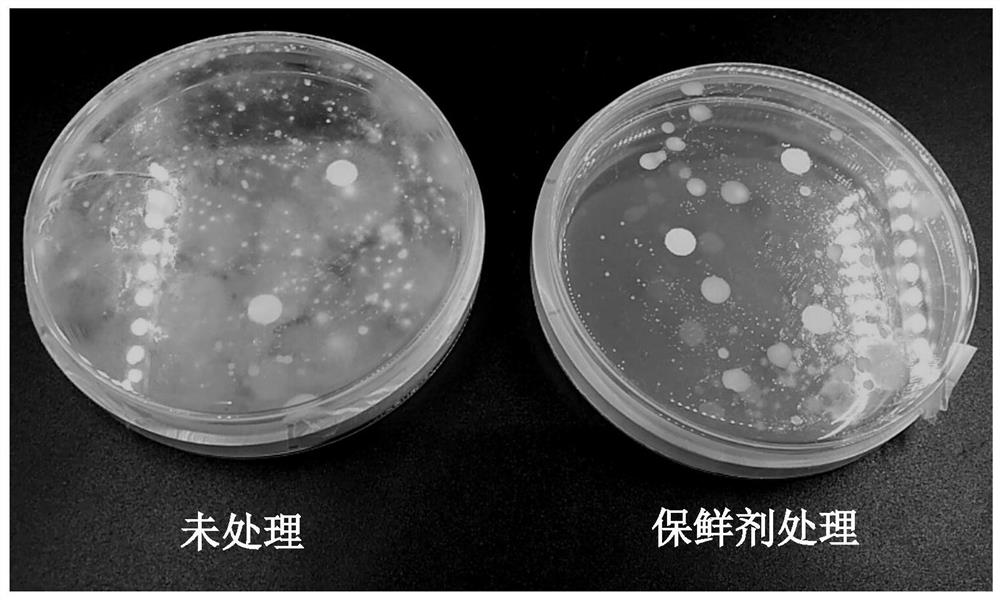
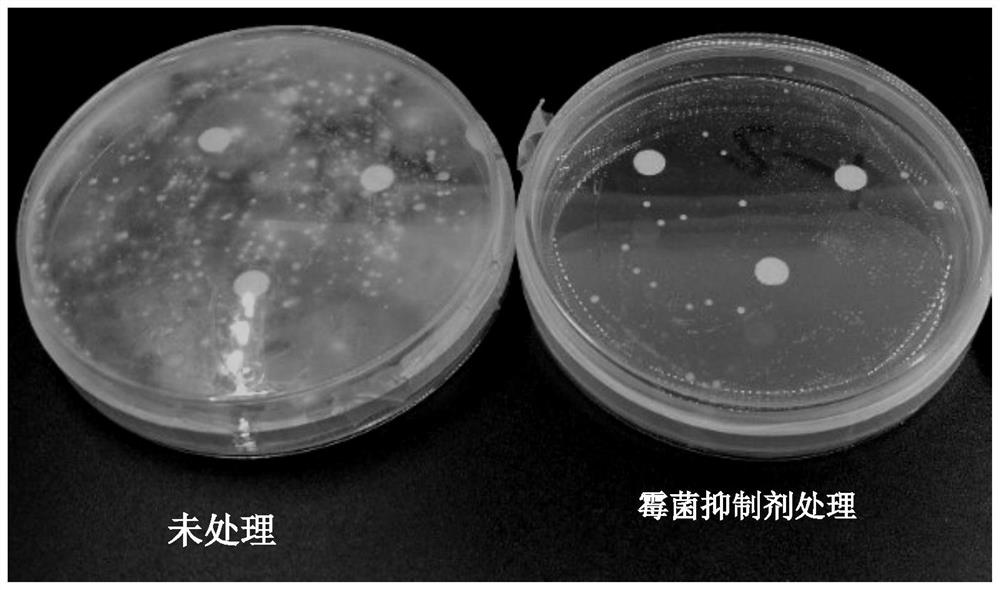
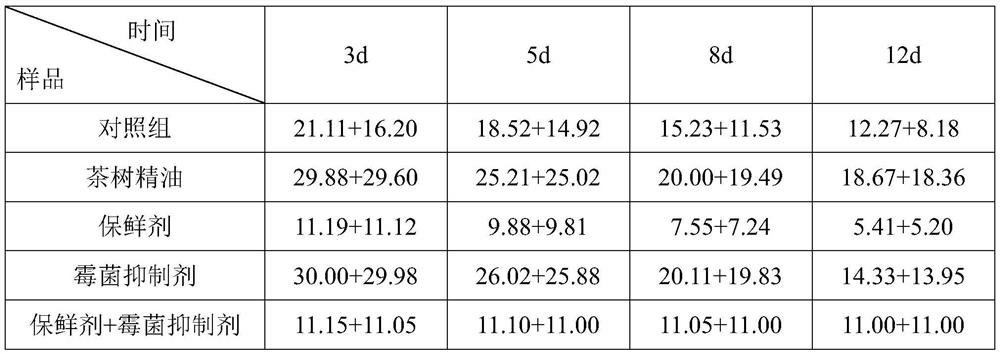
A method for preventing and treating postharvest mildew of galangal
A technology of galangal and mold, applied in the direction of application, protection of fruits/vegetables with coating protection layer, food ingredients as antimicrobial preservation, etc., can solve the problems of mildew pollution, gastrointestinal dysfunction, liver damage, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of promoting industrialization development, reducing environmental problems and saving costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Follow these steps to prevent postharvest mildew in galangal:
[0028] Step 1: Harvest fresh galangal medicinal materials and cut them into sections, spray, soak or smear with a preservative (25% of the weight of galangal) to prevent them from being evenly spread out and dry until the medicinal material surface is dry.
[0029] The antistaling agent used for preventing mold pollution of galangal after harvest is composed of the following components in parts by weight: 65% of the galangal stem extract liquid treated with lactic acid bacteria; 1% of sodium hypochlorite, 0.25% of sodium benzoate, and the rest is water.
[0030] The lactic acid bacteria-treated galangal stalk extract was obtained through the following steps: harvesting fresh galangal stalks, carrying out water extraction with a material-to-liquid ratio of 1:5 by weight, then cooling the extract, adding 10% by weight % lactic acid bacteria liquid fermentation for 12h.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Follow these steps to prevent postharvest mildew in galangal:
[0035] Step 1: Harvest fresh galangal medicinal materials and cut them into sections, spray, soak or smear with a preservative (35% of the weight of galangal) to prevent them from being evenly spread and dried until the medicinal material surface is dry.
