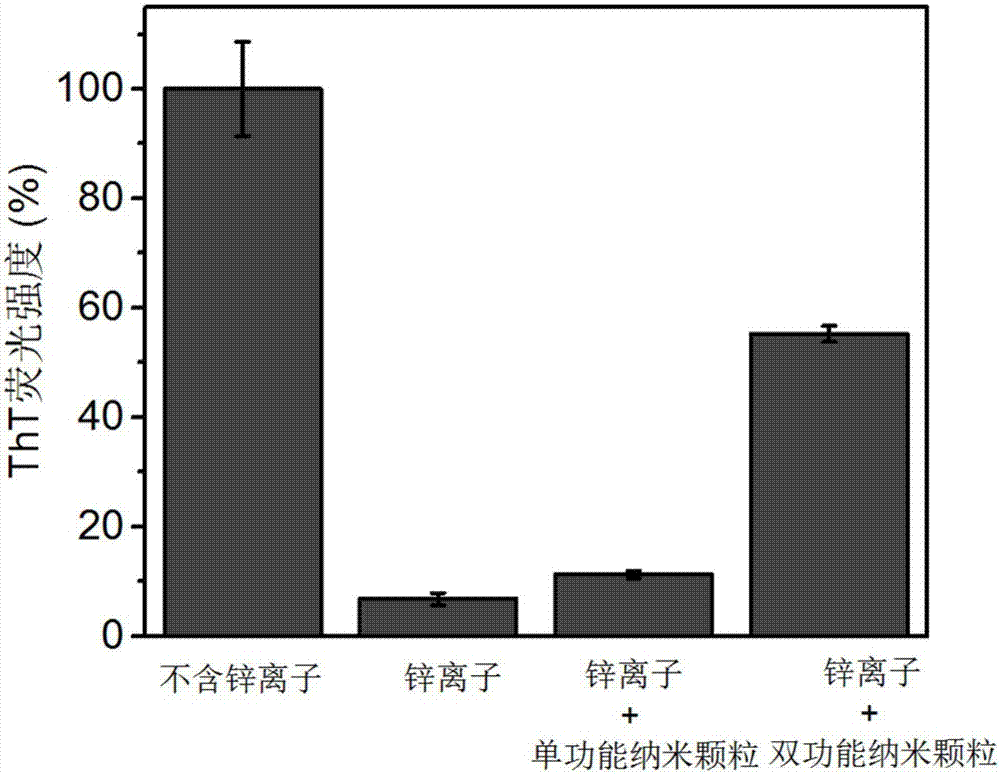
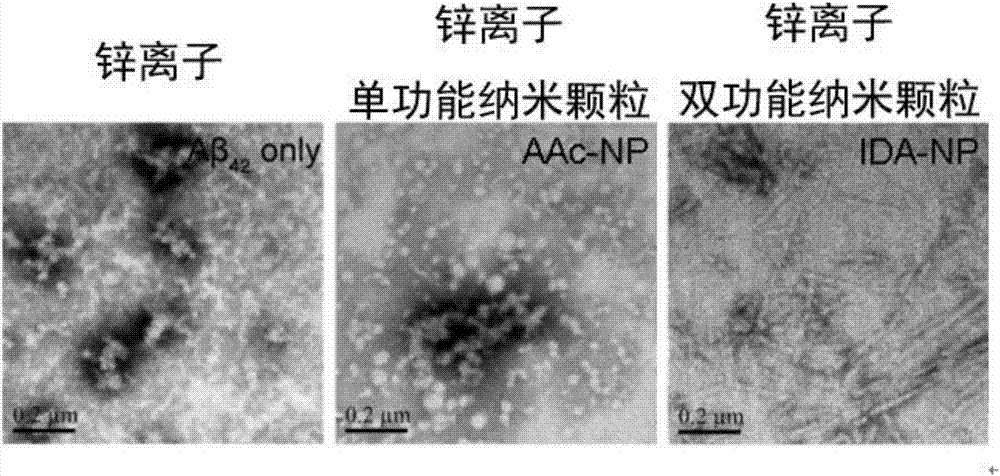
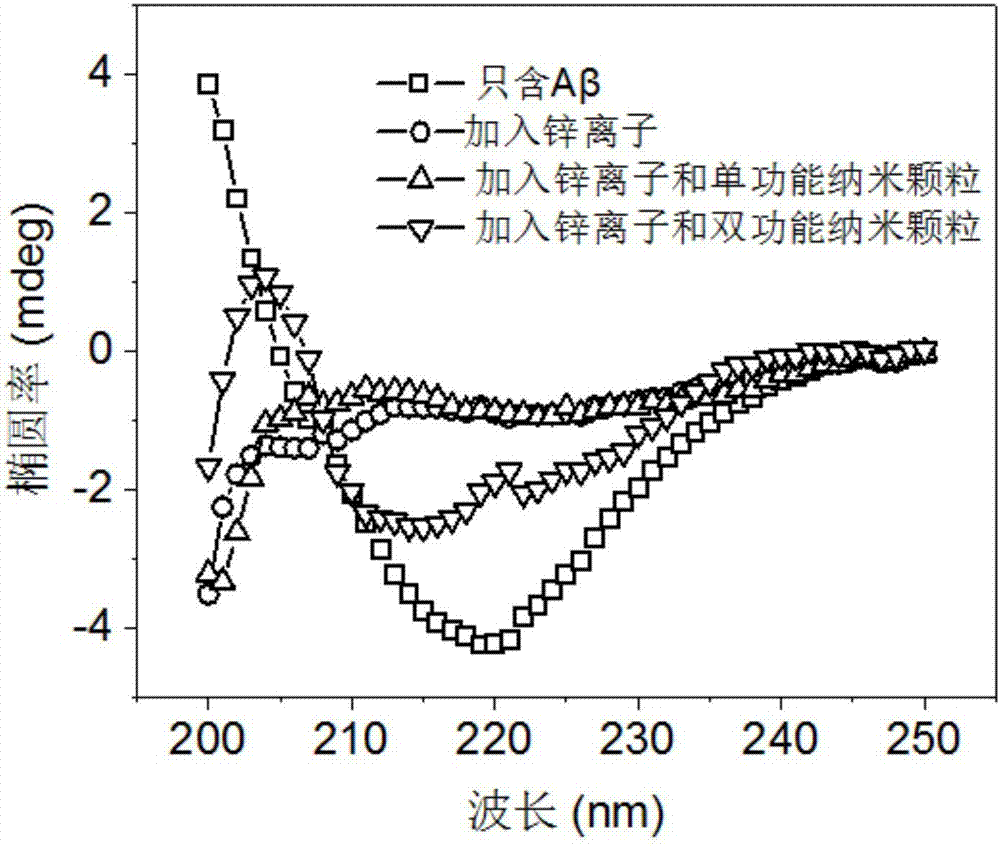
Preparation method of difunctional copolymerized nanoparticle inhibitor and application thereof in inhibition and detoxification of amyloid beta protein aggregation
A nanoparticle, dual-function technology, applied in the application field of inhibition and detoxification, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory inhibition and detoxification effects, and achieve the effect of good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Synthesis of Bifunctional Copolymeric Nanoparticle Inhibitors.
[0034]Copolymer nanoparticles were prepared by free radical copolymerization. (1) Mix N,-N'-methylenebisacrylamide, tert-butylacrylamide, N-isopropylacrylamide and GMA-IDA in molar ratios of 1%, 53%, 41%, and 5%, respectively. In the mixture, 15 mg of surfactant sodium cetyl sulfate was added, and the final volume of the mixed solution was 50 mL. The resulting solution was blown in nitrogen for about 30 minutes to remove the air. Add 60 mg / mL sodium persulfate initiator, and react on a shaker at 25° C. at 160 rpm for 12 hours under nitrogen protection. After the reaction, the resulting polymer was dialyzed against MilliQ water for 14 days (at least two water changes per day) to remove unreacted monomers. Nanoparticles were lyophilized and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C until use. The hydraulic particle diameter of the nanoparticles prepared under this condition is 118±6nm, and the surface Z...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: Synthesis of Bifunctional Copolymeric Nanoparticle Inhibitors.
