Remote-sensing-data-based geological mapping method of lunar-surface impact crater
A technology of remote sensing data and impact craters, applied in the field of planetary remote sensing and planetary geology, can solve the problems of low resolution of impact crater mapping, lack of detailed expression of shape and structure information, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0079] It should be pointed out that the following detailed description is exemplary and intended to provide further explanation to the present application. Unless defined otherwise, all technical and scientific terms used herein have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this application belongs.
[0080] It should be noted that the terminology used here is only for describing specific implementations, and is not intended to limit the exemplary implementations according to the present application. As used herein, unless the context clearly dictates otherwise, the singular is intended to include the plural, and it should also be understood that when the terms "comprising" and / or "comprising" are used in this specification, they mean There are features, steps, operations, means, components and / or combinations thereof.
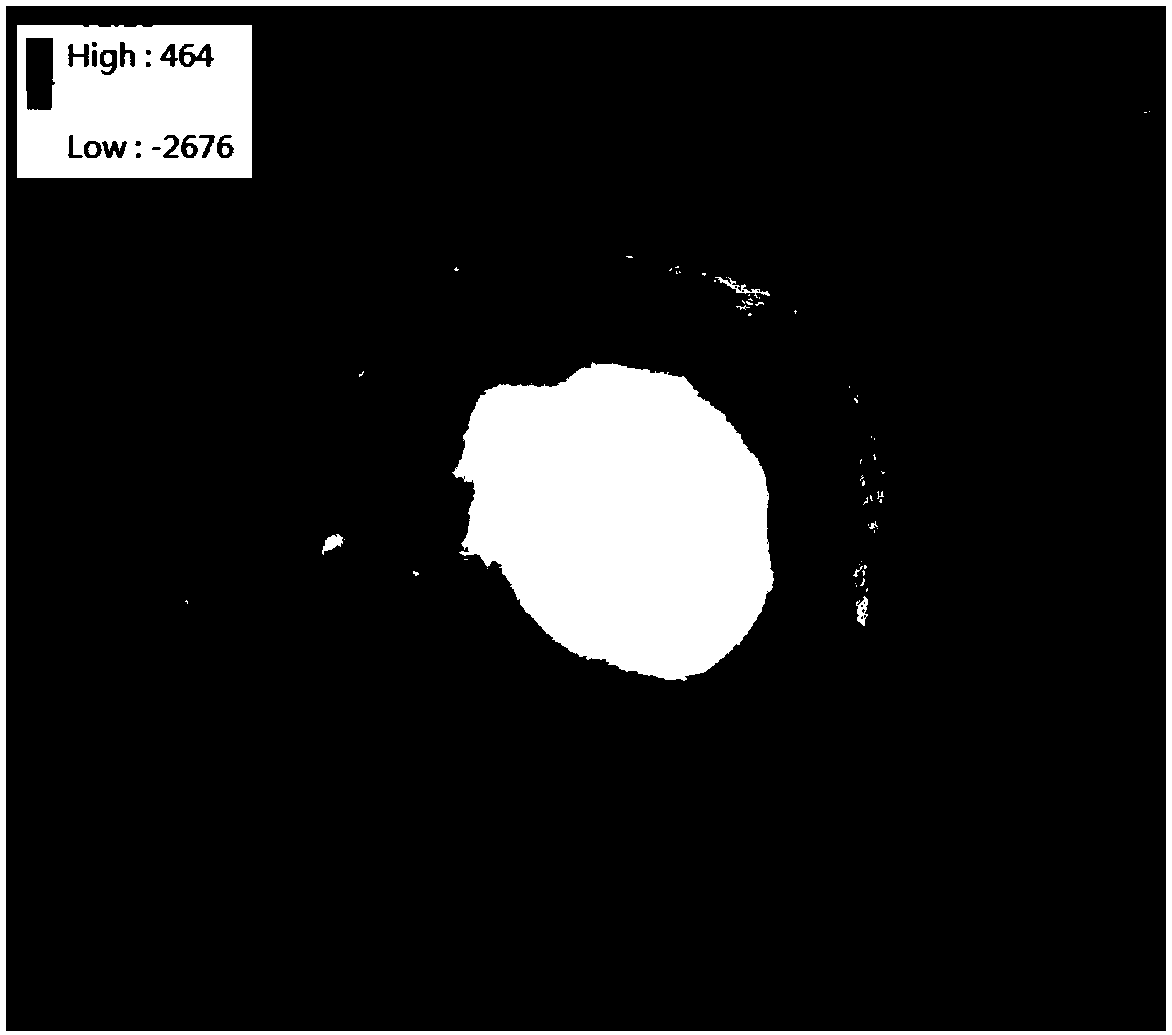
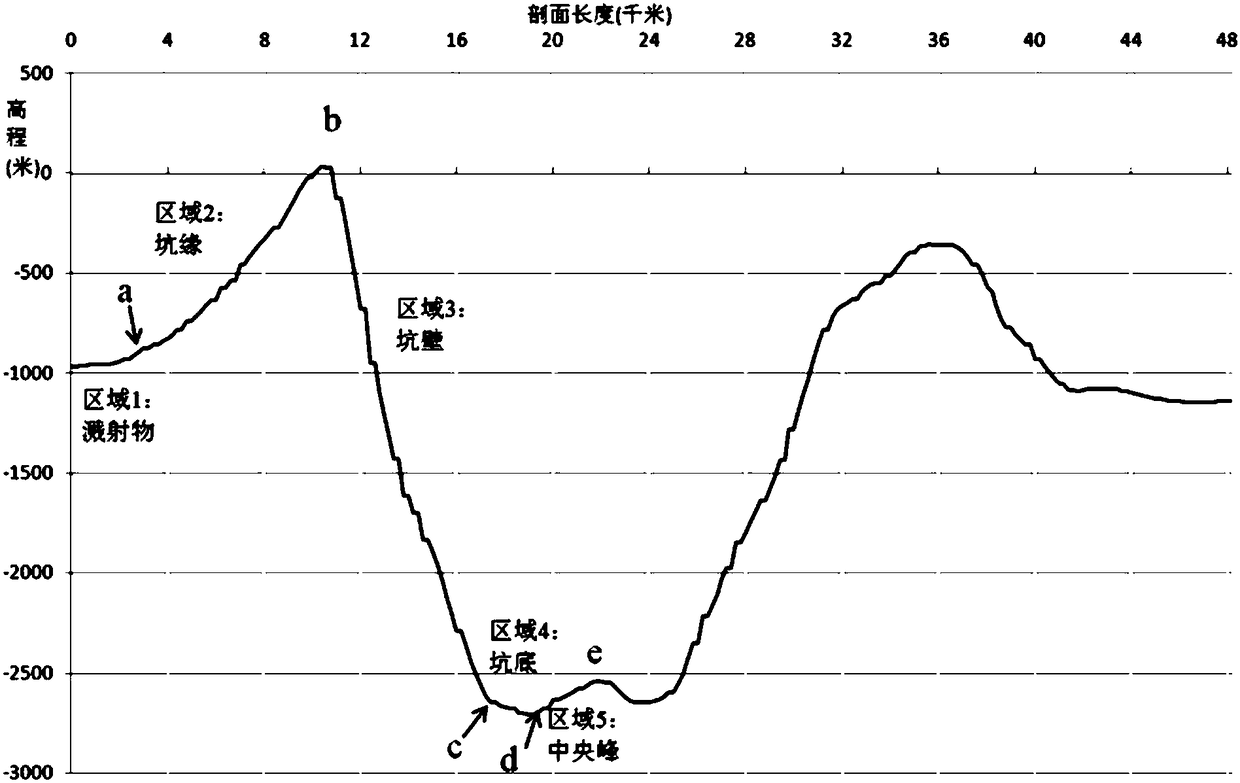
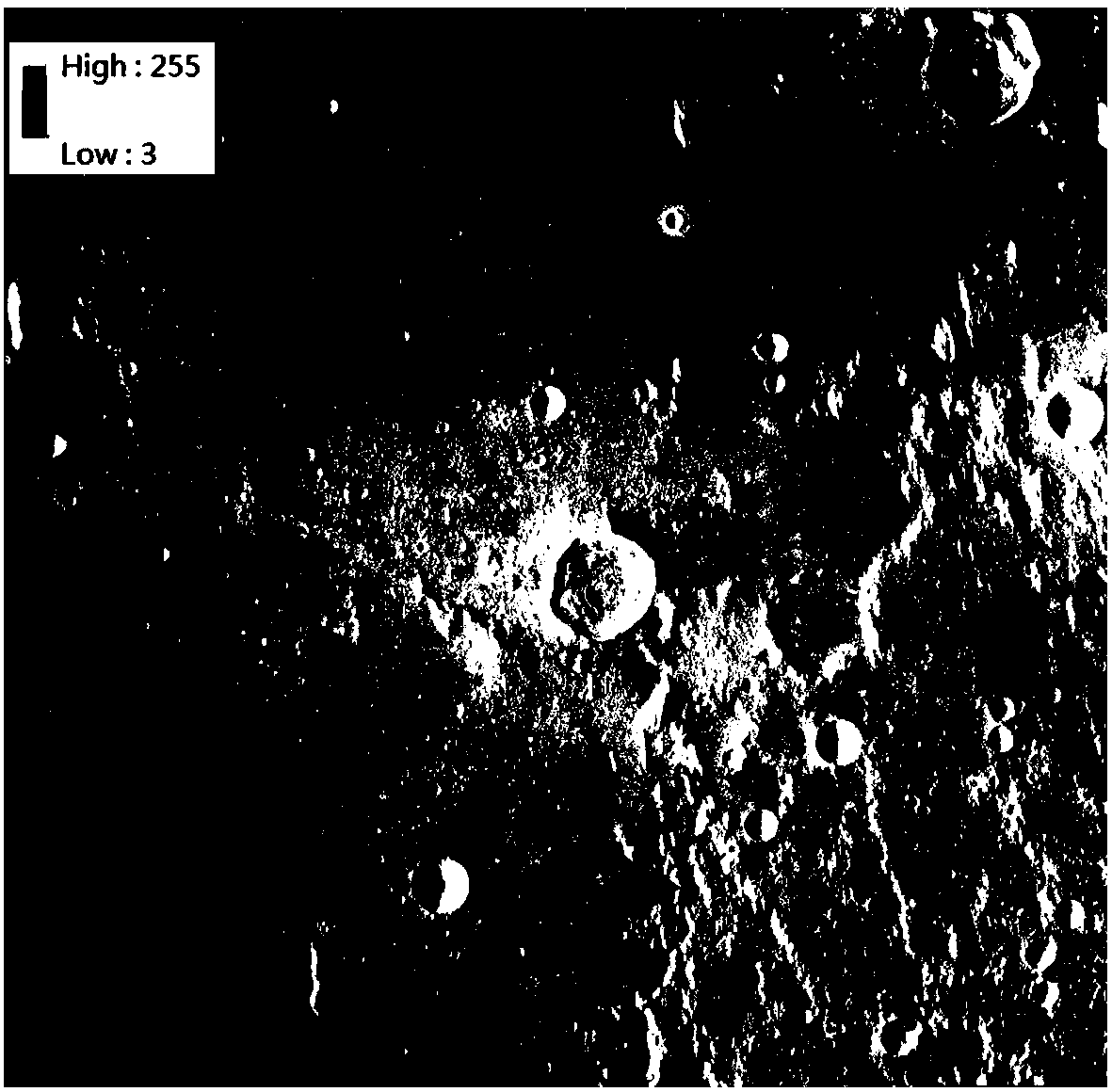
[0081] In a typical implementation of the present application, the process of geological mapping of lunar surfac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com