Method for detecting food-borne pathogenic bacteria based on nucleic acid chromatography biosensing technology
A nucleic acid and peptide nucleic acid technology, applied in the field of detection of food-borne pathogenic bacteria based on nucleic acid chromatography biosensing technology, to achieve the effects of improving detection sensitivity and stability, efficient capture, and expanding the scope of application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
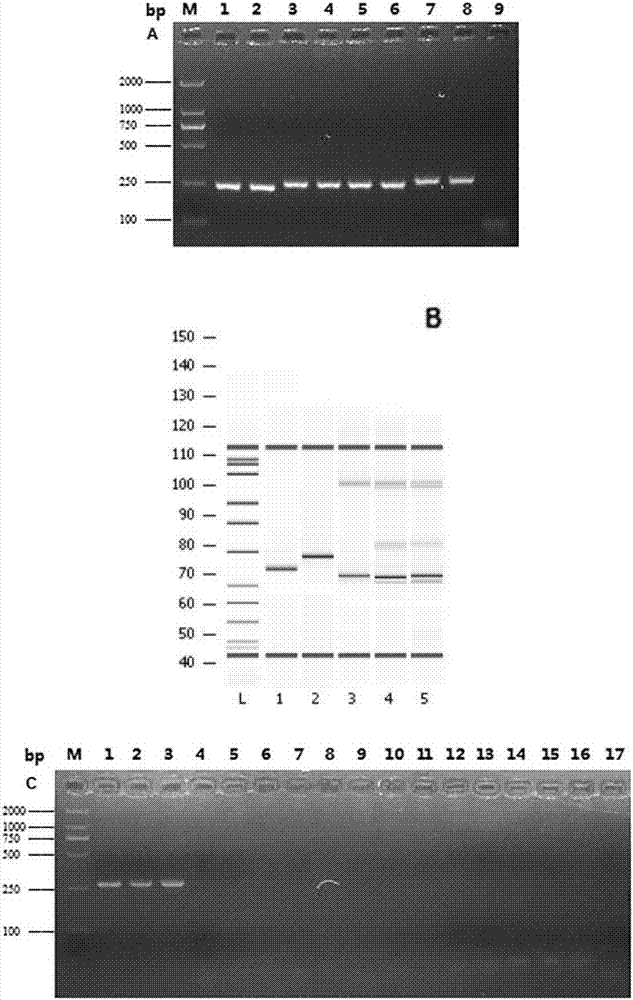
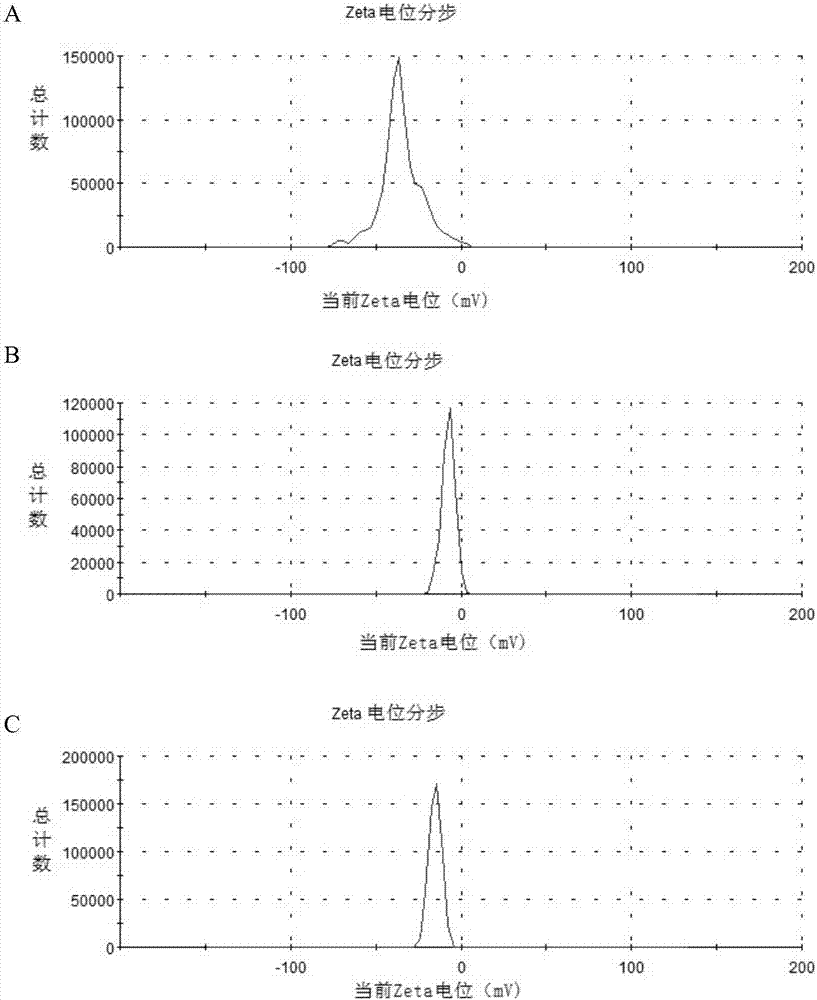
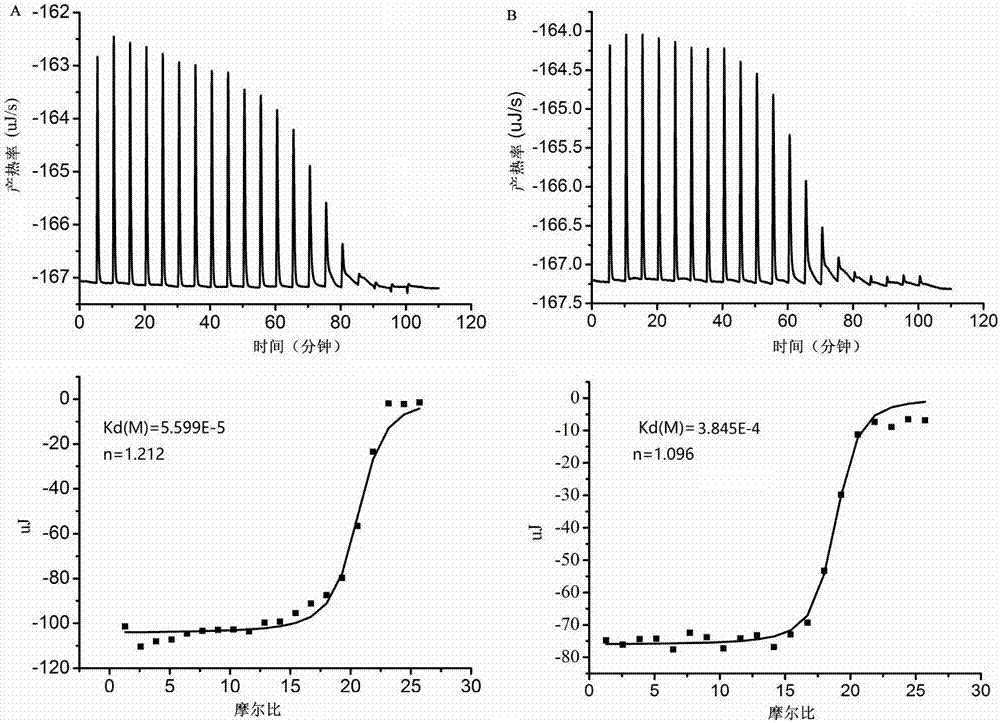
[0068] Embodiment 1 Method for detecting food-borne pathogenic bacteria based on nucleic acid chromatography biosensing technology
[0069] In this example, a total of 16 microorganisms were used for the construction of the biosensor, and Salmonella typhimurium was used as the model strain for the construction of the biosensor (Table 2).
[0070] Table 2
[0071]
[0072] All strains were activated with LB medium and cultured at 37°C for 16h, in which Salmonella typhimurium was serially diluted with 0.8% normal saline to ensure the final concentration was 1-10 6 CFU mL -1 .
[0073] 1. Primer and probe design
[0074] The invA gene of Salmonella was selected as the target sequence (GenBank: DQ644633.1), according to TwistAmp TM Guided by the reaction kit, self-designed RPA amplification primers (RPA-F, RPA-R). A universal adaptor and a C3 blocker were ligated to the 5' end of the RPA primers for the design of primers (RPA-UF, RPA-UR) for universal adaptor blocking recomb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com