[0036] Copolymer nanoparticles were prepared by free radical copolymerization. (1) Mix N,-N'-methylenebisacrylamide, tert-butylacrylamide, N-isopropylacrylamide and GMA-IDA in molar ratios of 2%, 40%, 48%, and 10%, respectively. In the mixture, 10 mg of surfactant sodium cetyl sulfate was added, and the final volume of the mixed solution was 50 mL. The resulting solution was blown in nitrogen for about 60 min to remove the air. Add 60 mg / mL sodium persulfate initiator, and react on a shaker at 25° C. at 160 rpm for 15 h under nitrogen protection. After the reaction, the resulting polymer was dialyzed against MilliQ water for 14 days (at least two water changes per day) to remove unreacted monomers. Nanoparticles were lyophilized and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C until use. The hydraulic particle size of the nanoparticles prepared under this condition is 88±6nm, and the surface Zeta potenti...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: Synthesis of Bifunctional Copolymeric Nanoparticle Inhibitors.
[0038] Copolymer nanoparticles were prepared by free radical copolymerization. (1) Mix N,-N'-methylenebisacrylamide, tert-butylacrylamide, N-isopropylacrylamide and GMA-IDA in molar ratios of 5%, 38%, 37%, and 20%, respectively. In the mixture, 20 mg of surfactant sodium cetyl sulfate was added, and the final volume of the mixed solution was 50 mL. The resulting solution was blown in nitrogen for about 10 min to remove the air. Add 60 mg / mL sodium persulfate initiator, and react on a shaker at 25° C. at 160 rpm for 10 h under nitrogen protection. After the reaction, the resulting polymer was dialyzed against MilliQ water for 14 days (at least two water changes per day) to remove unreacted monomers. Nanoparticles were lyophilized and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C until use. The hydraulic particle size of the nanoparticles prepared under this condition is 80.0±5nm, and the surface Zeta poten...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com