Passive optical access network and flow scheduling method thereof
A technology for network access and traffic scheduling, which is applied in the field of optical fiber communication, can solve the problems of inability to control traffic and PON real-time control, and achieve the effects of improving low utilization of network resources, avoiding signaling storms, and saving costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
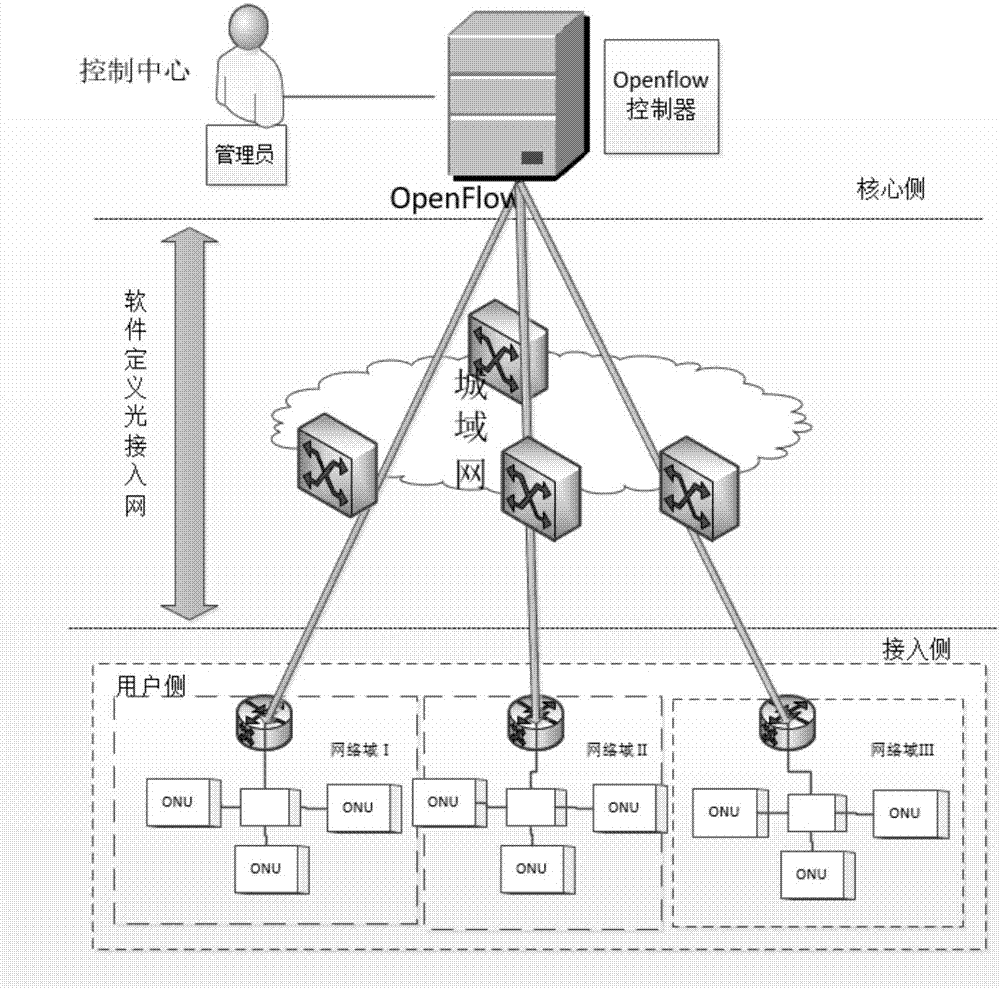
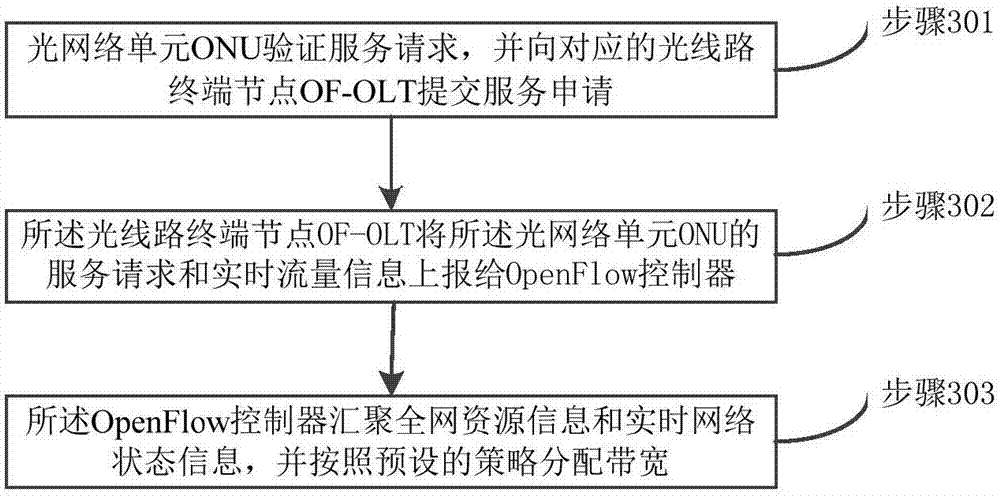
[0037] image 3 A flowchart showing a flow scheduling method for a passive optical access network provided by an embodiment of the present invention, as shown in figure 1 As shown, the method includes:
[0038] Step 301: the optical network unit ONU verifies the service request, and sends the service request to the corresponding optical line terminal node OF-OLT;
[0039] Step 302: The optical line terminal node OF-OLT reports the service request of the optical network unit ONU and its own real-time flow information to the OpenFlow controller;
[0040] Step 303: the OpenFlow controller aggregates the resource information of the entire network and real-time network status information, and allocates bandwidth according to a preset strategy.