[0036] The antistaling agent used for preventing mold contamination of galangal after harvest is composed of the following components by weight: 35% of the galangal stalk extract liquid treated with lactic acid bacteria; 3% hypochlorous acid, 0.15% sodium benzoate, and the rest are water .
[0037] The lactic acid bacteria-treated galangal stalk extract was obtained through the following steps: harvesting fresh galangal stalks, carrying out water extraction with a material-to-liquid ratio of 1:8 by weight, then cooling the extract, adding 5 weight percent % lactic acid bacteria liquid fermentation for 24h.
[0038] Step 2: Primary drying (drying at 60°C...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Follow these steps to prevent postharvest mildew in galangal:
[0042] Step 1: Harvest fresh galangal medicinal materials and cut them into sections, spray, soak or smear with a preservative (40% of the weight of galangal) to prevent them from being evenly spread and dried until the medicinal material surface is dry.
[0043] The antistaling agent used for preventing mold pollution of galangal after harvest is composed of the following components in parts by weight: 55% of the galangal stem extract liquid treated with lactic acid bacteria; 2% of sodium hypochlorite, 0.25% of sodium benzoate, and the rest is water.
[0044]The lactic acid bacteria-treated galangal stalk extract was obtained through the following steps: harvesting fresh galangal stalks, carrying out water extraction with a material-to-liquid ratio of 1:10 by weight, then cooling the extract, adding 10 weight percent % lactic acid bacteria liquid fermentation for 18h.
[0045] Step 2: Dry once (naturally ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com