Pixel circuit and driving method thereof, display panel and display device
A technology for pixel circuits and driving transistors, which is applied in the fields of pixel circuits, display panels and display devices, and can solve problems such as uneven display screens, achieve the effects of optimizing the selection range, stabilizing pixel circuits, and reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
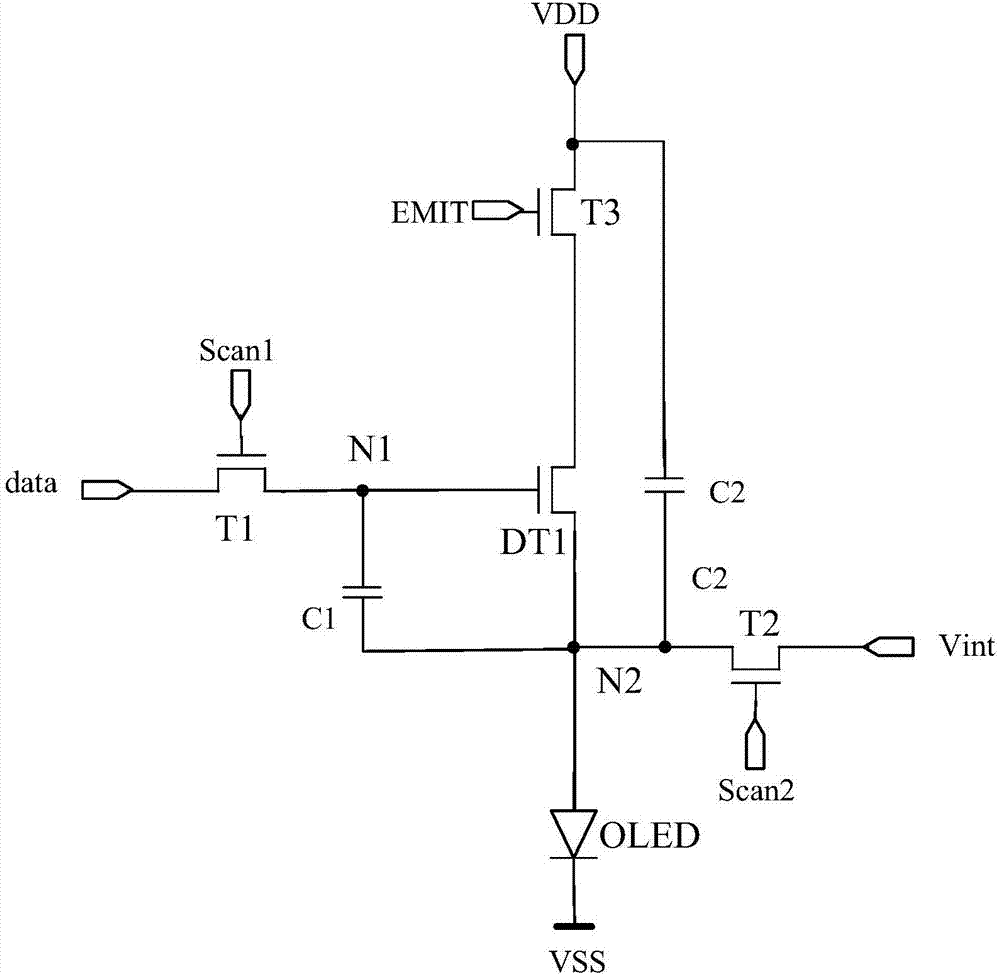
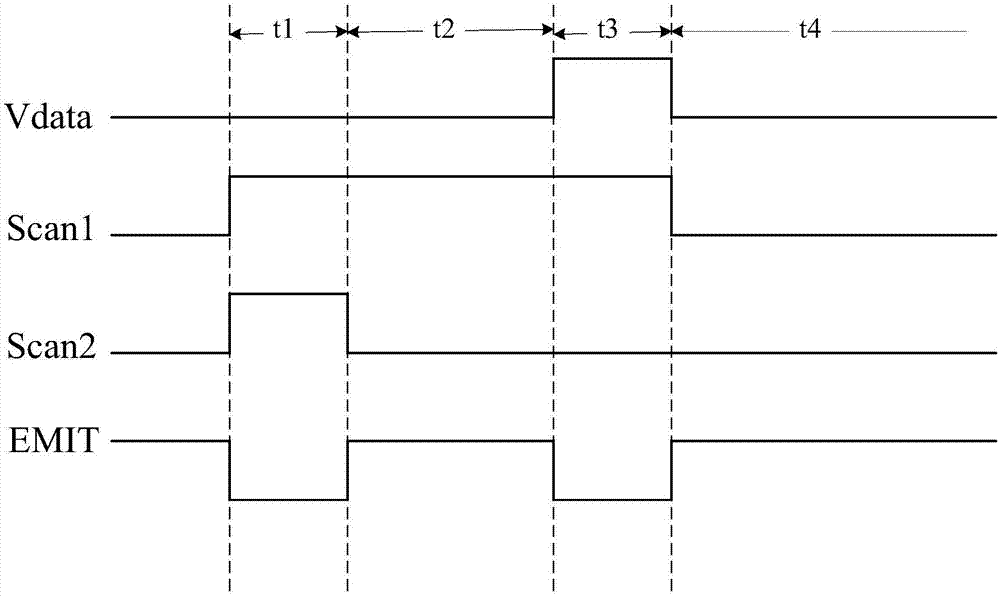
[0083] Optionally, with image 3 The structure of the pixel circuit shown is taken as an example to illustrate, and the corresponding input and output timing diagram is as follows Figure 9 as shown, Figure 9 for image 3 The structure shown corresponds to a timing diagram. Specifically, the main selection of Figure 9 There are four stages in the shown input-output timing diagram: the node initialization stage P1, the threshold detection stage P2, the data writing stage P3 and the lighting stage P4.
