Method for calibrating parabolic catadioptric camera using spatial straight lines
A camera and catadioptric technology, applied in the field of computer vision, can solve the problems of the limited range of cameras and the inability of effective information to meet people's needs, and achieve simple results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
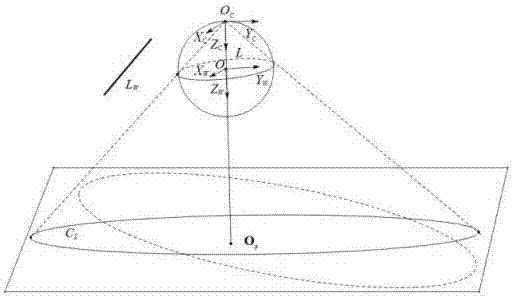
[0055] The invention proposes a method for linearly solving the internal parameters of a parabolic catadioptric camera by using three straight lines in space as targets. The experimental template structural schematic diagram that the present invention adopts is as figure 1 shown. The implementation of the present invention will be described in more detail with an example below.
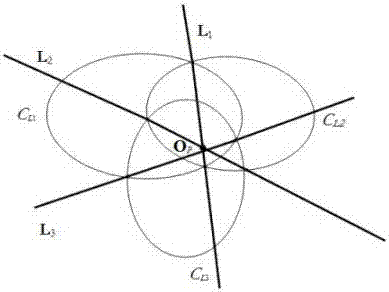
[0056] The template used to calibrate the parabolic catadioptric camera is a unit viewing sphere model in space and three non-parallel straight lines in space, such as figure 1 shown. Utilize the method among the present invention to carry out calibration for the parabolic catadioptric camera that is used for experiment, concrete steps are as follows:
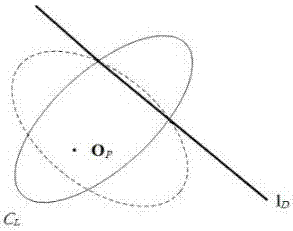
[0057] 1. Fit the equation of the image of three straight lines in the image
[0058] The image size used in the present invention is 600×800. Use a parabolic catadioptric camera to take an experimental image containing three non-parallel straight...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com