Method for catalytically producing bacterial cellulose by using resting cells of acetic acid bacteria
A technology of bacterial cellulose and resting cells, which is applied in the field of microorganism and fermentation engineering, can solve the problems of high price and low yield, and achieve the effects of simplified production process and equipment requirements, simple nutritional components, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
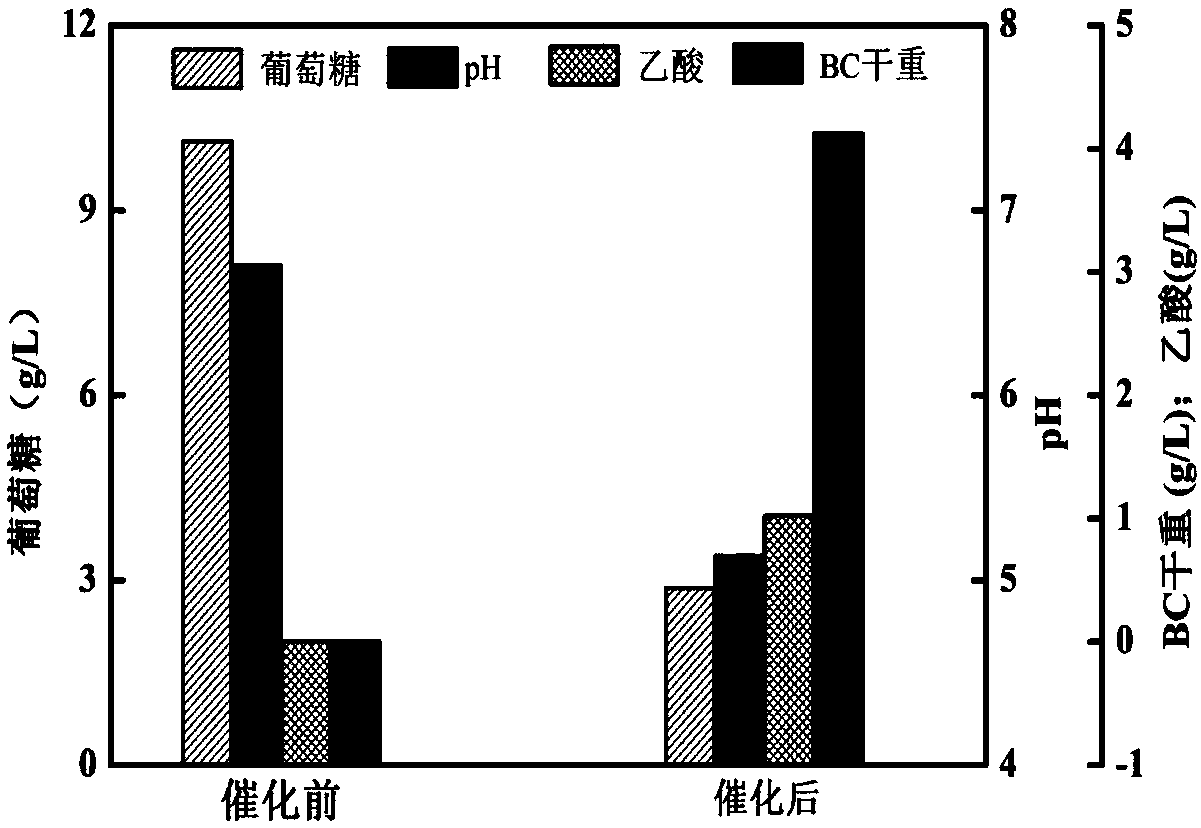
[0023] Embodiment 1: the glucose concentration in the reaction liquid is 10g / L.
[0024] (1) Strain activation: the gluconacetobacter hansenii preserved on the subculture medium was taken out, inoculated on a new subculture medium by streak transfer, and cultured at 30° C. for 5 days.
[0025] (2) Preparation of resting cells: Transplant and culture the activated strains in the same way to obtain sufficient cultures, use an inoculation loop to pick out the single colonies and lawns formed on the plate as much as possible, and place them in normal saline , use a vortex mixer to disperse as much as possible, then centrifuge at 10,000r / min and 4°C for 10min to collect the bacteria, wash, resuspend, and centrifuge twice, and then store in the refrigerator for later use.
