Light-sheet microscope
A microscope and light sheet technology, applied in the field of microscopy, can solve the problems of reducing the penetration depth of illumination, insufficient penetration depth of turbid samples, and sample damage.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
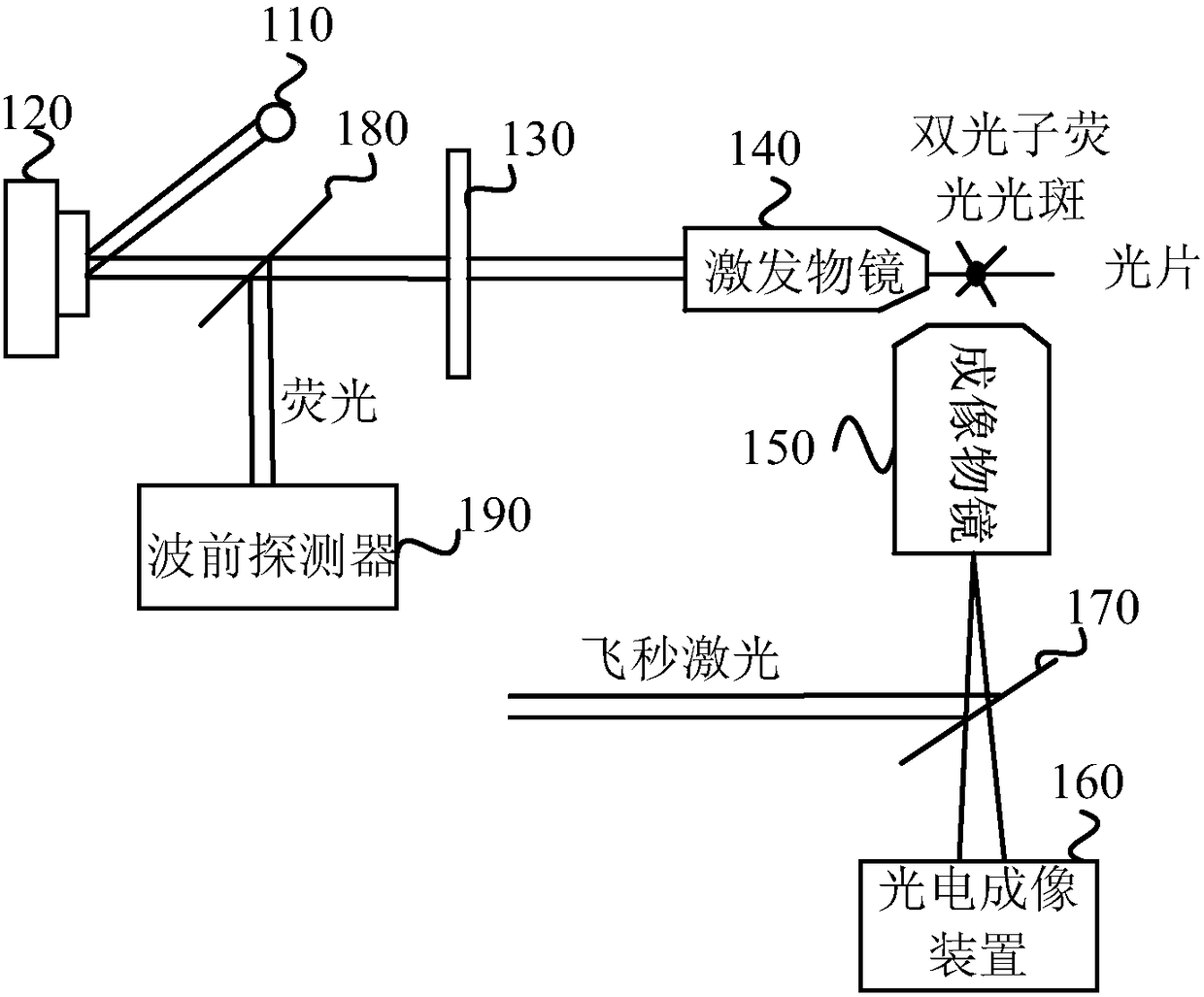
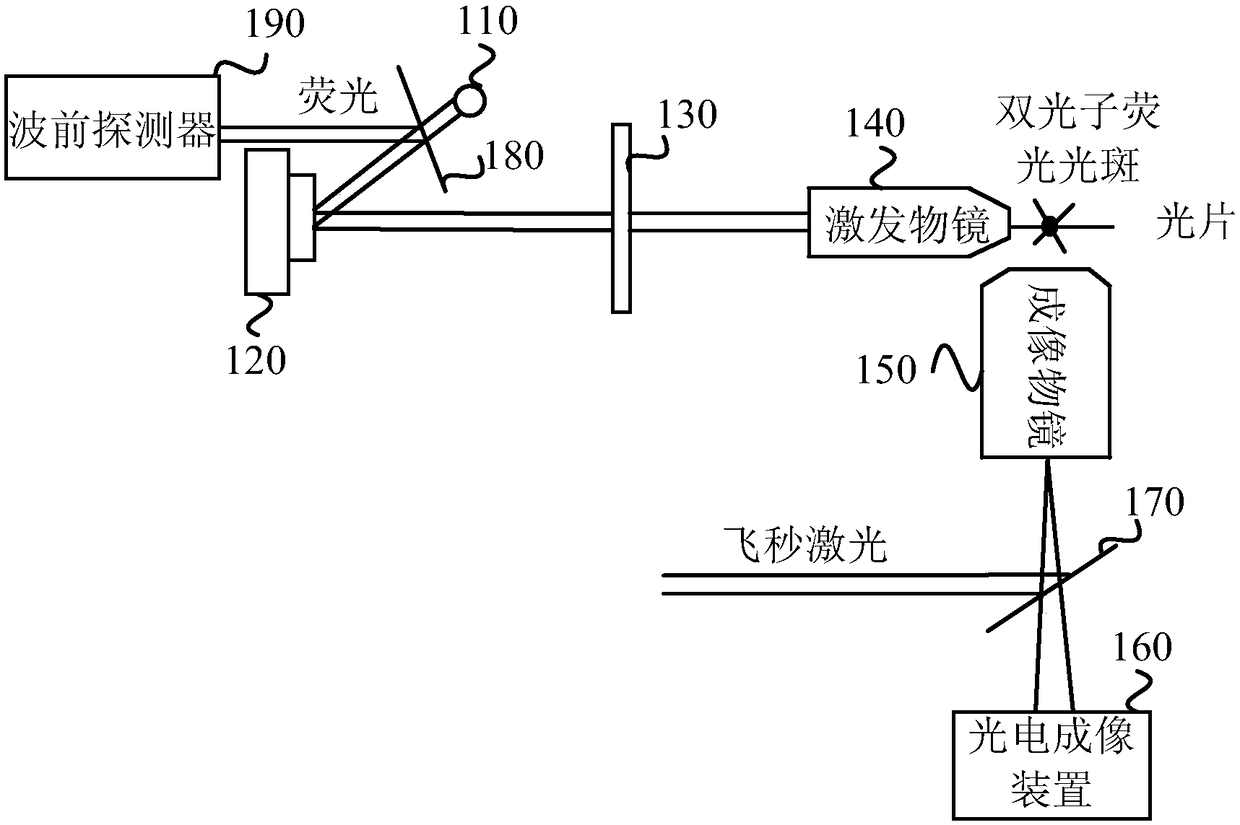
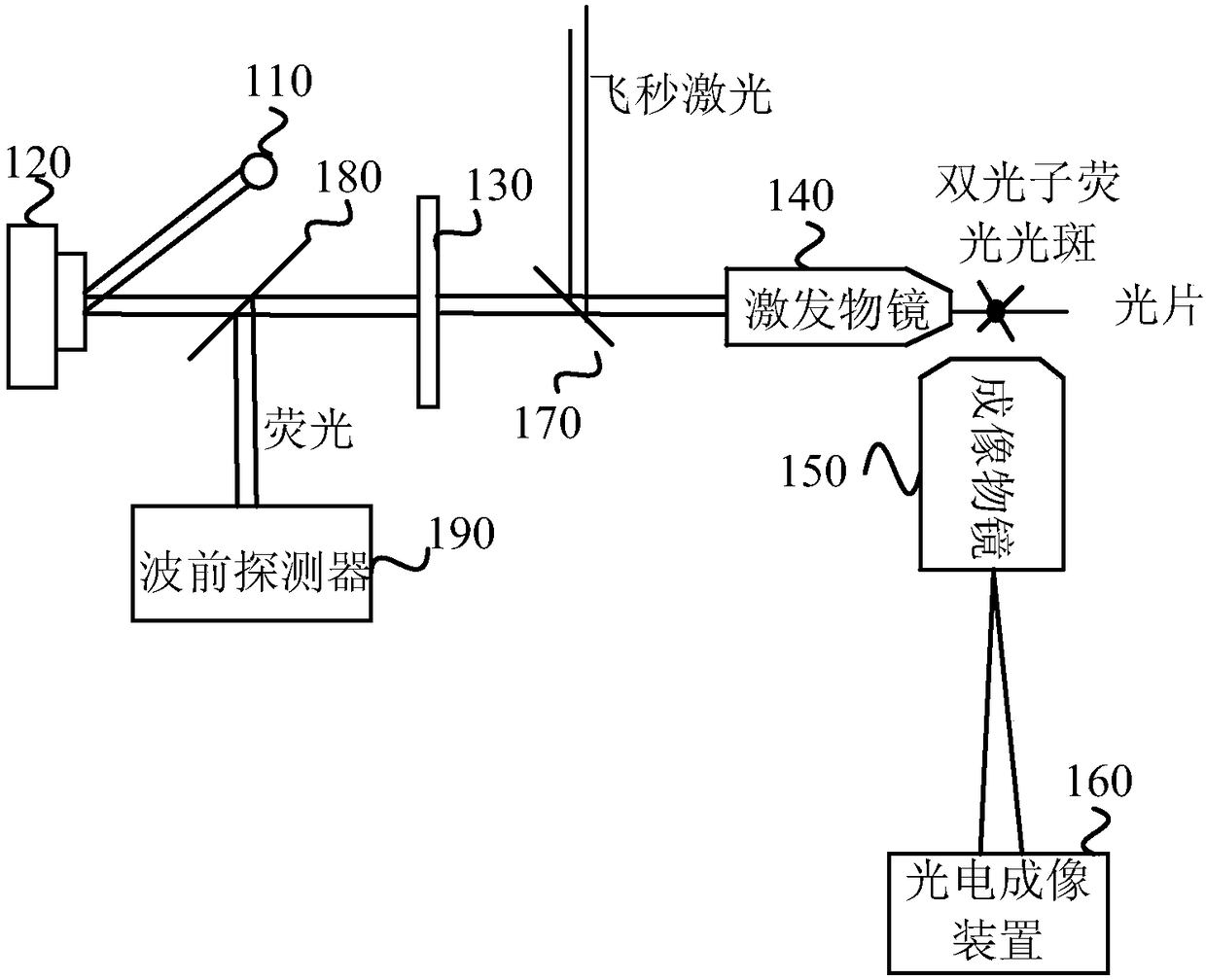
[0034] figure 1 It is a schematic structural diagram of a light-sheet microscope provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, and the light-sheet microscope can realize deep imaging of turbid samples. Such as figure 1 As shown, the light sheet microscope includes: a laser light source 110, a light wave phase adjuster 120, a light sheet generating device 130, an excitation objective lens 