Block chain key trusteeship and recovery method and device based on secrecy sharing technology
A secret sharing and key recovery technology, applied in the blockchain field, can solve problems such as low security, user key loss, and difficult recovery, and achieve the effects of improving reliability, backup and recovery security, and intrusion tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
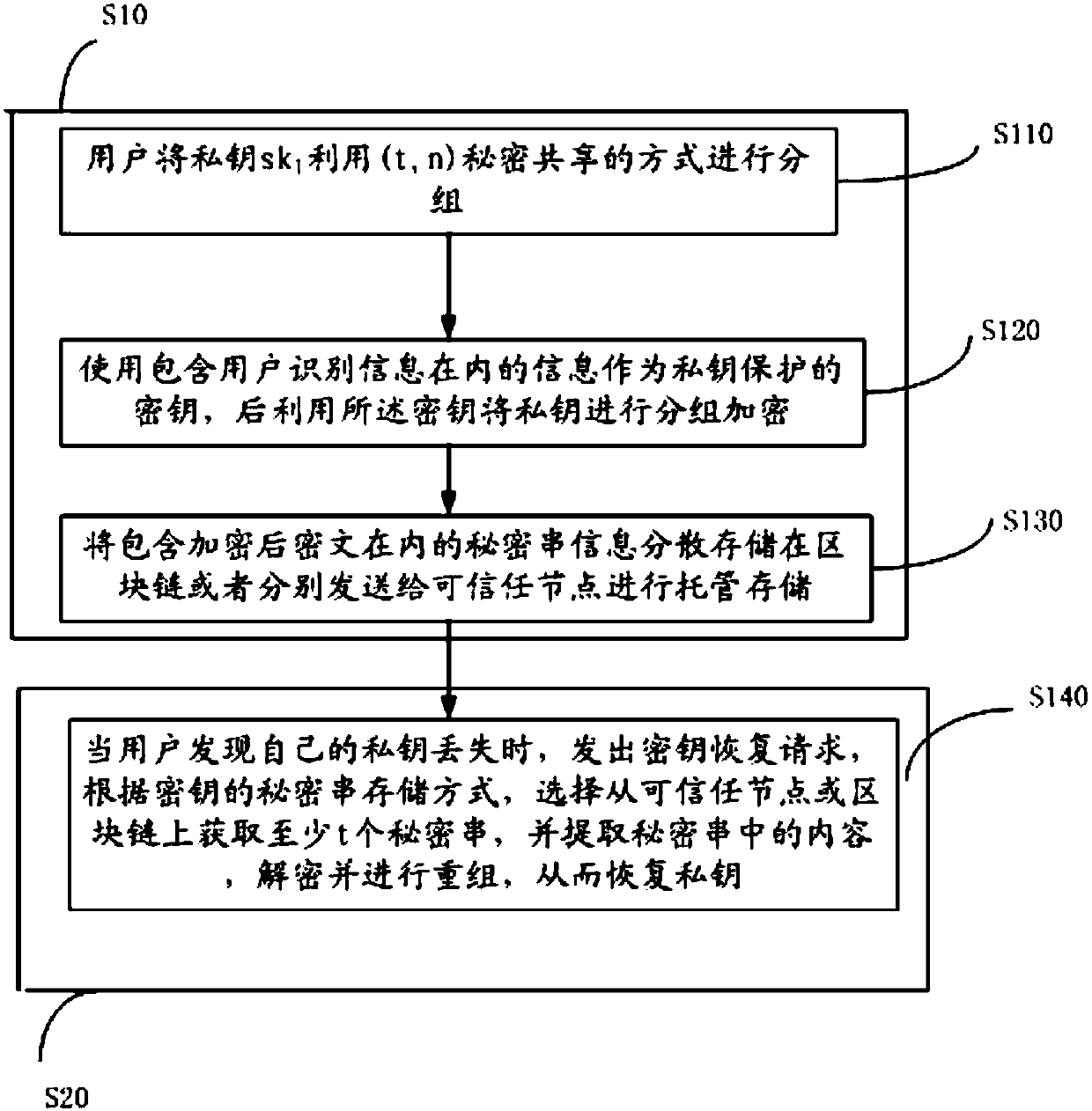
[0041] The key recovery scheme is divided into the release phase and the key recovery phase. Considering the identity of any common user node in the system, the detailed process is as follows:
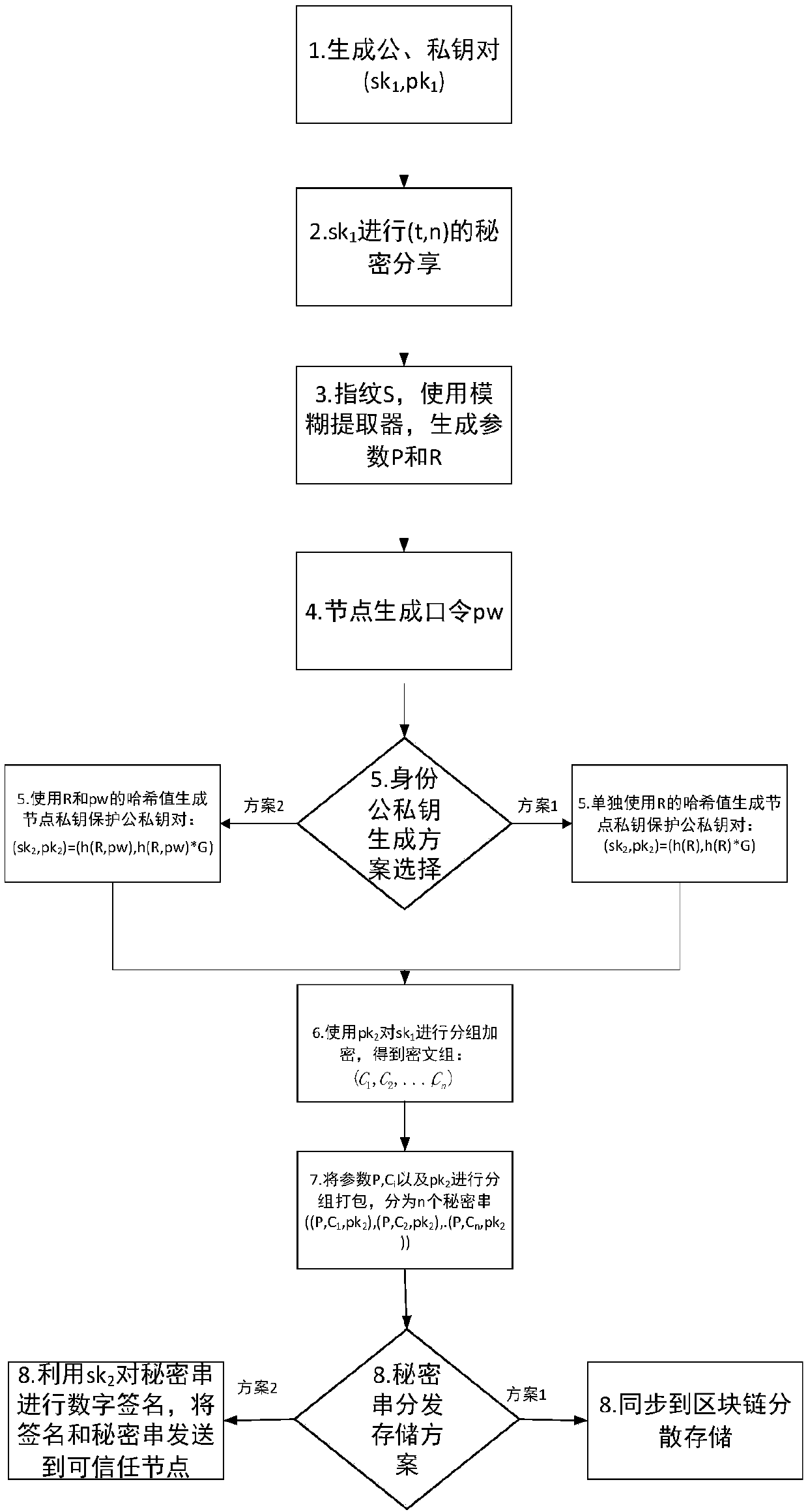
[0042] Publishing stage: the user disperses and stores the encrypted private key ciphertext group and the public key information formed by the user's biological information and / or password in the blockchain to host the encrypted private key. The specific process is as follows: image 3 :
[0043] 1. The user generates a public-private key pair on the elliptic curve (sk 1 , pk 1 )=(x, x·G), where G is the generator. Of course, other existing algorithms can also be used to generate the public-private key pair.
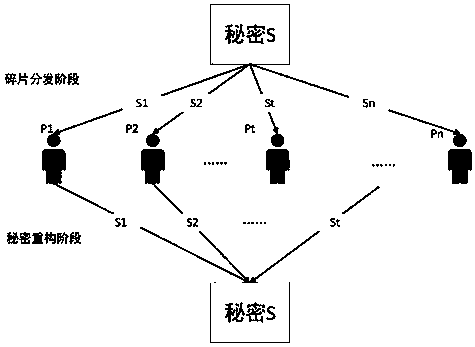
[0044] 2. will sk 1 For (t, n) secret sharing, decomposed into sk 1 →(sk 1 1 ,sk 1 2 ,...,sk 1 n ), where 1≤t≤n, that is, sk 1 Split the shared secret into n fragments, and use any t or more shared fragments to restore sk 1 ;
[0045] 3. The user uses his biometric...
example 2
[0057] Publishing stage: the user stores the encrypted private key ciphertext group and the public key information formed by the user's biological information and / or password in the trusted node to host the encrypted private key. Any node can be pre-defined in the blockchain system.
[0058] 1. The user generates a public-private key pair on the elliptic curve (sk 1 , pk 1 )=(x, x·G), where G is the generator. Of course, other existing algorithms can also be used to generate the public-private key pair.
[0059] 2. will sk 1 For (t, n) secret sharing, decomposed into sk 1 →(sk 1 1 ,sk 1 2 ,...,sk 1 n ), where 1≤t≤n, that is, sk 1 Split the shared secret into n fragments, and use any t or more shared fragments to restore sk 1 ;
[0060] 3. The user uses his biometric feature B (which may include fingerprints, iris, palm veins, face shape, etc.), and uses an existing fuzzy extractor or other existing algorithms to generate parameter public parameters P and secret pa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com