sent to receivers A and B, the information received by A and B is |α ac > and |α bc >, and then the two receivers exchange the information they received from the sender, compare and finally confirm the accuracy and authenticity of the sent information:
[0038] Broadcaster C, receivers A and B, share a three-mode continuous variable quantum unweighted graph state, expressed as follows:
[0039]
[0040]
[0041]
[0042] in is the quadrature amplitude component of the i-th mode, e r Indicates...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com