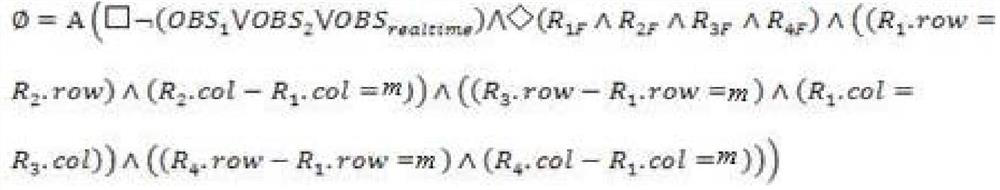A multi-robot cooperative motion control method
A technology of collaborative motion and control methods, applied in the direction of program control manipulators, manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of lack of robustness and scalability of the system, complex system model, and difficult solution of the system, so as to overcome the lack of robustness of the system and the effect of scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Most of the research in the prior art assumes that the global environment information is known. However, in the actual system, the general robot can only know the environment information within the range of the sensor, and static obstacles may be added in the environment at any time. Therefore, the offline path planning algorithm proposed with known global environment information is not suitable for practical systems.
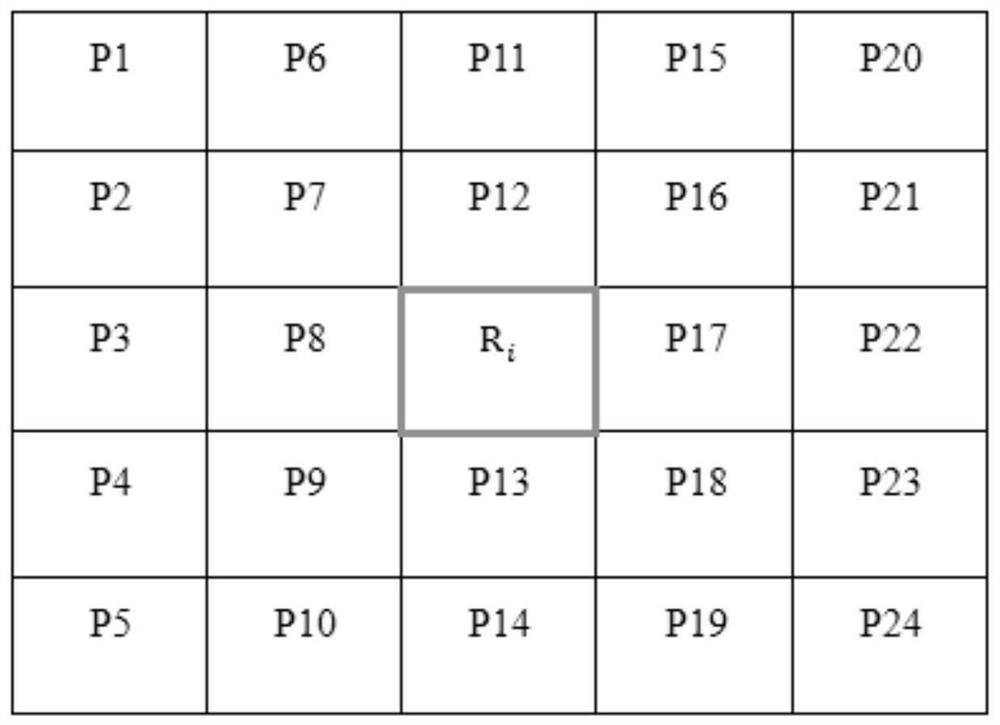
[0038] In order to solve the problems existing in the prior art, this embodiment provides a multi-robot cooperative motion control method, which uses a two-dimensional grid graph to represent the robot work area, decomposes the work area into blocks, and uses the collaborative control algorithm and real-time heuristic Algorithm, so that each robot can find the next position with the least total cost, satisfy the total CTL and move to the target position, avoid static obstacles in real time, and reach the target position through coordinated movement;
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0043] On the basis of Embodiment 1, this embodiment provides a multi-robot cooperative motion control method, and the cooperative control algorithm includes the following steps:
[0044] Step 1) Initialize start i , close_list i , is_end i =False, among them, start i Indicates the current position of robot i, close_list i Indicates the position point that robot i no longer retrieves, is_end i Indicates whether the robot i has reached the target position, i=1, 2, 3, 4,..., n;
[0045] Step 2) if is_end i =False, then continue to execute the following steps, if is_end i =True then skip to step 8);
[0046] Step 3) Determine whether to add a static obstacle in real time, if so, add the position of the static obstacle to OBS realtime ;OBS realtime A collection of static obstacle positions added in real time;
[0047] Step 4) Start the current position of each robot i The coordinates of the eight surrounding points are calculated according to the heuristic algorithm and...
Embodiment 3
[0059] On the basis of the foregoing embodiments, this embodiment is described by taking the coordinated motion of four robots as an example.
[0060] The specific steps of the collaborative control algorithm are as follows:
[0061] Step 1) Initialize start i , close_list i , is_end i =False, among them, start i Indicates the current position of robot i, close_list i Indicates the position point that robot i no longer retrieves, is_end i Indicates whether the robot i has reached the target position, i=1, 2, 3, 4;
[0062] Step 2) if is_end i =False, then continue to execute the following steps, if is_end i =True then skip to step 10;
[0063] Step 3) Determine whether to add a static obstacle in real time, if so, add the position of the static obstacle to OBS realtime ;OBS realtime A collection of static obstacle positions added in real time;
[0064] Step 4) Start the current position of each robot i The coordinates of the eight surrounding points are calculated ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com