Sirt1-T177 site phosphorylation as a biomarker in aging-related diseases
A SIRT1-T177, 3.SIRT1-T177 technology, applied in biological testing, genetic material components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to provide suitable targets and intervention strategies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
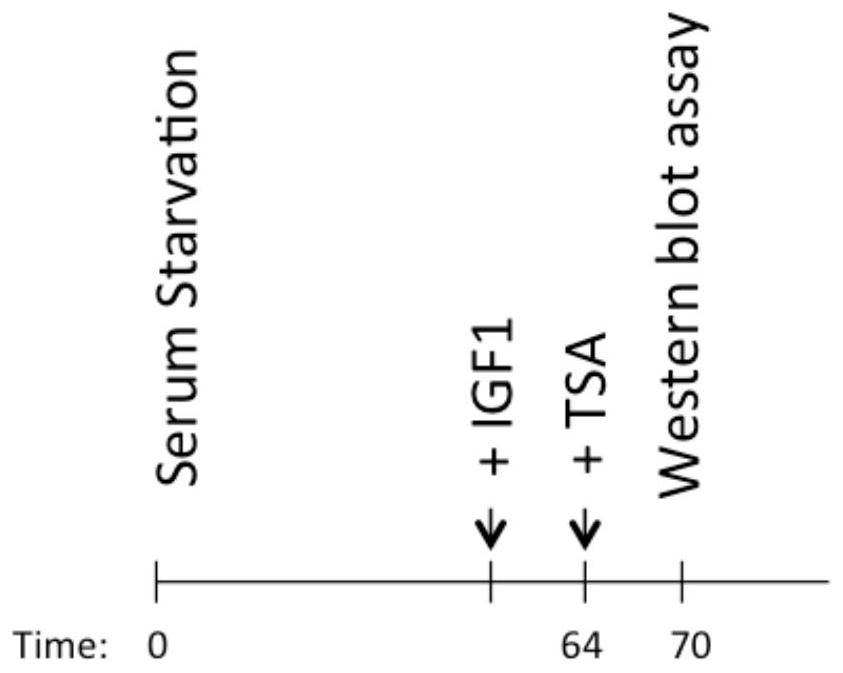
[0030] Example 1 Use of SIRT1-T177 site non-phosphorylation mutation to inhibit IGF1-mediated cell senescence
[0031] Figures 1a-1d The experimental conditions are: overexpress SIRT1, SIRT1-T177A and SIRT1-T177E site mutations in MCF7 cells, and treat the stable cell lines with IGF1, according to Figure 1a IGF1 processing time and method processing; Figure 1b The senescence markers of the above stable cell lines were detected by immunoblotting, p53, Ac-p53 (p53 acetylated at lysine 382, p53 protein with high transcriptional activity), p21, p16 and GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase). GAPDH was used as an internal reference. Figure 1c and 1d Assay for senescence-associated β-galactosidase activity. The β-galactosidase activity of each stable cell line under the above treatment conditions. Figure 1c to detect pictures; Figure 1d It is the relevant statistics of β-galactosidase activity in each stable cell line.
[0032] Such as Figures 1a-1d As sho...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2 Application of Phosphorylation at SIRT1-T177 Site to Inhibit SIRT1 Deacetylation Ability
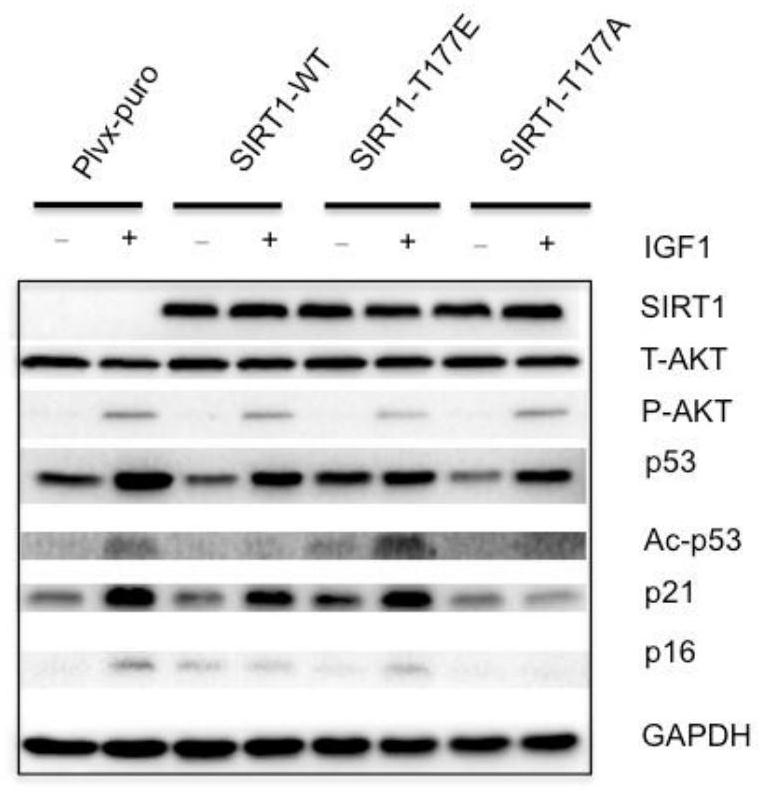
[0034] Figure 2a and 2b The experimental conditions were as follows: p53 and SIRT1-WT, SIRT1-T177E, SIRT1-T177A and SIRT1-T344E were co-expressed in HepG2 cells. After 48 hours of transfection, the cells were treated with 50 μM TSA (Trichostatin A) for 6 hours and collected for western- blot detection.
