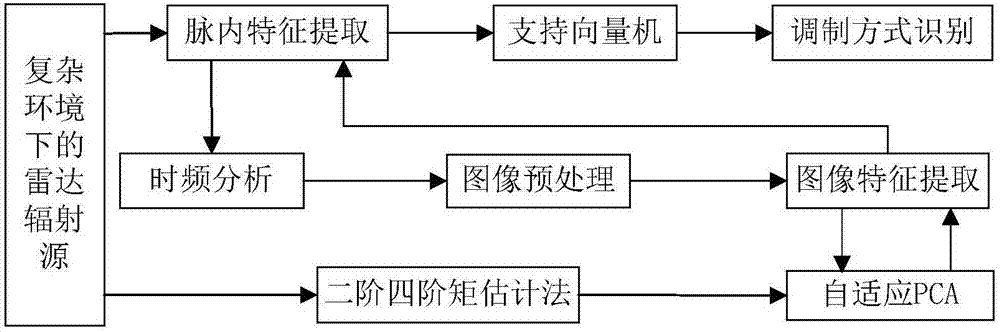
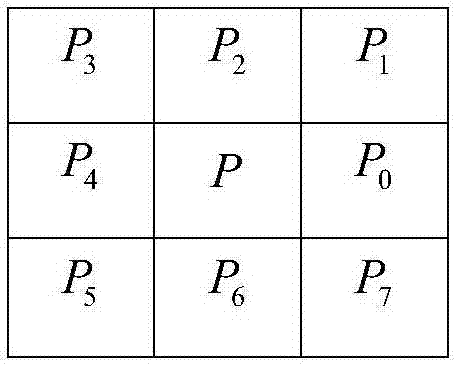
Adaptive radiation source modulation identification method based on time-frequency analysis
A time-frequency analysis and modulation recognition technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, computer parts, etc., can solve the problems of high signal-to-noise ratio feature redundancy and low signal-to-noise ratio feature missing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0061] 1. The experimental parameters are set as follows: Simulate and analyze the radar emitter signals of four modulation modes: LFM, BPSK, COSTAS, and FRANK. The carrier frequency is 20MHz, the sampling frequency is 100MHz, the pulse width is 10us, and BPSK is 7-bit Barker code. . For each signal to be classified, the simulation test is carried out every 2dB when the signal-to-noise ratio is between -2 and 20dB. Each signal generates 200 samples under the current signal-to-noise ratio, and each signal randomly selects 140 samples. SVM training is carried out, and the remaining 60 samples are used for testing the recognition rate of the SVM classifier. Test results such as Figures 3 to 5 shown.
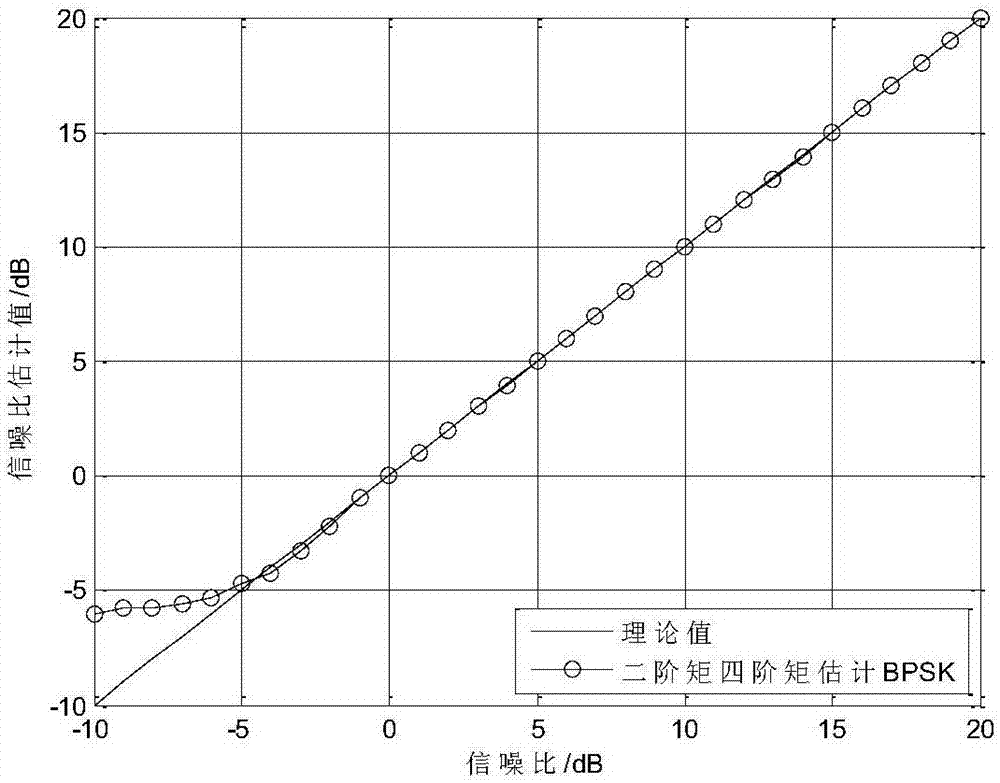
[0062] in image 3 Indicates the determination of the estimated value of the signal-to-noise ratio of the radiation source. According to the estimation of the AWGN channel in step 3, taking the BPSK modulation signal as an example, the range of the signal-to-noise ratio to be es...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com