High-accuracy resonant grounding system single-phase earth fault line selection method
A single-phase grounding fault and resonant grounding technology, applied in fault location, fault detection according to conductor type, measurement device, etc., can solve the problem of affecting the accuracy of line selection, modal aliasing of EMD algorithm, small amplitude of high frequency components, etc. problem, to avoid modal aliasing, enhance amplitude, and ensure reliability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
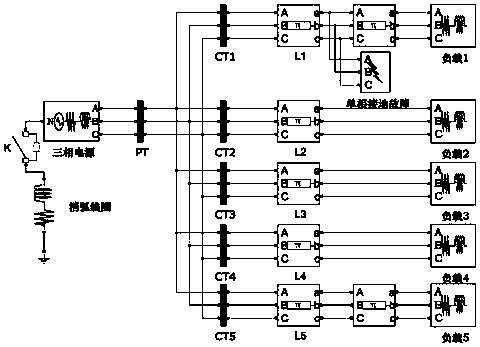
[0026] Set outgoing line L 1 A single-phase ground fault occurs at a distance of 3km from the busbar, the fault closing angle is 0°, and the transition resistance is 10Ω.
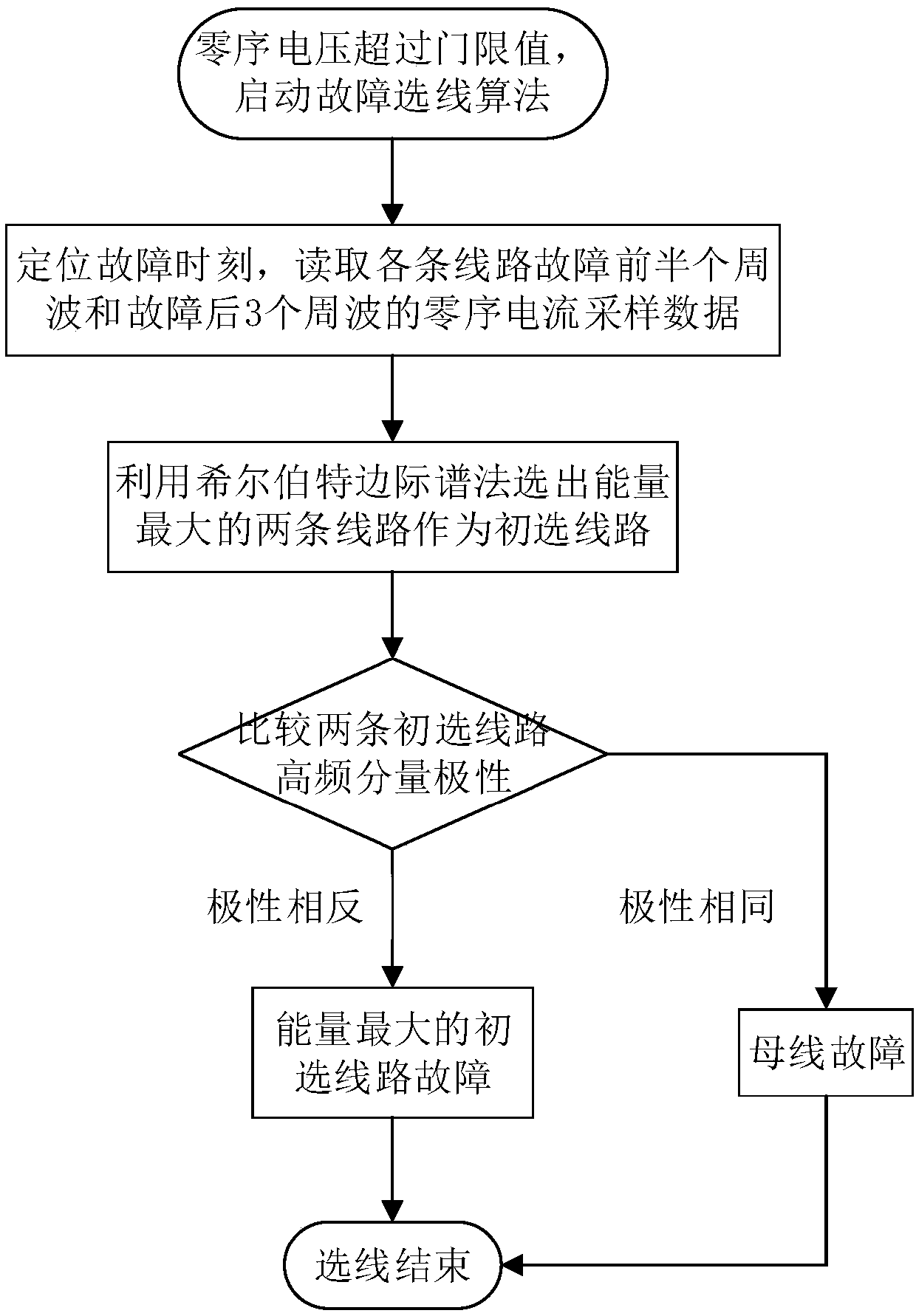
[0027] After the fault occurs, the line selection algorithm is started, and the zero-sequence current sampling data of the half cycle before the fault and the 3 cycles after the fault are read.
[0028] Firstly, Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition (EEMD) is performed on the zero-sequence current sampling data of each outgoing line, and the signal is decomposed into several Intrinsic Mode Function (IMF) components and residual components to facilitate further fault feature extraction.
[0029]
[0030] In the formula: S(t) is the original signal; n is the number of IMF components; C i (t) is the i-th layer IMF component, where C 0 (t) is the remaining component. The intrinsic mode functions of different layers represent the components of the signal at different time scales.
[0031] Afterwards, the ...
example 2
[0049] Set the bus fault, the fault closing angle is 30°, and the transition resistance is 50Ω.
[0050]After the fault occurs, the line selection algorithm is started, and the zero-sequence current sampling data of the half cycle before the fault and the 3 cycles after the fault are read.
[0051] Firstly, Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition (EEMD) is performed on the zero-sequence current sampling data of each outgoing line, and the signal is decomposed into several Intrinsic Mode Function (IMF) components and residual components to facilitate further fault feature extraction.
[0052]
[0053] In the formula: S(t) is the original signal; n is the number of IMF components; C i (t) is the i-th layer IMF component, where C 0 (t) is the remaining component. The intrinsic mode functions of different layers represent the components of the signal at different time scales.
[0054] Afterwards, the Hilbert transform is performed on the IMF components of each layer and the re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com