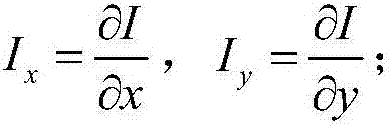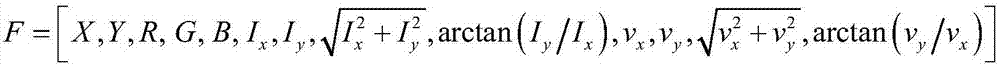Behavior recognition method of nuclear covariance descriptors based on dense tracks
A recognition method and descriptor technology, applied in the field of video processing, can solve problems such as low accuracy of behavior recognition, ignoring the nonlinear relationship of features, and the inability to obtain complex relationships of features, so as to achieve the effect of improving accuracy and description ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] The implementation of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
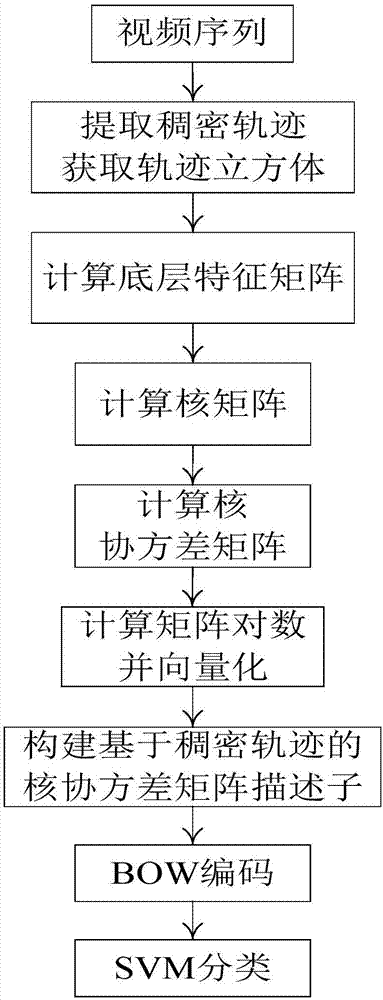
[0020] refer to figure 1 , the behavior recognition steps based on the dense trajectory kernel covariance descriptor of the present invention are as follows:
[0021] Step 1, extract dense trajectories from the video sequence, and obtain trajectory cubes that curve along the trajectories.
[0022] (1.1) Densely sample the video sequence to obtain feature points;
[0023] (1.2) track the feature points obtained in subsequent video frames, and obtain a dense track with a length of L=15;
[0024] (1.3) In each trajectory, take each trajectory point on the trajectory as the center to select an image block of W×H size, and obtain a trajectory cube with a size of W×H×L that curves along the trajectory, W=32, H= 32;
[0025] This example uses the method in the article Action recognition by dense trajectories published by Wang H et al. on Co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com