140, an imaging objective lens 150, a photoelectric detection device 160, a first beam splitter 170, a second beam splitter 180 and Wavefront detector 190 .
[0035] The laser light source 110 is used to generate laser beams. The light wave phase adjuster 120 is used for receiving the laser beam generated by the laser light source 110 and adjusting the phase of the laser beam. The optical sheet generating device 130 is configured to receive the laser beam emitted by the optical wave phase adjuster 120 and shape the laser beam into an optical sheet. The excitation objective lens 140 is...
Embodiment 2
[0054] figure 2 A schematic structural diagram of a light sheet microscope provided in Embodiment 2 of the present invention, as a further description of the above embodiment, as shown in figure 2 As shown, the light sheet microscope includes: a laser light source 201, a spatial light modulator 202, a first lens 203, a mirror 204, a second lens 205, an X-axis vibrating mirror 206, a third lens 207, a fourth lens 208, and a Y Axis galvanometer 209, fifth lens 210, sixth lens 211, excitation objective lens 212, imaging objective lens 213, photodetection device 214, first beam splitter 215, second beam splitter 216, wavefront detector 217 and relay lens 218 .
[0055]In this implementation, the working process of the light sheet microscope can be that the laser beam generated by the laser light source 201 enters the spatial light modulator 202, enters the first lens 203 after the phase is modulated by the spatial light modulator 202, and converges through the first lens 203 A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com