Method for determining stability critical force of crane nth-order telescopic boom
A determination method, a technology for telescopic arms, applied in computer-aided design, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inability to meet
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
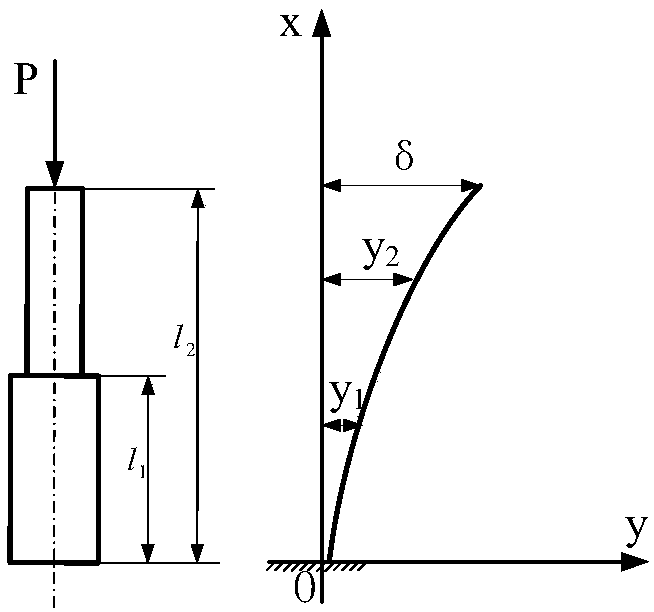
[0106] Embodiment 1: Known as figure 2 The shown second-order stepped column model calculates its critical force, l 1 = 15.5m, l 2 =29.9m, I 1=43.26×10 -3 m 4 , I 2 =26.09×10 -3 m 4
[0107] A method for determining the stability critical force of the n-order telescopic boom of a crane disclosed in this embodiment includes the following steps:
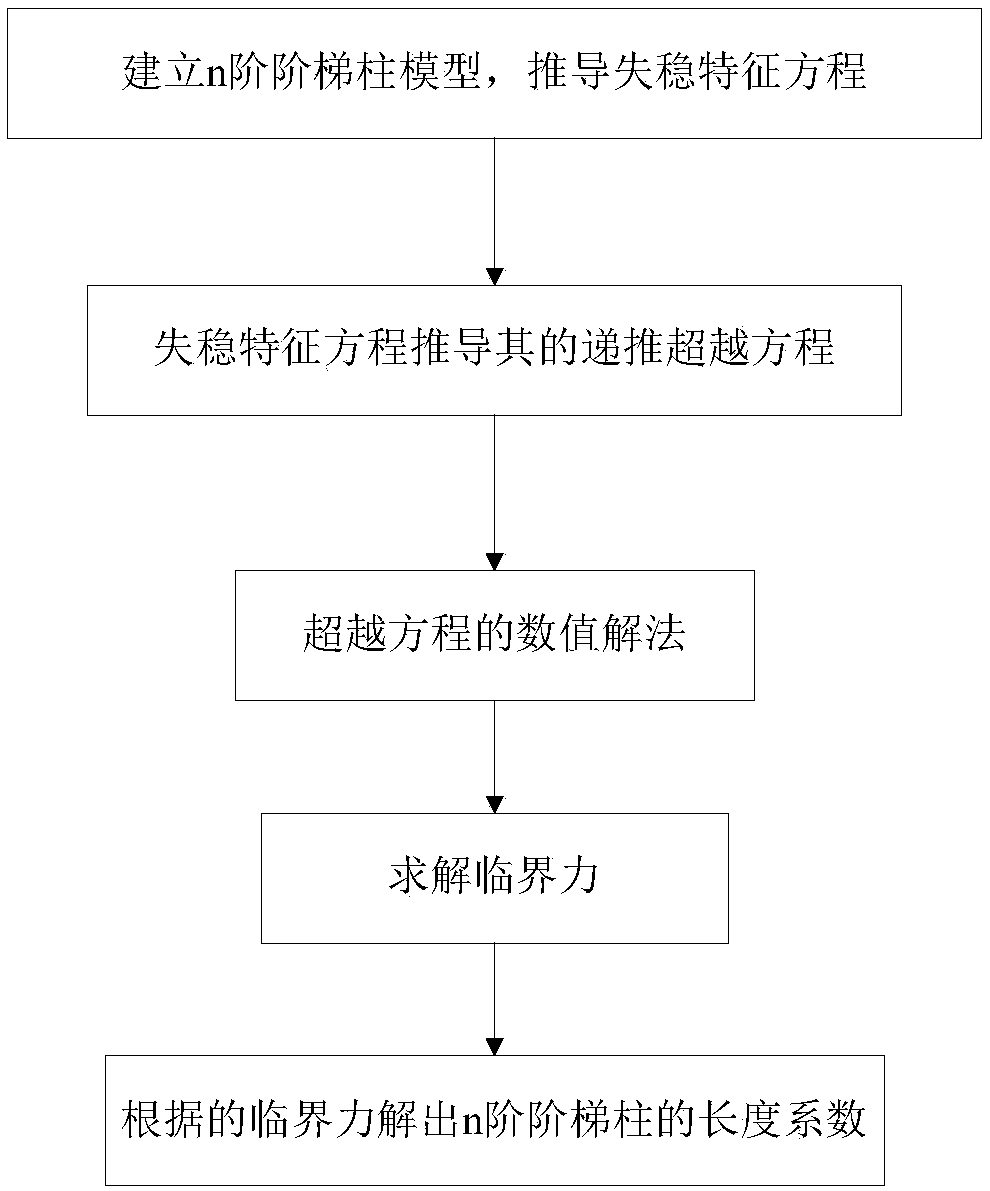
[0108] Step 1: Establish an n-step stepped column model and derive the instability characteristic equation.
[0109] Such as figure 2 As shown, the n-order telescopic arm stepped column model refers to a combination of n equal-section columns, from the fixed and constrained end of the bottom surface to the free end of the top, respectively 1st, 2nd, 3rd, ...... The nth step ladder column; and the cross-sectional area of the column also decreases sequentially. The length from the fixed restraint end of the bottom surface to the top of the first step ladder column is l 1 , the length from the fixed constraint end of the b...
Embodiment 2
[0154] For the second-order stepped column, in order to compare with the length coefficient in the national standard GB3811, use such as Figure 4 The model shown is valid for combinations of jib lengths and sections (α 1 =0.51, 0.52, 0.53, 0.54, 0.55, 0.56, 0.57, 0.58, 0.59, 0.60, 0.61, 0.62, 0.63, 0.64, 0.65, 0.66, 0.67, 0.68, 0.69, 0.70) (β 2 =1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.6, 1.9, 2.2, 2.5) were calculated respectively and compared with the calculation results using ANSYS17.0, the results are as follows Figure 5 Place.
