Transdermal microneedle array patch
A technology of microneedle array and patching, applied in medical science, sensors, catheters, etc., can solve the problems of not saving data, wasting system power, wasting resources, etc., and achieve the effect of saving system power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] The implementation of the present invention will be described below by specific specific examples, and those skilled in the art can easily understand other advantages and effects of the present invention from the content disclosed in this specification, and can also be improved by other different specific examples. implement or apply.
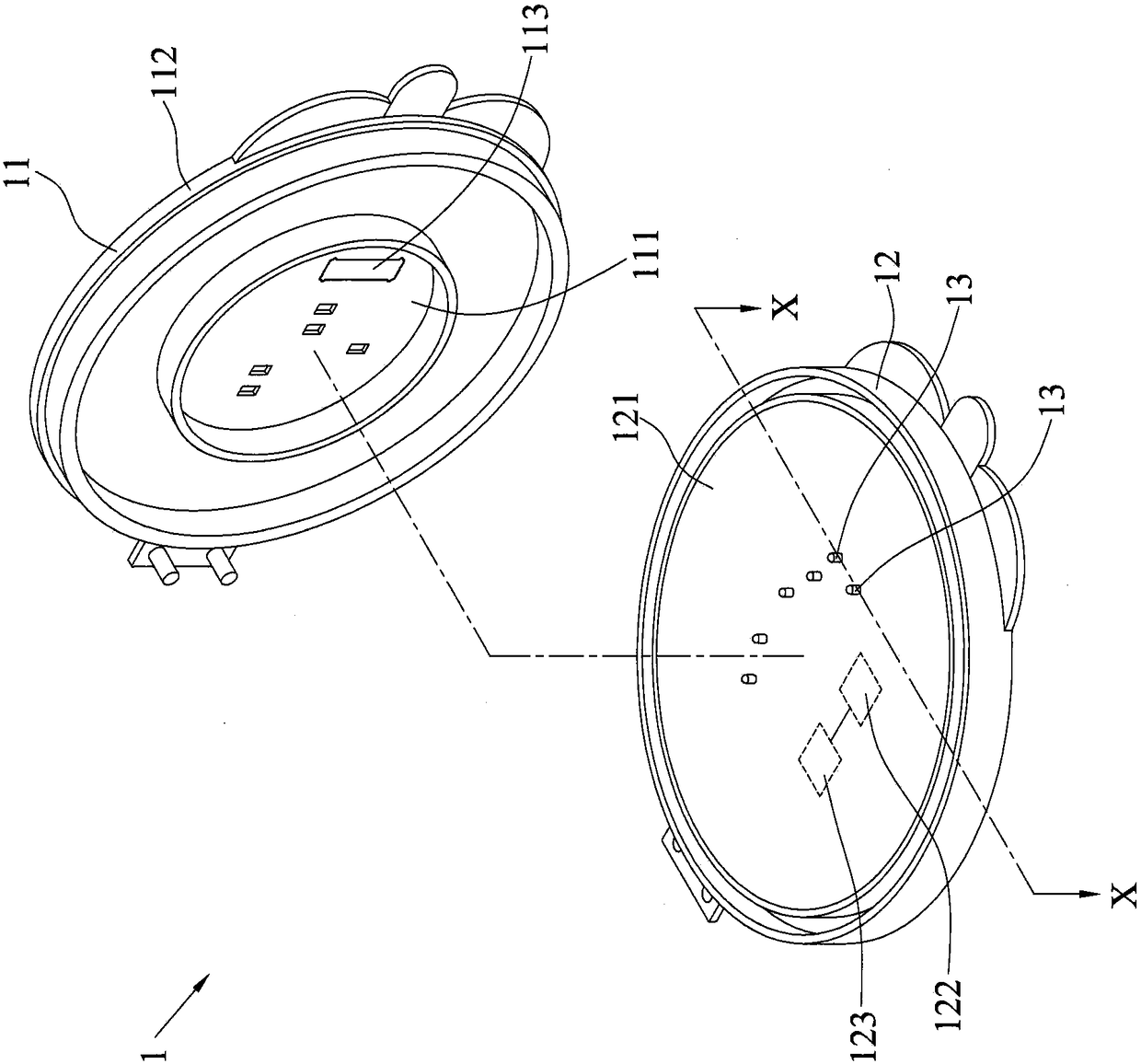
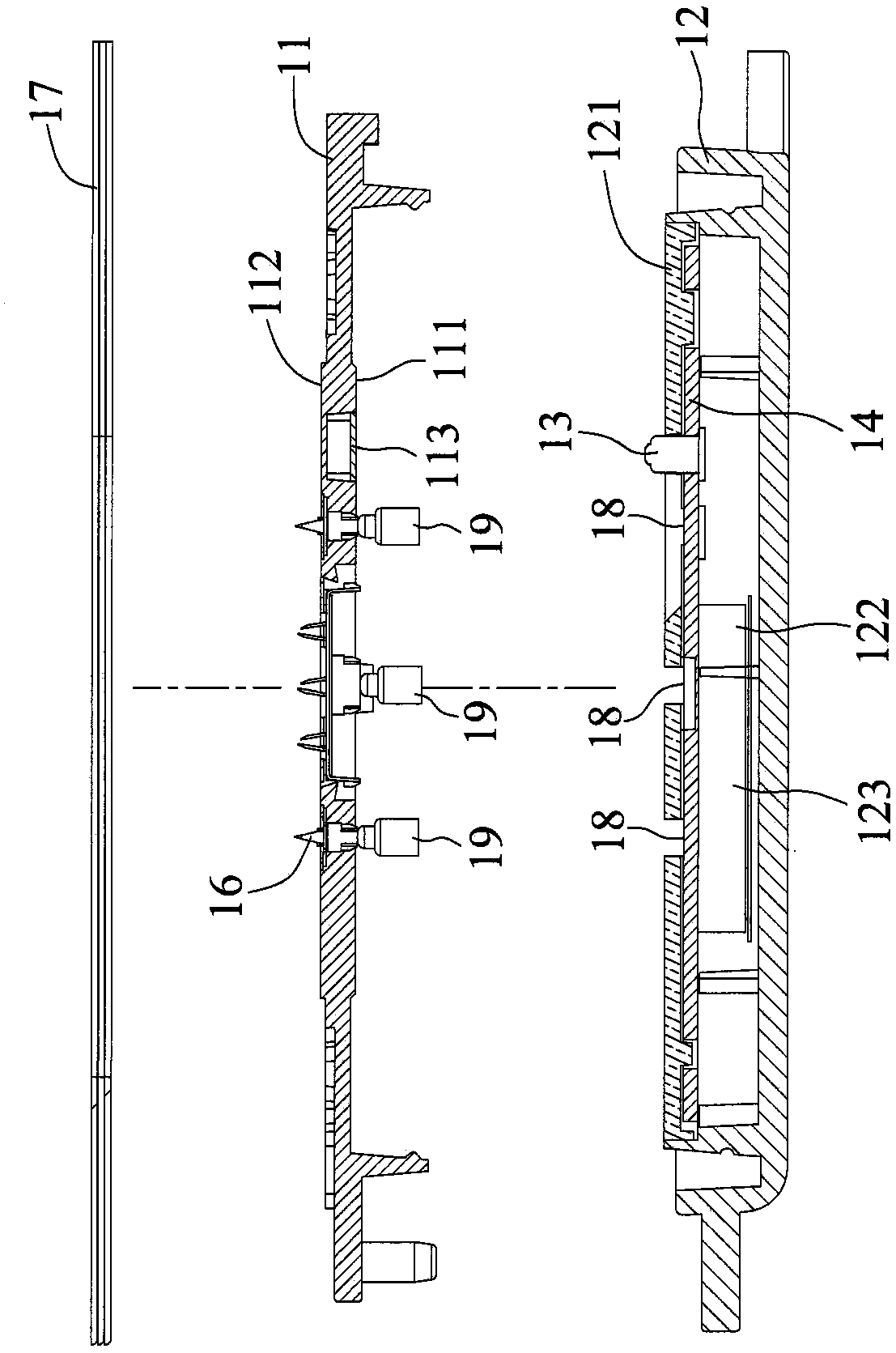
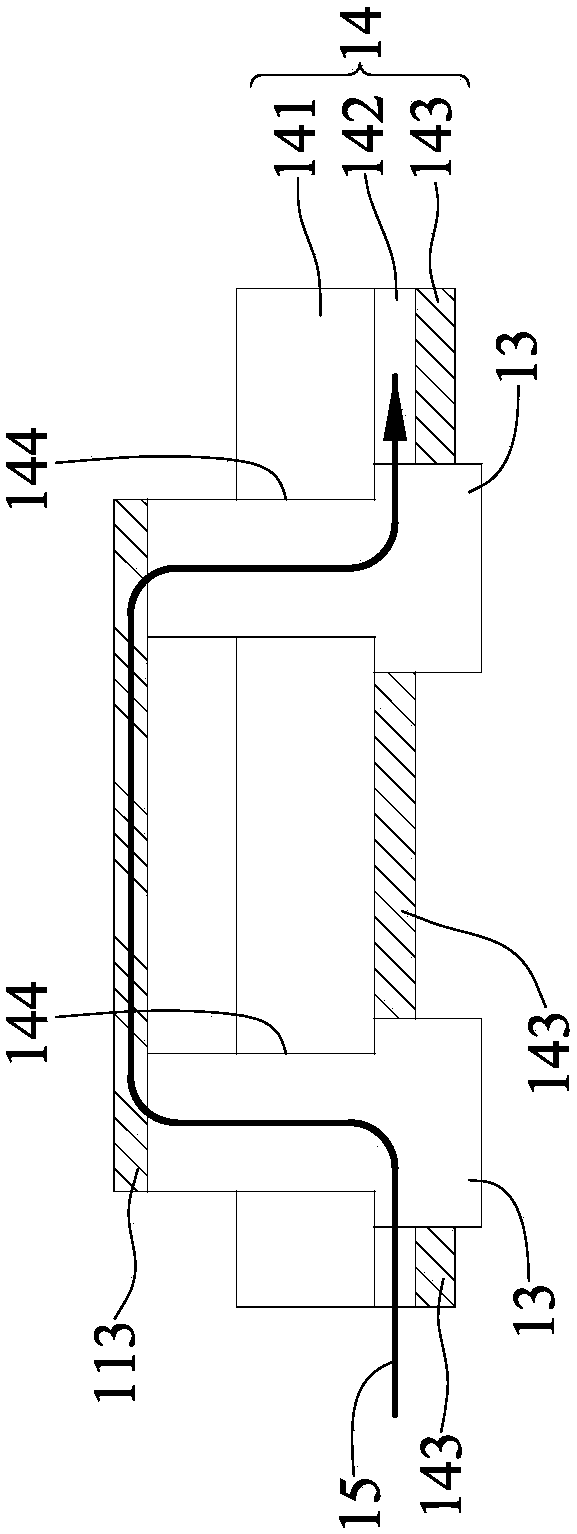
[0045] see figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 , the transdermal microneedle array patch 1 of the present invention includes a lower cover 11 and an upper cover 12 . The lower cover 11 has a first surface 111 and a second surface 112 opposite to the first surface 111 , and the first surface 111 is provided with a metal sheet 113 . A substrate 14 is disposed inside the upper cover 12 , and the substrate 14 has two probes 13 exposed on the inner surface 121 of the upper cover 12 , wherein the two probes 13 are disconnected from each other.
[0046] In one embodiment, the two probes 13 may not be arranged on the substrate 14 at the same t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com