Method for producing hydrocarbon raw material rich in monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
A technology for single-ring aromatics and hydrocarbons, which is applied in the field of producing hydrocarbon raw materials rich in single-ring aromatics. It can solve the problems of poor selectivity of single-ring aromatics and achieve the effects of improving activity and stability, high activity, and preventing aggregation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
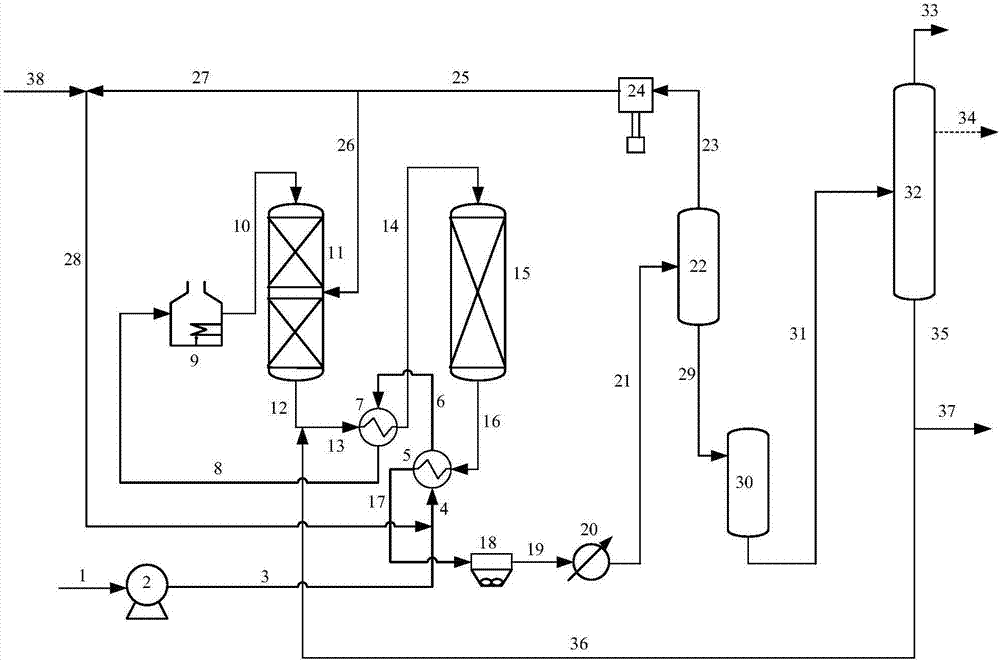
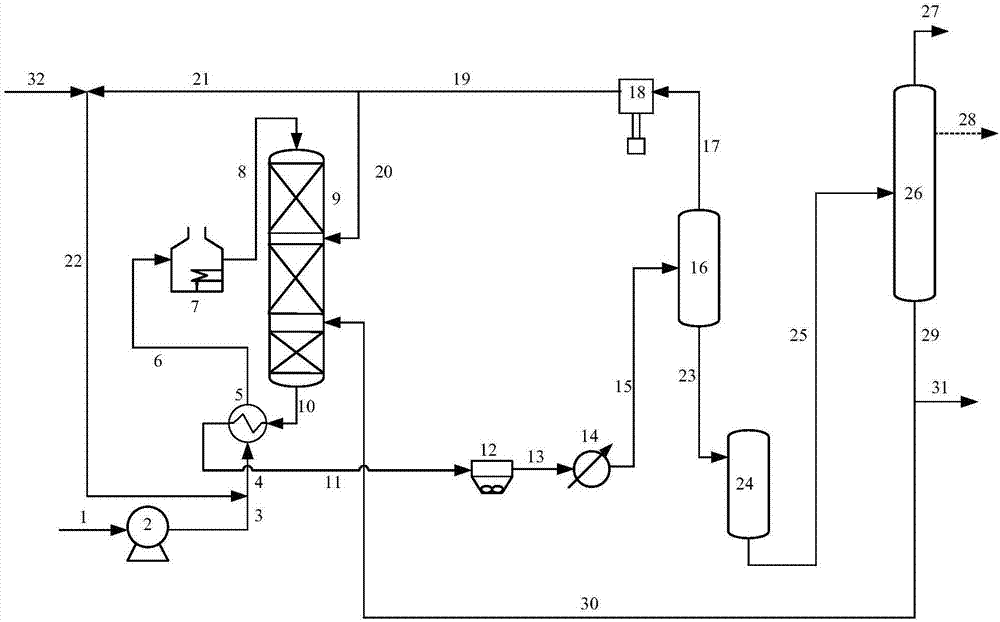
[0088] use figure 1 The flow shown is for feed oil D. The feed oil D is mixed with hydrogen and enters the first reaction zone and the second reaction zone in turn, and reacts with the hydrotreating catalyst A. The weight ratio of the feed oil D to the recycled product is 8:1. The hydrogenation reaction conditions and product properties of the two reaction zones are as shown in Table 2, as can be seen from Table 2, the saturation rate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the liquid stream is 85.29%, the saturation rate of total aromatic hydrocarbons is 11.40%, and the saturation rate of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is 11.40%. The selectivity is 80.17%.
[0089] Compared with Comparative Example 2, it can be seen that under the equivalent saturation rate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, the product monocyclic aromatics obtained by the present invention has higher selectivity and lower hydrogen consumption, which shows that the present invention can be used for catal...
Embodiment 2
[0091] use figure 1 The flow shown is for feed oil D. The feed oil D is mixed with hydrogen and enters the first reaction zone and the second reaction zone in turn, and reacts with the hydrotreating catalyst C. The weight ratio of the feed oil D to the recycled product is 8:1. The hydrogenation reaction conditions and product properties of the two reaction zones are as shown in Table 2, as can be seen from Table 2, the saturation rate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the liquid stream is 85.11%, the saturation rate of total aromatic hydrocarbons is 11.15%, and the saturation rate of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is 11.15%. The selectivity is 80.56%.
Embodiment 3
[0093] use figure 1 The flow shown is for feed oil D. The raw oil D is mixed with hydrogen and enters the first reaction zone and the second reaction zone in turn, and reacts with the hydrotreating catalyst C. The weight ratio of the raw oil D to the recycled product is 1:1. The hydrogenation reaction conditions and product properties of the two reaction zones are as shown in Table 2. As can be seen from Table 2, the saturation rate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the liquid stream is 88.05%, the saturation rate of total aromatic hydrocarbons is 10.78%, and the saturation rate of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is 10.78%. The selectivity is 81.84%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com