[0035] Such as Figure 2a-2b As shown, the inventors found that the SIRT1-T177E simulated phosphorylation mutation can inhibit the deacetylation ability of SIRT1 ( Figure 2a ). However, SIRT1-T177A mimics the non-phosphorylated mutant protein and its sirtuin activity is almost identical to that of wild-type SIRT1 ( Figure 2b ). It shows that the point mutation of SIRT1-T177A, which simulates non-phosphorylation, has little effect on its activity, and the protein still has a strong deacetylation effect, that is, the simulated phosphorylation mutation of SIRT1-T17...
Embodiment 3
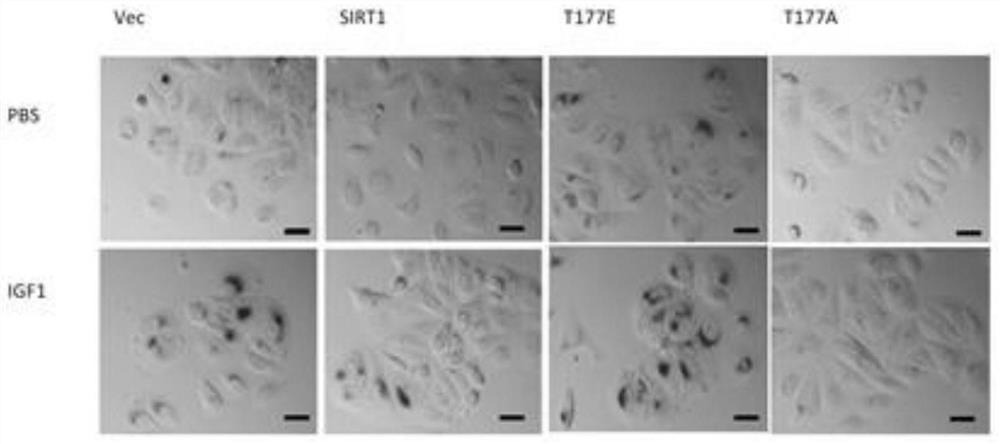
[0037] Example 3 Application of Inhibiting Phosphorylation of SIRT1-T177 Site to Delay Aging
[0038] Such as image 3 As shown, the inventors further performed immunofluorescence staining analysis on MCF7 cells stably expressing plvx-puro empty load, SIRT1-WT wild-type protein, SIRT1-T177A non-phosphorylated mutant protein, and SIRT1-T177E phosphorylated mutant protein. SIRT1 immunofluorescence results showed that SIRT1 was localized in the nucleus in MCF7 cell lines stably expressing plvx-puro empty load, SIRT1-WT, SIRT1-T177A, and there was no distribution of SIRT1 protein in the cytoplasm. However, in cell lines overexpressing SIRT1-T177E, SIRT1-T177E also had a large amount of distribution in the cytoplasm. It shows that the phosphorylation of T177 site of SIRT1 protein is the key factor to promote the cytoplasmic localization of SIRT1, and the cytoplasmic localization of SIRT1 makes it lose the ability to deacetylate p53, thus the phosphorylation of SIRT1-T177 site preven...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com