Method for measuring and calculating human-robot minimum distance in collaborative environment
A collaborative environment and the smallest technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve problems such as unfavorable real-time performance, reduced precision, and large amount of calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0067] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, technical scheme of the present invention is described in further detail:
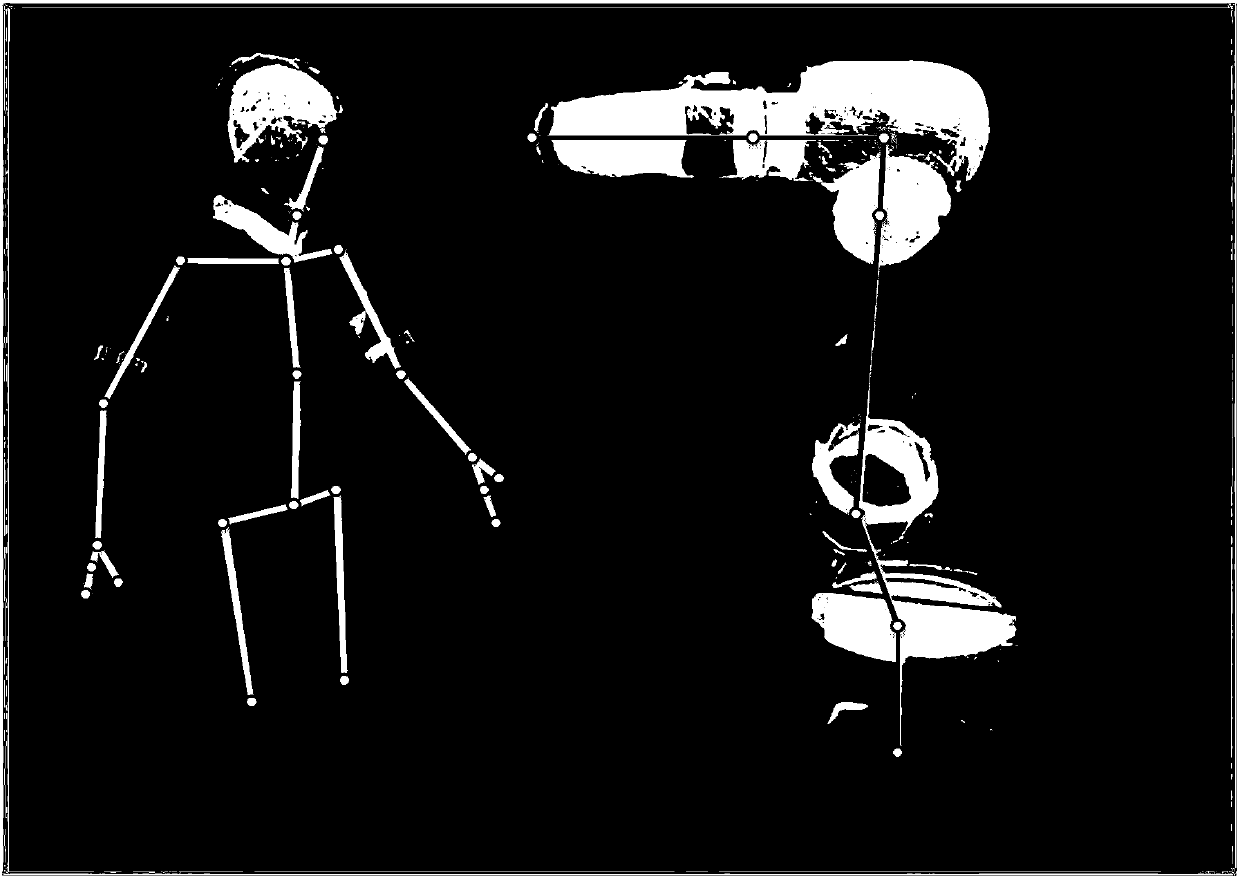
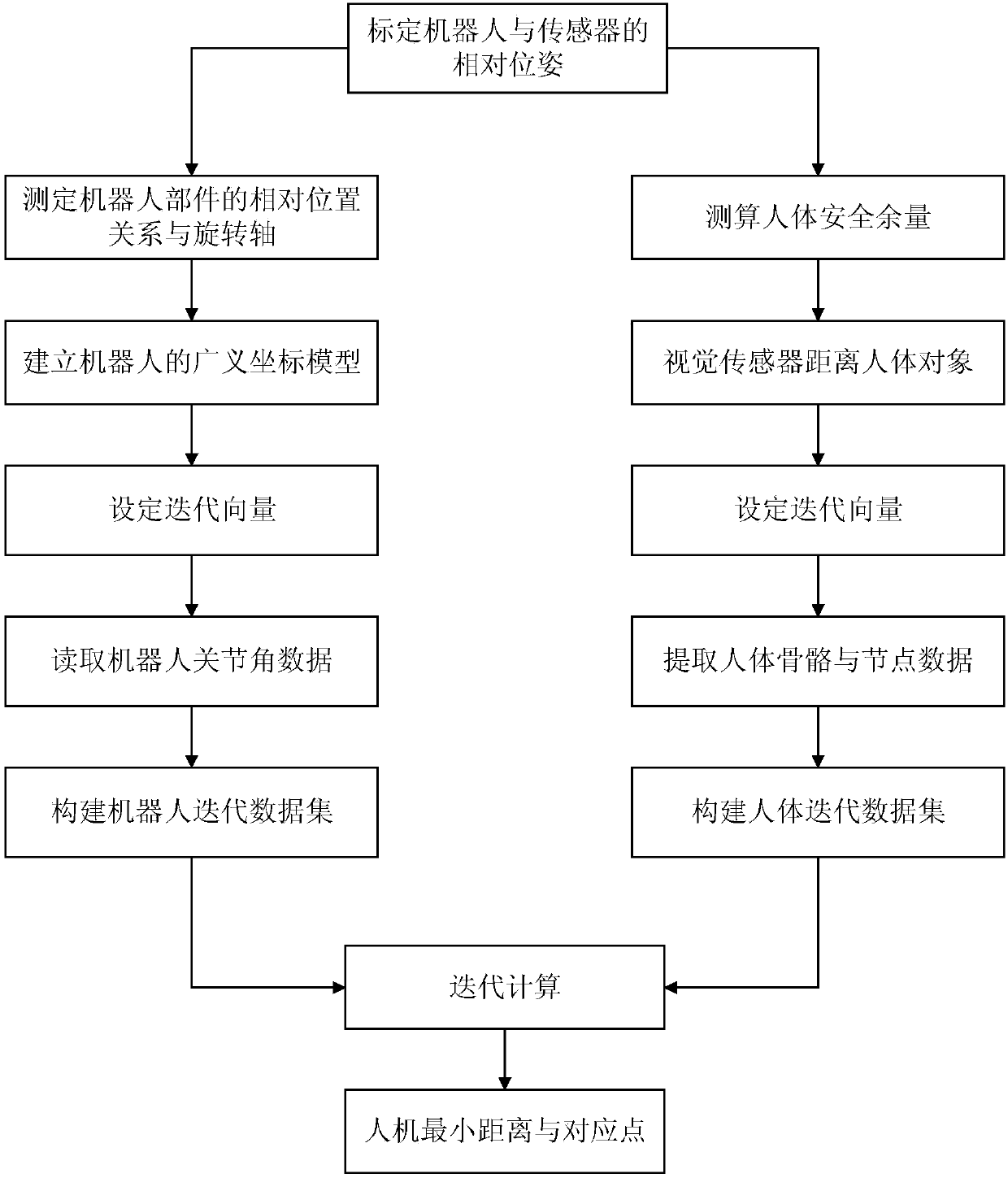
[0068] This specific embodiment discloses an iterative calculation method for the minimum distance between man and machine in a collaborative environment, including the following steps:
[0069] S1: Use the position measurement and calibration system to determine the relative pose relationship between the robot and the 3D vision sensor, and obtain the conversion relationship between the robot base coordinate system and the 3D vision sensor coordinate system;
[0070] S2: According to the relative position relationship and the rotation relationship between the parts of the robot, the reference coordinate system of the parts is established. The origin of the reference coordinate system is the key motion node of the robot, and according to the relative pose between the key motion nodes of the robot relationship, establish the generalized coordinate mo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com