Winding modular permanent-magnet motor
A permanent magnet motor, modular technology, applied to the magnetic circuit, the shape/style/structure of winding conductors, electric components, etc., can solve the problems of complex processing and assembly technology, large torque ripple, large amount of permanent magnets, etc., to achieve The structure of the rotor is simple and reliable, the electromagnetic coupling is small, and the effect of improving the reliability of the motor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
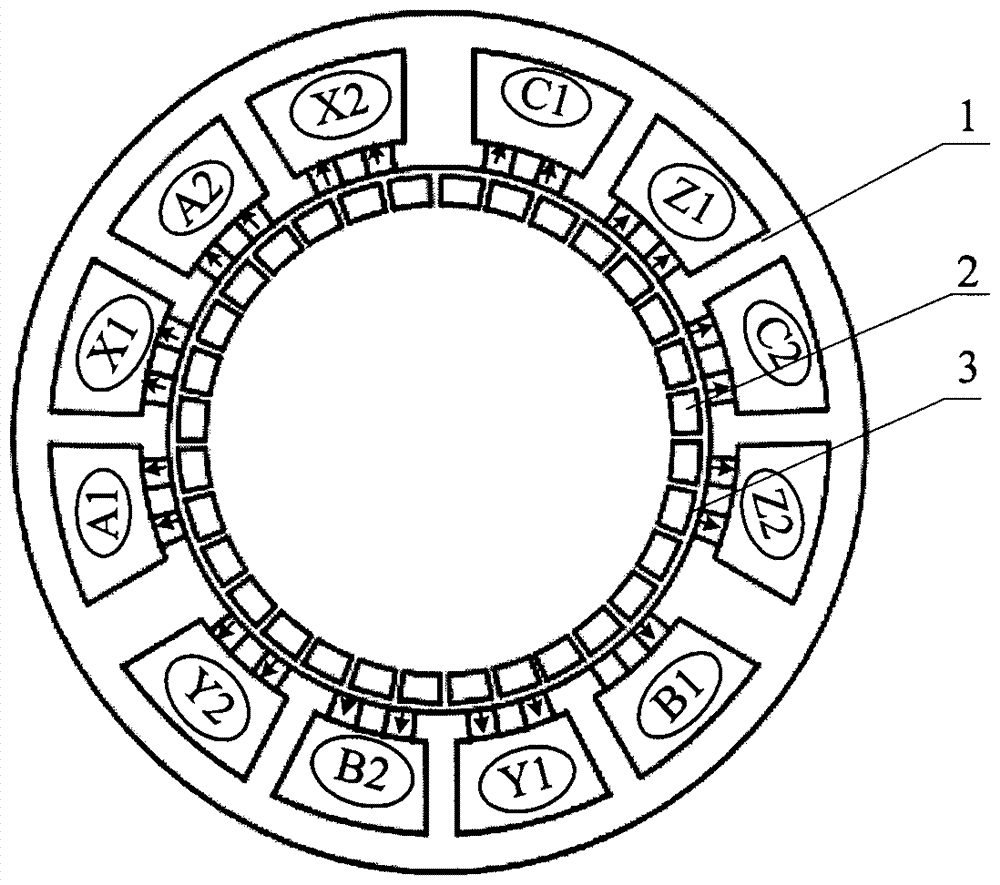
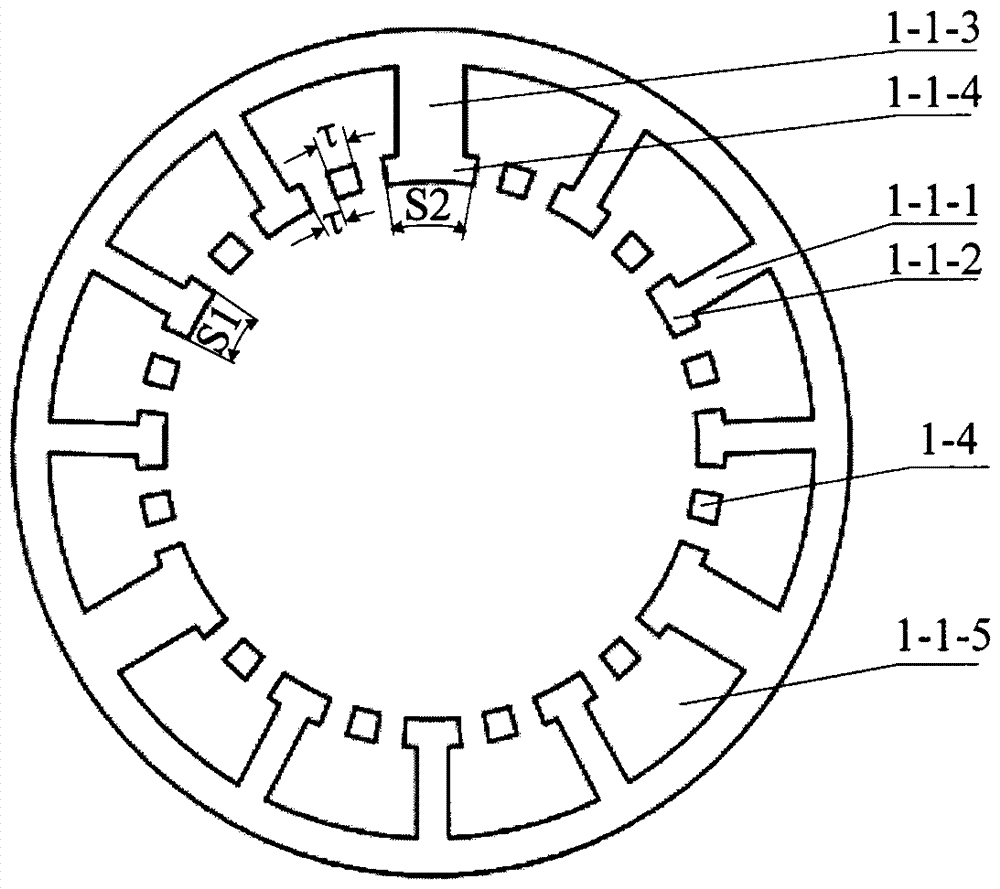
[0024] Such as figure 1 , 2 , 3, and 4, the winding modular permanent magnet motor of this embodiment includes a stator 1, a rotor 2 and an air gap 3. The stator is composed of a stator core 1-1, an armature winding 1-2, a permanent magnet 1-3 and magnetically conductive small teeth 1-4. Large slots 1-1-5 are opened inside the stator core 1-1, permanent magnets 1-3 and magnetically conductive small teeth 1-4 are installed at intervals facing the slots of the air gap 3, permanent magnets 1-3 and magnetically conductive small teeth 1- The arc length of 4 is . The magnetization directions of the permanent magnets 1-3 are all the same. The number of pieces of permanent magnets 1-3 in each notch is 2 pieces, the number of pieces of magnetically conductive small teeth 1-4 is 1 piece, between two permanent magnets 1-3 is magnetically conductive small teeth, and permanent magnets 1-3 The sum of the block numbers with the magnetic conduction small teeth 1-4 is an odd number.
[00...
Embodiment approach 2
[0028] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: the number of pieces of permanent magnets 1-3 in each notch of the motor is 1 piece, the number of pieces of magnetically conductive small teeth 1-4 is 0 pieces, and the number of pieces of the first tooth The arc length of the width of the top 1-1-2 is S1=Kτ (K is selected as 4), and the arc length of the width of the second tooth top 1-1-4 is S2=(M±2 / 3)τ (M is selected as 4). The cost of the motor is reduced by reducing the amount of permanent magnets, and the motor assembly process is simpler.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com