Dialysate regeneration method and blood purification system
A blood purification and dialysate technology, applied in dialysis systems, peritoneal dialysis, blood circulation treatment, etc., can solve the problems of easy decomposition and inactivation of urease, inconvenient operation, complex system, etc., to achieve convenient use, avoid acid-base and ion concentration , The effect of simple system structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
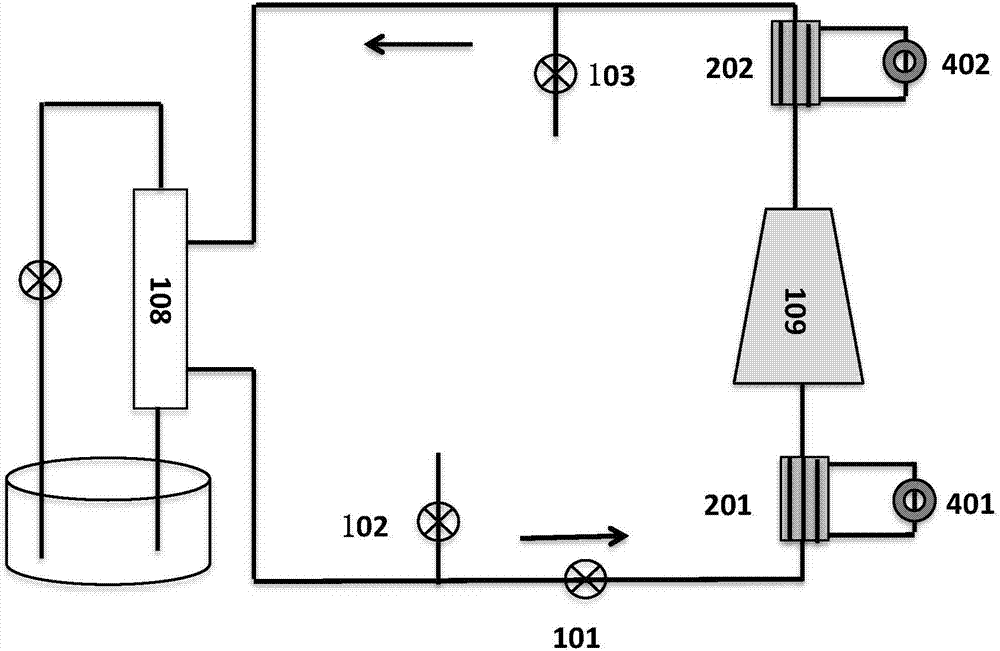
[0052] A blood purification system such as image 3 As shown, it includes dialyzer 108, ultrafiltration pump 102, power pump 101, first heat exchanger 201, adsorption column 109, second heat exchanger 201, infusion pump 103 connected in series in sequence; 108, so that the dialysate enters the dialyzer 108 for exchange treatment after passing through the infusion pump 103; the first heat exchanger 201 and the second heat exchanger 201 are respectively connected with a refrigeration pump 401 and a heat pump 402; the adsorption column 109 can be set as Two or more in series or in parallel; when the blood purification system is in operation, multiple adsorption columns 109 can work simultaneously or switch regularly. When multiple adsorption columns are switched regularly, one or more of them can be regenerated by flushing with hot aqueous solution.
[0053] The working process of the blood purification system: after the dialysate is exchanged with the blood in the dialyzer 108,...
Embodiment 2
[0060] A blood purification system is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
[0061] The blood purification system is used for blood purification treatment, and the cow blood is placed at the blood end, and the flow rate is 100mL / min. Dialysate, the flow rate is 100mL / min. After the dialysate is exchanged with the simulated fluid, it enters the regeneration system through the power pump 101 . The dialysate first enters the refrigeration exchanger 201, the temperature drops from 37°C to 8±0.5°C, and then enters the adsorption column 109. After the dialysate passes through the second heat exchanger 201, the temperature is heated from 8°C to 37±0.5°C, and returns to to the dialyzer for exchange with blood. Blood, dialysate inlet and outlet samples were taken respectively, and the concentration changes of each component were detected. The results are shown in Table 2 and Figure 8 .
[0062] In this embodiment, two adsorption columns 109 are connected in parallel, and each is fill...
Embodiment 3
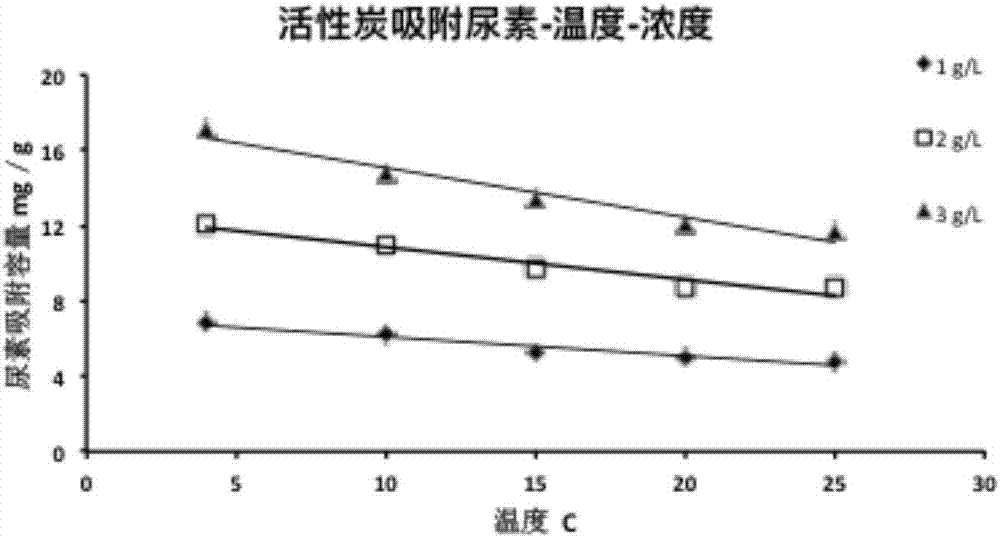
[0066] Prepare 1L of dialysate, keep the temperature at 25°C, and use a peristaltic pump to flow through the adsorption column (filled with 100g of activated carbon and 10g of sodium polystyrene sulfonate), and detect the concentration changes of the components in the effluent. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0067] Related parameters of the activated carbon: BET specific surface area 2300m 2 / g, micropore volume: 1.35cm 3 / g, average pore diameter: 2.7nm.
[0068] Table 3 adopts simulation liquid experiment (3L) result
[0069]
[0070]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com