[0026] (3) Preparation of the reaction solution: Weigh 10 g of glucose and 2.7 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate, simply dilute to 1 L with distilled water, adjust the pH to about 6.7, and sterilize at 115° C. for...
Embodiment 2
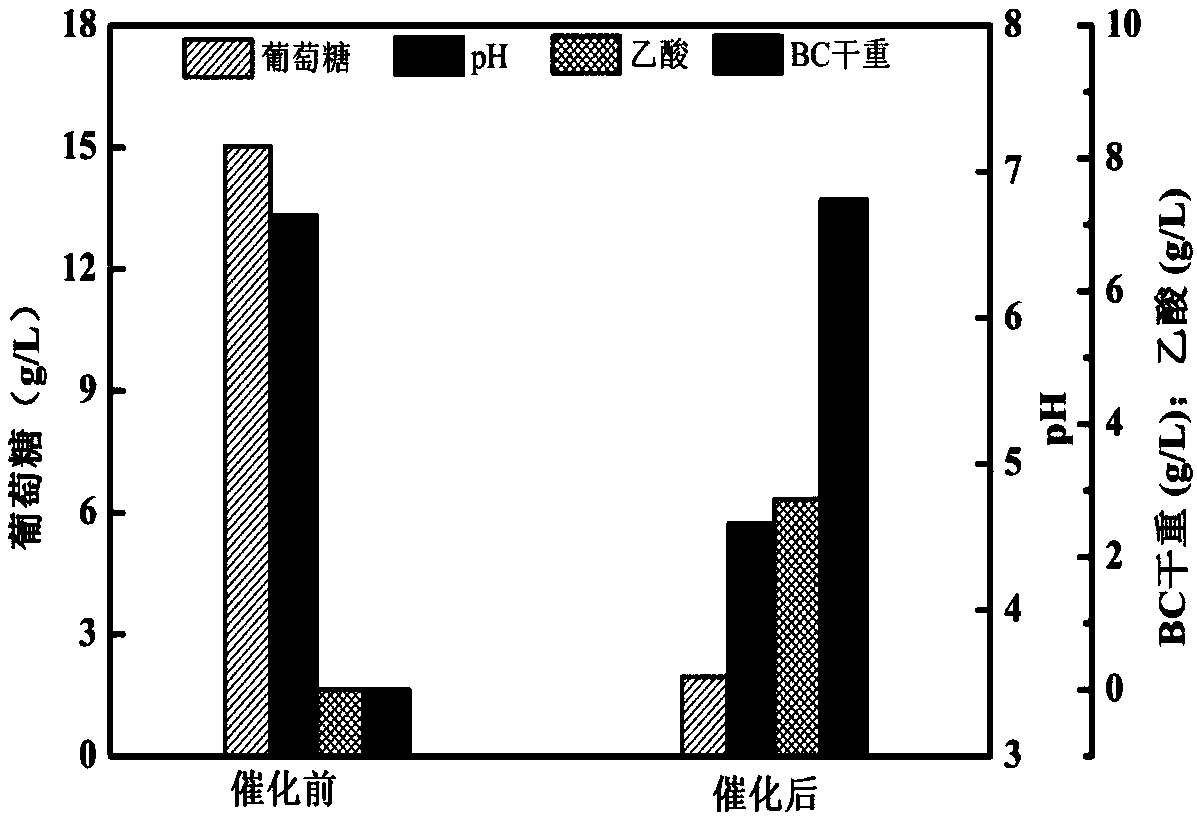
[0034] Embodiment 2: the glucose concentration in the reaction liquid is 15g / L.
[0035] (1) Strain activation: the gluconacetobacter hansenii preserved on the subculture medium was taken out, inoculated on a new subculture medium by streak transfer, and cultured at 30° C. for 5 days.
