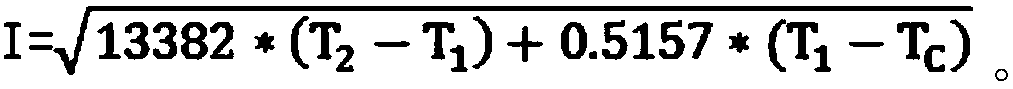Cable load measurement device and measurement method
A technology for measuring devices and cable loads, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, measuring electrical variables, and measuring electricity, etc. It can solve the problems of not considering the influence of air and cable convection heat dissipation and contact thermal resistance, etc., and achieve the effect of convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
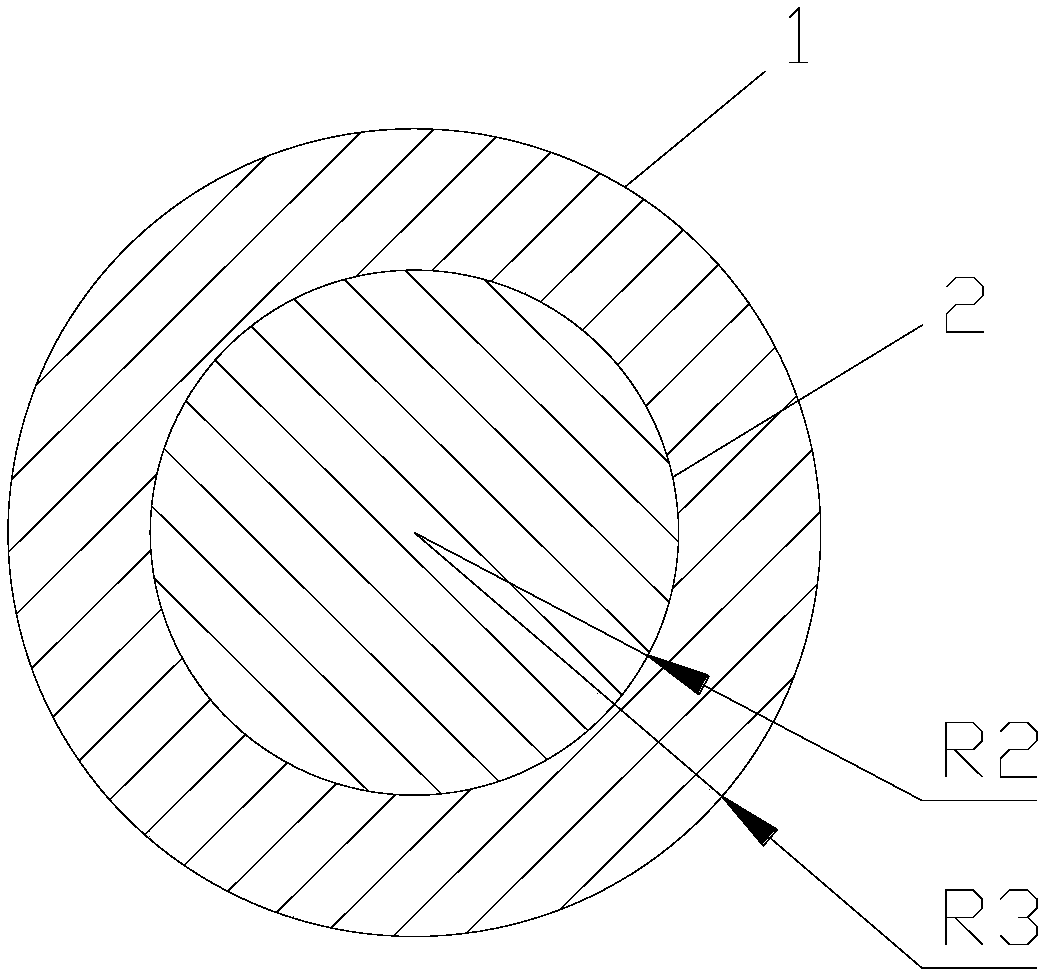
[0058] Cable dimensions such as figure 2 As shown, when the conductor 2 is Cu and the insulating layer 1 is PA66, the air convection heat dissipation coefficient α is 25W / m 2 ·K,R t =5500W / m K, λ t =0.3W / m·K, r 1 =0.003m, r 2 = 0.002m, resistance R per unit length Cu = 0.00137Ω, α = 25W / m 2 · K, substitute into formula (3) to get
[0059]
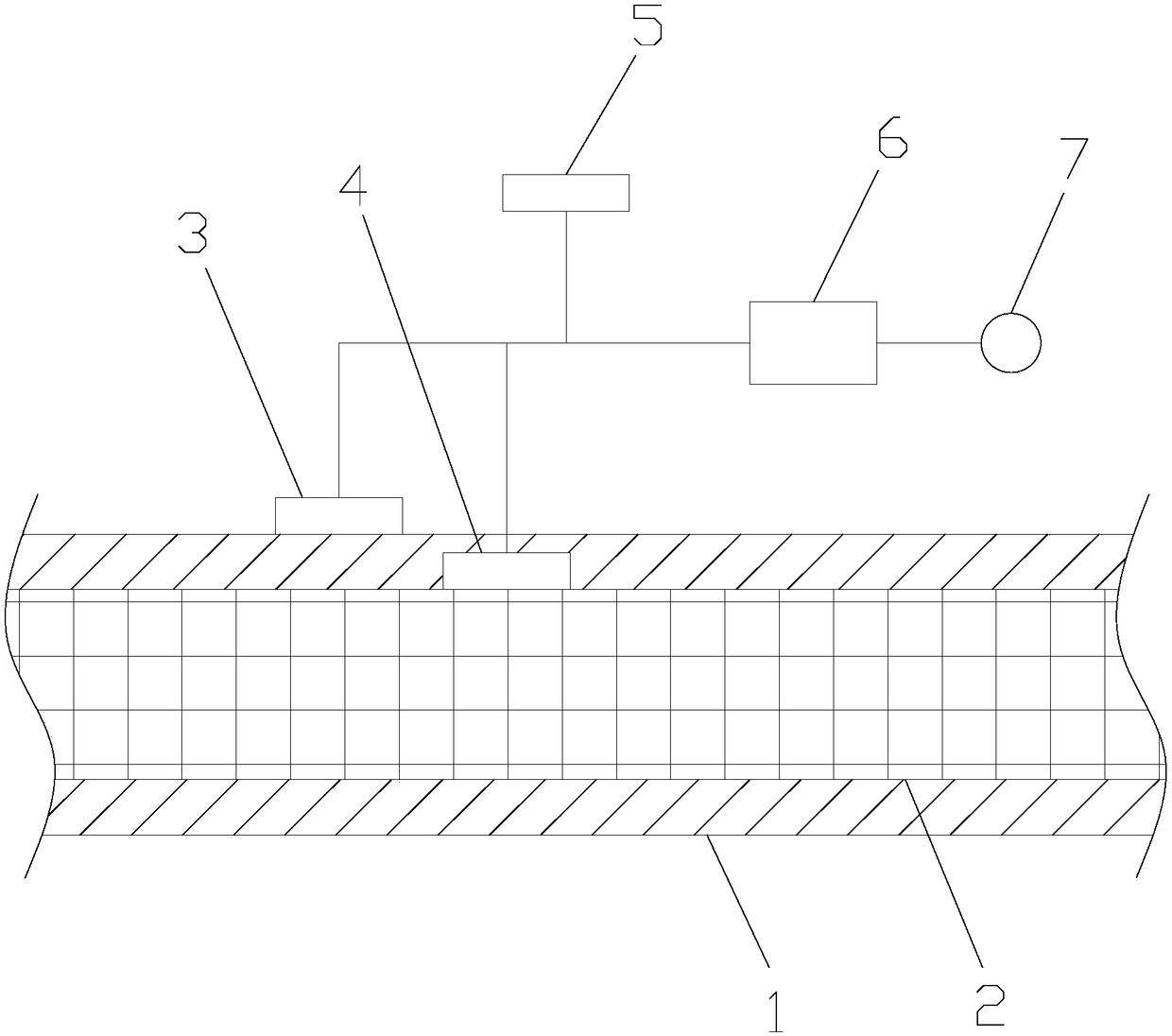
[0060] Set the temperature probe to a 3T 1 , temperature probe two 2T 2 The outer surface temperature of conductor 2 insulation layer 1, the temperature of conductor 2 and the ambient temperature measured by temperature probe 3 and 5 are brought into formula (4) respectively, and the working current I of conductor 2 can be calculated, and then the working current I of conductor 2 can be calculated with the rated current I of conductor 2 0 Compare if I > I 0 , then it shows that the cable is in an overload operation state at this time, and the controller 6 controls the alarm 7 to buzz to remind the staff to pay attention.
Embodiment 2
[0062] Cable dimensions such as figure 2 As shown, when the conductor 2 is made of aluminum and the insulating layer 1 is made of PA66, the air convection heat dissipation coefficient α is 25W / m 2 ·K,R t =4500W / m K, λ t =0.3W / m·K, r 1 =0.003m, r 2 = 0.002m, the resistance of aluminum per unit length R = 0.00222Ω, α = 25W / m 2 K, substitute into formula (3) to get
[0063]
[0064] The outer surface temperature T of conductor 2 insulation layer 1 measured by temperature probe 1 3, temperature probe 2 2 and temperature probe 3 5 respectively 1 , conductor 2 temperature T 2 and ambient temperature T c Putting them into formula (5) respectively, the working current I of conductor 2 can be calculated, and then the working current I of conductor 2 and the rated current I of conductor 2 0 Compare if I > I 0 , then it shows that the cable is in an overload operation state at this time, and the controller 6 controls the alarm 7 to buzz to remind the staff to pay attention. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com