Fictitious force-based aggregation node re-positioning method
A node aggregation and relocation technology, applied in location-based services, advanced technologies, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of lack of flexibility and scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
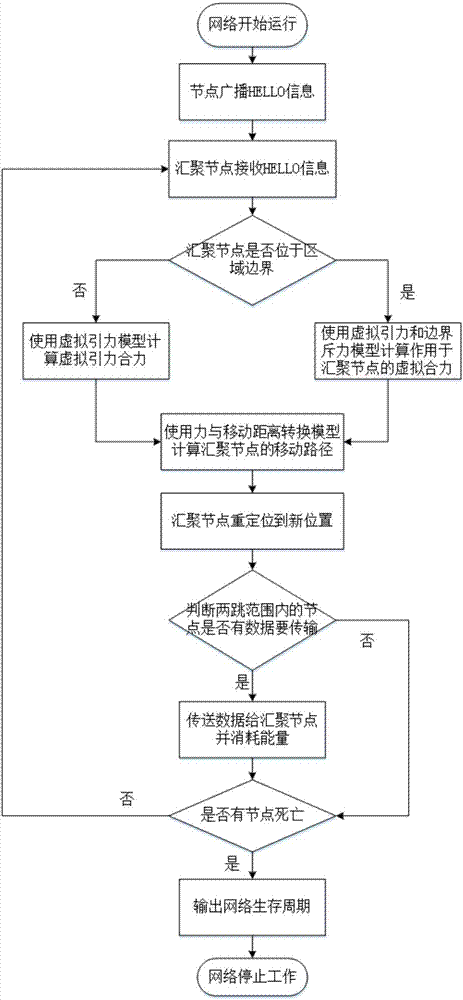
[0061] Embodiment 1: as Figure 1-9 As shown, a virtual force-based sink node relocation method includes the following steps:
[0062] Step1. When the network starts, the sink node s collects the position and remaining energy information of all nodes. The specific steps are:
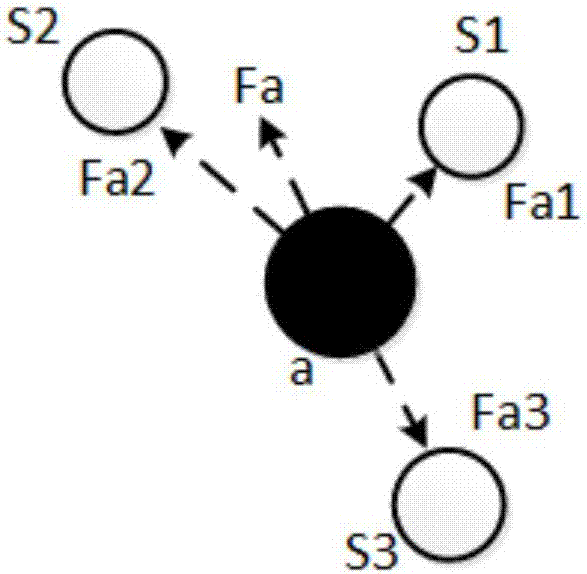
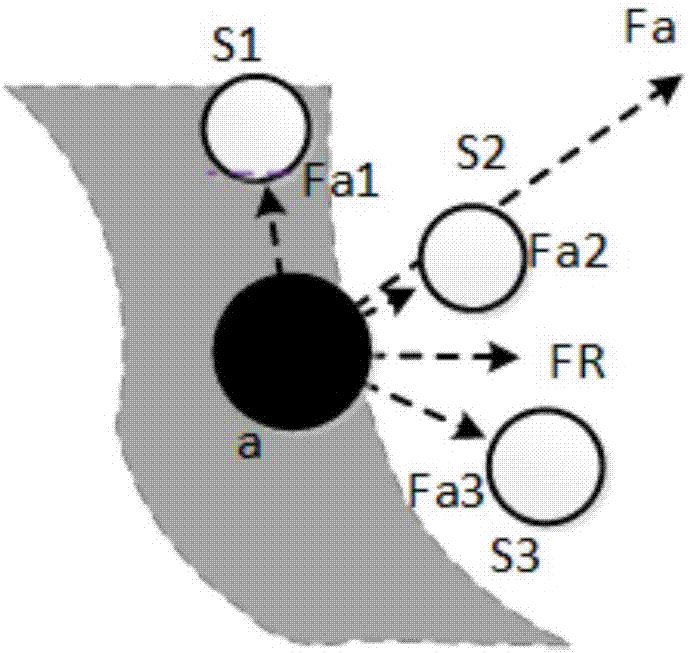
[0063] Step1.1. Establish a virtual gravity model
[0064] All sensor nodes have a virtual gravitational force on the sink node s, which is just like universal gravitation, so according to the universal gravitational force in physics The formula analogy obtains the virtual gravitational model of sensor node i where a i and a respectively represent the remaining energy of node i and sink node s, because the energy of sink nodes is generally regarded as infinite and it does not consume energy, so a is a constant and can be merged into k A , and then calculate the virtual gravitational force between node i and sink node s, namely:
[0065]
[0066] where k A is a constant representing the virtual...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com