[0155] The length coefficient value μ obtained by the method of this embodiment 2 It is very close to the difference calculated by using ANSYS17.0, and the maximum relative error is 1.7×10 -4 . With the second stepped column (I 2 ) of the moment of inertia increases, the length coefficient μ 2 decreases, that is, the critical force of the stepped column increases gradually; with the second stepped column (I 2 ) relative to the reduction in length, the length coe...
Embodiment 3
[0156] Embodiment 3: compare with national standard GB3811
[0157] Table 3 is a comparison of the length coefficients using the three-step ladder column of the present invention,
[0158] Table 1 Calculation length coefficient μ of the three-step ladder column 2 and compare
[0159]
[0160]
[0161] It can be seen from Table 1 that for the three-step ladder column, its length coefficient value μ 2 It is very close to the difference calculated by using ANSYS17.0, and the maximum relative error is 1.8×10 -5 , and found that the missing μ in GB3811 2 The value is calculated according to the interpolation method, and its value has high linearity in a small range, and the interpolation error is small.
[0162] Table 2 Calculation length coefficient μ of four-step ladder column 2 and compare
[0163]
[0164]
[0165]
[0166]
[0167] Table 2 gives the value of the length coefficient μ of the four-step ladder column 2 , the missing μ in GB3811 2 The valu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com