In-situ remediation method for heavy metal contaminated soil and application thereof
An in-situ restoration and contaminated soil technology, applied in the restoration of contaminated soil, etc., can solve the problems of inappropriate restoration of large-scale contaminated soil, loss of soil biological function, and impact on soil biological activity, etc., to achieve strong engineering applicability , prevent secondary pollution, and have obvious ecological benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
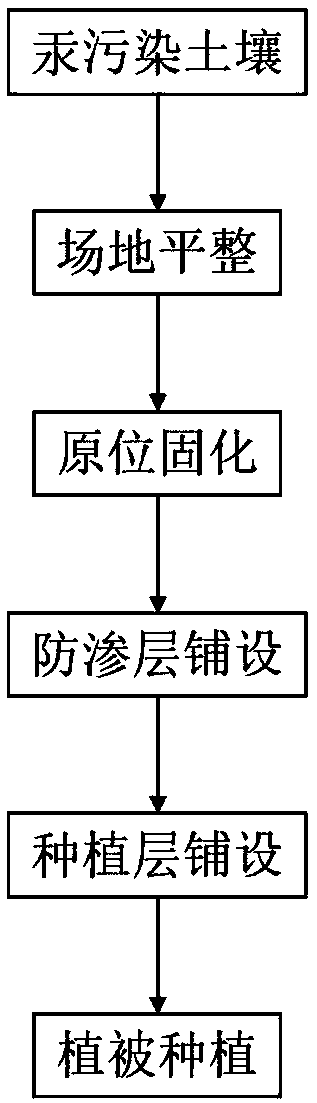
[0054] This example provides an in-situ remediation method for mercury-contaminated soil, the remediation land area is 10m×10m, and the remediation process is as follows figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0055] 1) Site leveling: do all kinds of preparatory work, such as clearing all ground and underground obstacles in the site, removing ground water, paving temporary roads, etc.
[0056] 2) In-situ solidification: Sprinkle coal fly ash on the surface of the mercury-contaminated soil to solidify the soil, and then lay 30-35cm thick clay on the surface of the solidified soil as an anti-seepage layer.
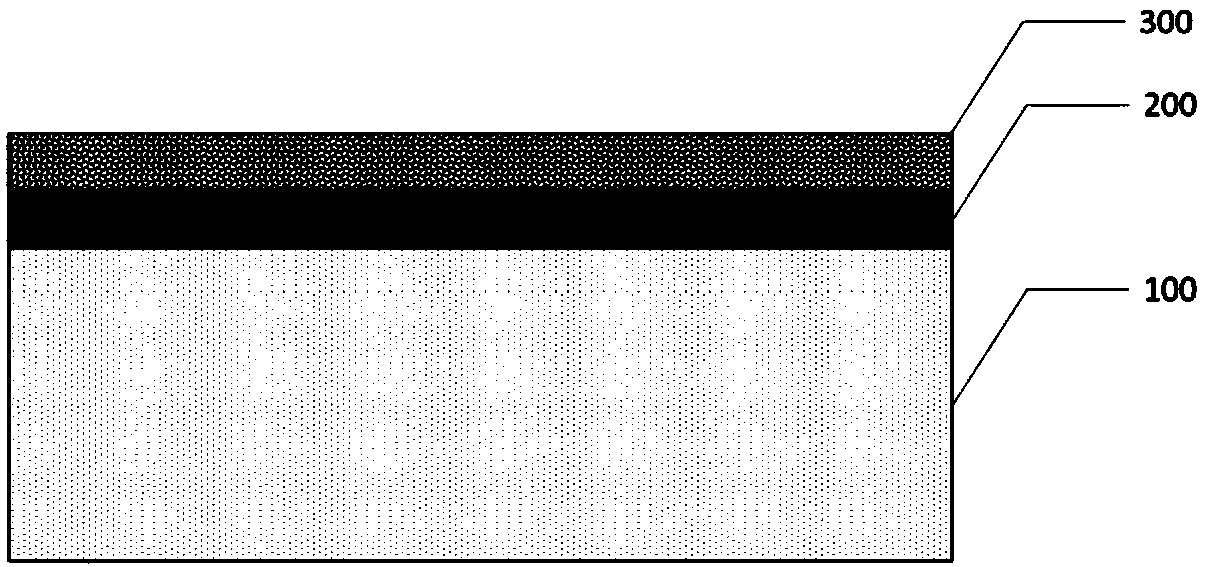
[0057] 3) Lay the planting soil layer, and backfill the planting soil on the surface of the working surface after anti-seepage treatment. The thickness of the planting soil layer is 40-45cm, and the physical and chemical indicators of the planting soil meet the requirements of "Green Planting Soil" (CJ / T340-2016). The schematic diagram of the soil structure is as ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] This embodiment provides an in-situ repair method for mercury-contaminated soil. The repaired land area is 10m×10m, including the following steps:
[0062] 1) Site leveling: do all kinds of preparatory work, such as clearing all ground and underground obstacles in the site, removing ground water, paving temporary roads, etc.
