Decision tree behavior decision algorithm based on demonstration learning
A decision algorithm and decision tree technology, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control, non-electric variable control, instruments, etc., to reduce frequency and ensure maximum rationality and safety.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] The present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings and examples. The embodiments of the present invention include but are not limited to the following examples.
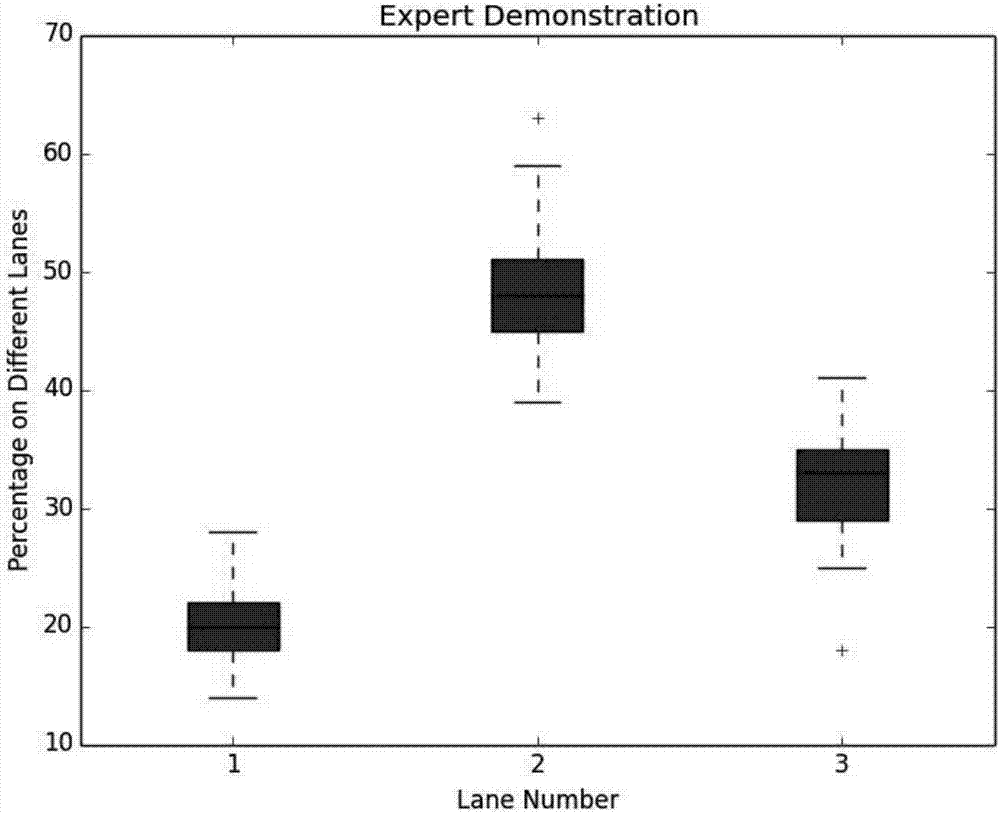
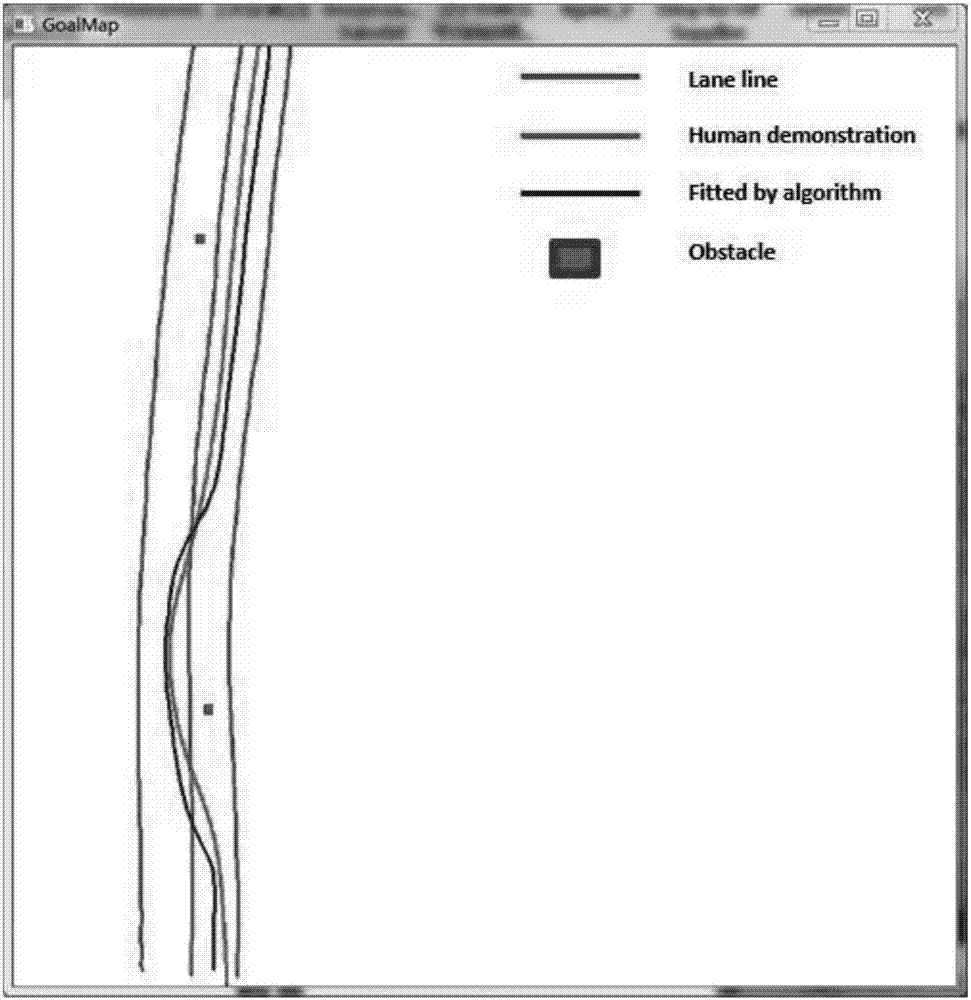
[0037]In the entire algorithm framework, the decision tree algorithm is in the middle position, accepting the law of state transition upward, and connecting downward to strengthen or modify the law of state transition. For the teaching rules of human drivers, the present invention defines two matrices of state transition frequency and state transition probability for description. The state transition frequency is to record the number of times the state will be visited in the current state, and the state transition probability is the transition probability value obtained by calculating such times. When the transition probability outputs the upcoming selection action, the decision tree algorithm needs to check and evaluate the rationality or safety of the current ac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com