Powered artificial ankle based on electro-hydraulic direct drive technology
A direct-drive, electro-hydraulic technology, applied in artificial legs, medical science, prostheses, etc., can solve problems such as inconvenience, consumption, adjustment of gait and control of torque
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
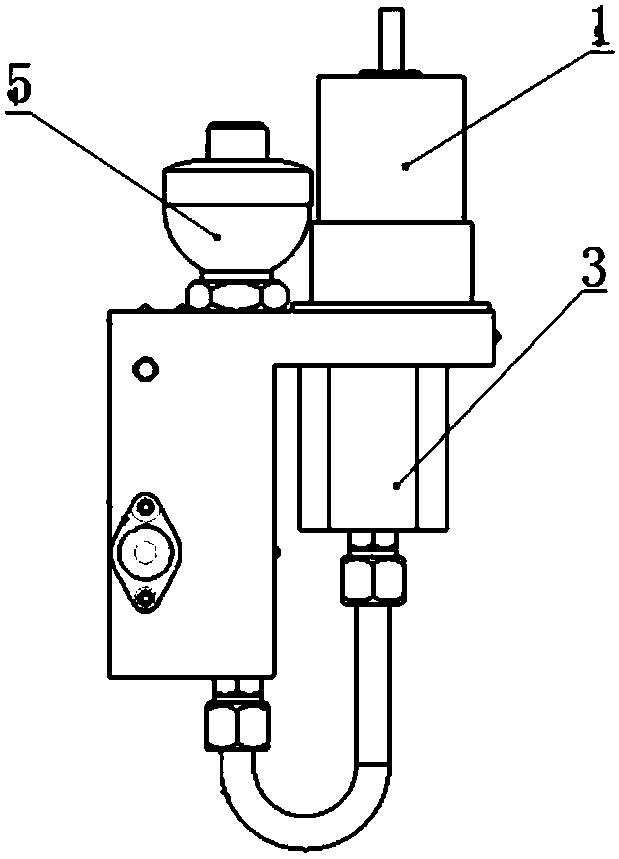
[0023] A powered artificial ankle based on electro-hydraulic direct drive technology, including an electro-hydraulic direct drive actuator, a lower leg prosthesis, an angle sensor, a force sensor, and a control module. signal connections such as Figure 1-2 As shown, the electro-hydraulic direct drive actuator includes a servo motor 1, a hydraulic cylinder 11, a bidirectional gear pump 3, a hydraulic valve block and an accumulator 5, the hydraulic valve block is connected to the hydraulic cylinder 11, the servo motor 1 and the bidirectional gear The pump 3 is fixed on the hydraulic valve block, the servo motor 1 and the two-way gear pump 3 are connected through the coupling 2; the hydraulic valve block is equipped with three one-way valves 4.6.10, two throttle valves 7.9 and two-position three-way solenoid The reversing valve 8; the oil inlet of the first one-way valve 10 is connected with the oil outlet of the first throttle valve 9; the oil outlet of the two-position three-w...
Embodiment 2
[0025] The movement process of a powered artificial ankle based on electro-hydraulic direct drive technology is as follows: Figure 5 Shown:
[0026] Plantarflexion control: the rear heel touches the ground first, the servo motor does not work at this time, and the artificial ankle is in a passive state. The first throttle valve 9, the first one-way valve 10, and the hydraulic cylinder 11 form a closed loop. The first throttle valve 9. The damping is large, which buffers the movement of the piston rod of the hydraulic cylinder 11 at this time, and achieves the shock-absorbing and buffering effect of controlling the plantar flexion stage when the heel 42 touches the ground. From the heel 42 touches the ground to the entire arch 40, the plantar flexion angle gradually Increase, and reach the maximum value when the entire arch 40 touches the ground. At this stage, the artificial ankle acts as a buffer, which is equivalent to a linear spring, and the torque of the artificial ankle...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com