[0063] 2) In-situ solidification: Sprinkle lime on the surface of the mercury-contaminated soil to solidify the soil, and then lay 40-45cm thick clay on the surface of the solidified soil as an anti-seepage layer.
[0064] 3) Lay the planting soil layer, and backfill the planting soil on the surface of the working surface after anti-seepage treatment. The thickness of the planting soil layer is 30-35cm, and the physical and chemical indicators of the planting soil meet the requirements of "Green Planting Soil" (CJ / T340-2016).
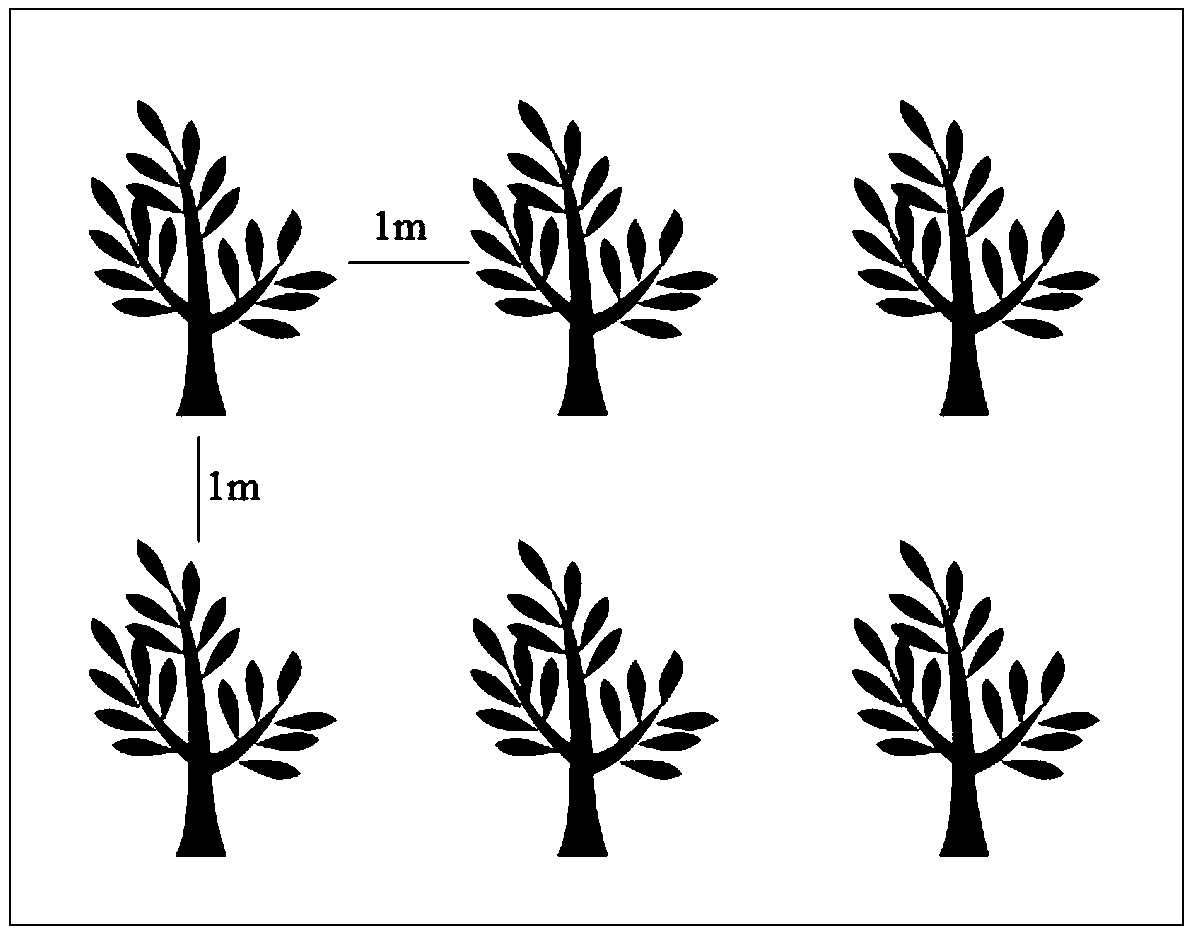
[0065] 4) Vegetation planting: plant shrubs and herbaceous plants, plant Junexue and raspberry for shrubs, the planting r...
Embodiment 3
[0067] This embodiment provides an in-situ repair method for mercury-contaminated soil. The repaired land area is 10m×10m, including the following steps:
[0068] 1) Site leveling: do all kinds of preparatory work, such as clearing all ground and underground obstacles in the site, removing ground water, paving temporary roads, etc.
[0069] 2) In-situ solidification: spread bentonite on the surface of the mercury-contaminated soil to solidify the soil, and then lay 20-25cm thick clay on the surface of the solidified soil as an anti-seepage layer.
[0070] 3) Lay the planting soil layer, and backfill the planting soil on the surface of the working surface after anti-seepage treatment. The thickness of the planting soil layer is 45-50cm, and the physical and chemical indicators of the planting soil meet the requirements of "Green Planting Soil" (CJ / T340-2016).
[0071] 4) Vegetation planting: plant shrubs and herbaceous plants, the shrubs are planted with June Snow, and the plan...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com