[0036] (2) Preparation of resting cells: Transplant and culture the activated strains in the same way to obtain sufficient cultures, use an inoculation loop to pick out the single colonies and lawns formed on the plate as much as possible, and place them in normal saline , use a vortex mixer to disperse as much as possible, then centrifuge at 10,000r / min and 4°C for 10min to collect the bacteria, wash, resuspend, and centrifuge twice, and then store in the refrigerator for later use.
[0037] (3) Preparation of the reaction solution: Weigh 15 g of glucose and 2.7 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate, simply dilute to 1 L with distilled water, adjust the pH to about 6.7, and sterilize at 115° C. for...
Embodiment 3
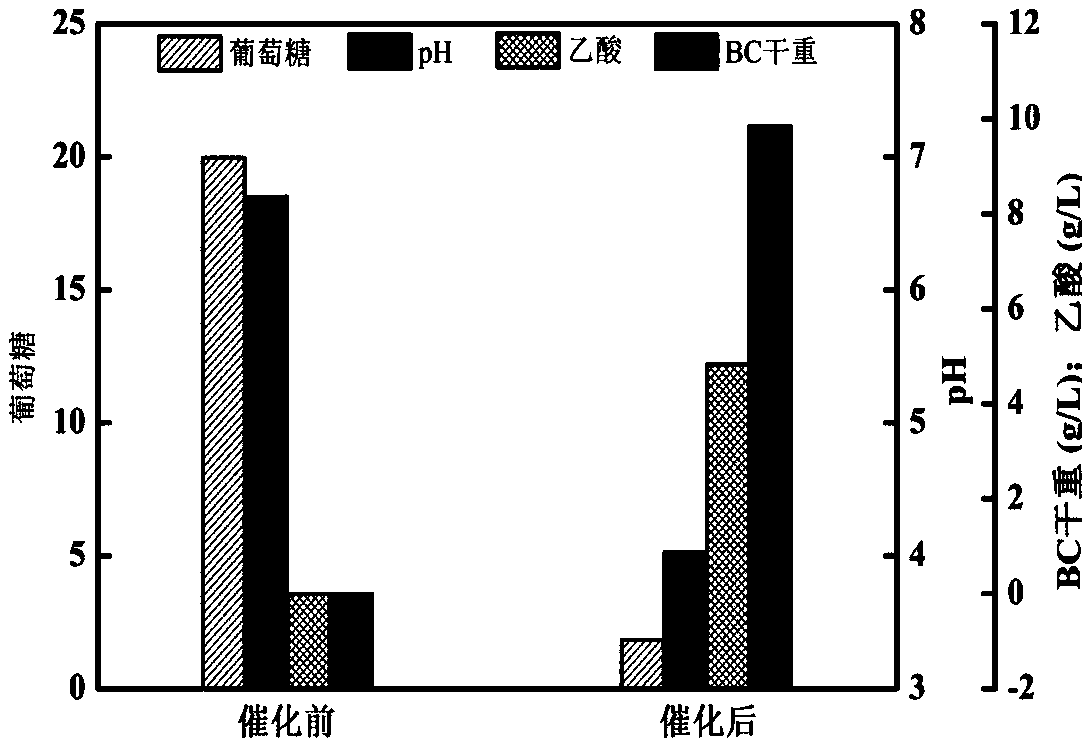
[0046] Embodiment 3: the glucose concentration in the reaction liquid is 20g / L.
[0047] (1) Strain activation: the gluconacetobacter hansenii preserved on the subculture medium was taken out, inoculated on a new subculture medium by streak transfer, and cultured at 30° C. for 5 days.
[0048] (2) Preparation of resting cells: Transplant and culture the activated strains in the same way to obtain sufficient cultures, use an inoculation loop to pick out the single colonies and lawns formed on the plate as much as possible, and place them in normal saline , use a vortex mixer to disperse as much as possible, then centrifuge at 10,000r / min and 4°C for 10min to collect the bacteria, wash, resuspend, and centrifuge twice, and then store in the refrigerator for later use.
[0049] (3) Preparation of reaction solution: Weigh 20 g of glucose and 2.7 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate, dilute to 1 L with distilled water, adjust the pH to about 6.7, and sterilize at 115° C. for 15 minutes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com