[0084] In the node initialization phase P1, EMIT=0, Scan1=1, Scan2=1.
[0085] Since Scan1=1, the second switch transistor T2 is turned on to provide the reference signal V1 sent by the data signal terminal data to the first node N1, and the potential of the first node N1 is V1; the third switch transistor T3 is turned on to connect the reference signal V1 to the first node N1. The reference signal V1 sent by the signal terminal Vref is provided to the third node N3, and t...
Embodiment 2
[0093] Optionally, with image 3 The structure of the pixel circuit shown is taken as an example to illustrate, and the corresponding input and output timing diagram is as follows Figure 10 as shown, Figure 10 for image 3 Another timing diagram corresponding to the structure shown. Specifically, the main selection of Figure 10 There are five stages in the shown input-output timing diagram: the node initialization stage P1, the holding stage P5, the threshold detection stage P2, the data writing stage P3 and the light emitting stage P4. Wherein, the timing is applicable to include a row of zeroth row of pixels before the first row of pixels, and it is stipulated that the extending direction of the gate lines is the row direction. During the scanning process of each row of pixel circuits, the node initialization phase P1 and the holding phase P5 of the next row of pixels are carried out simultaneously with the threshold detection phase P2 and data writing phase P3 of the...
Embodiment 3
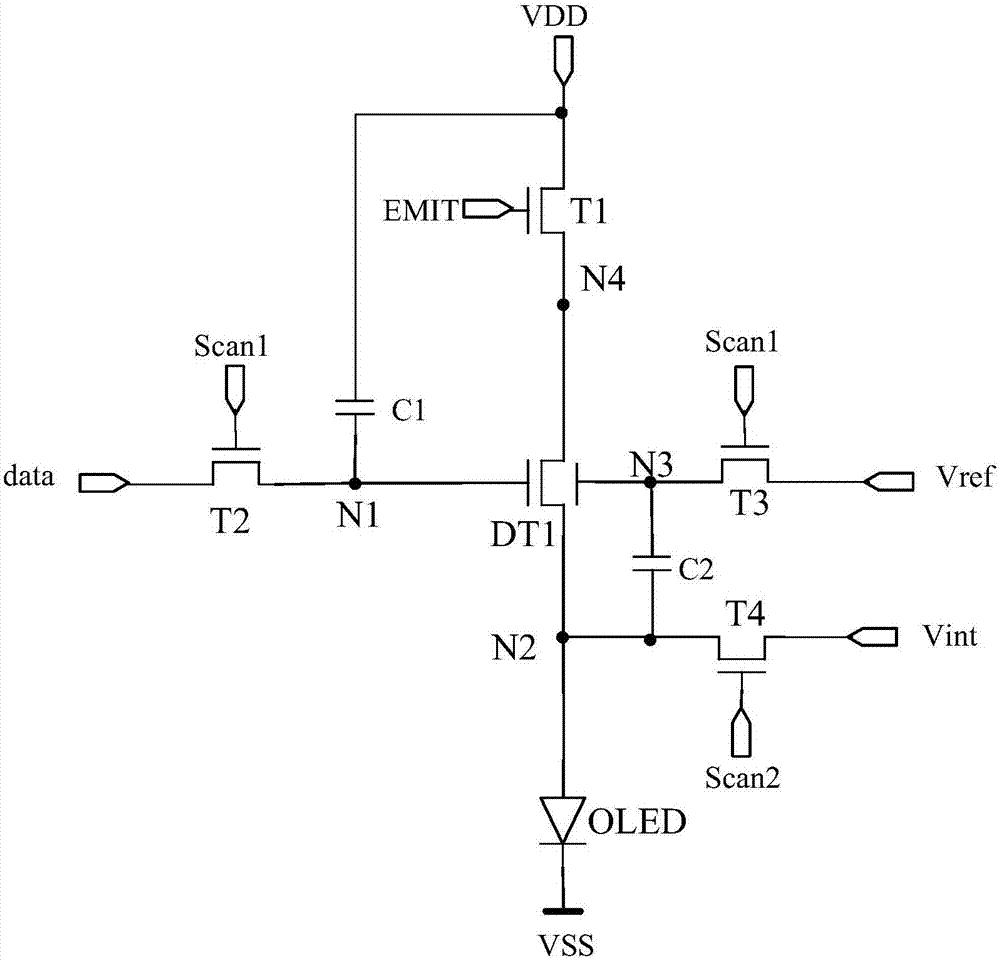
[0105] Optionally, with Figure 5 The structure of the pixel circuit shown is taken as an example to illustrate, and the corresponding input and output timing diagram is as follows Figure 9 as shown, Figure 9 for Figure 5 The structure shown corresponds to a timing diagram. Specifically, the main selection of Figure 9 There are four stages in the shown input-output timing diagram: the node initialization stage P1, the threshold detection stage P2, the data writing stage P3 and the lighting stage P4.
[0106] In the node initialization phase P1, EMIT=0, Scan1=1, Scan2=1.
[0107] Since Scan1=1, the second switch transistor T2 is turned on to provide the reference signal V1 sent by the data signal terminal data to the first node N1, and the potential of the first node N1 is V1; the third switch transistor T3 is turned on to connect the reference signal V1 to the first node N1. The reference signal V1 sent by the signal terminal Vref is provided to the third node N3, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com