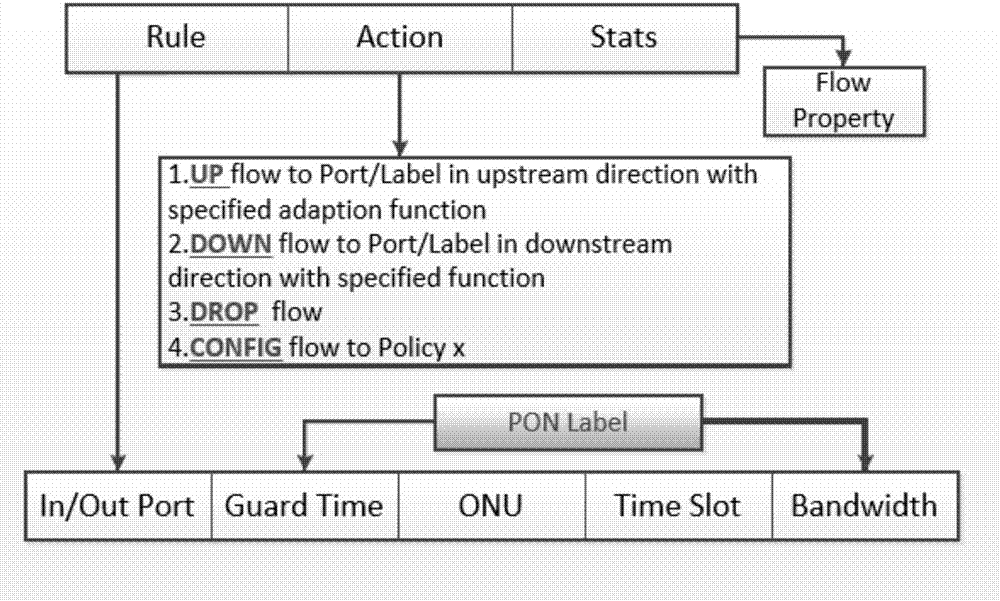
[0041] In the present invention, when a service request arrives, the ONU verifies the service request and maps it to the request parameter TR i (d, t), submit an application to the corresponding OF-OLT through the OAM protocol, and each ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Figure 4 A flowchart showing an implementation of step 303, such as Figure 4 As shown, step 303 can be implemented as the following steps:
[0045] Step 401: The OpenFlow controller according to the past t 0 OLT resource utilization expectation, OLT service queue length expectation, and service data volume expectation in the service request within a certain period of time, calculate the future time t 1 The bandwidth requirements of the internal network;
[0046] Step 402: The OpenFlow controller allocates bandwidth for the service request according to the principle of the lowest cost or the principle of the best user experience, and allocates the total uplink bandwidth of the optical line terminal node OLT.
[0047] Due to the time-varying nature of the network state, the present invention uses a dynamic resource prediction scheme to predict the current and future parameter changes by sampling resource changes in the past period of time. i.e. statistical past t 0...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Figure 5 A flow chart showing an implementation of step A2 in Embodiment 2, such as Figure 5 As shown, step A2 can be implemented as the following steps:
[0052] Step 501: When the available bandwidth of the optical line terminal node OLT is greater than the minimum required bandwidth of the network, allocate bandwidth to the service request according to the principle of the lowest cost or the principle of optimal user experience, and allocate bandwidth to the optical line terminal node OLT The total uplink bandwidth is allocated;
[0053] Optionally, the minimum cost principle includes: when the minimum required bandwidth of the network is met, reducing the total bandwidth of the OLT link of the idle optical line terminal node, increasing the total bandwidth of the OLT link of the busy optical line terminal node, and starting the sleep wake-up of the device mechanism.
[0054] The principle of the lowest cost is to allocate bandwidth according to the maximum dela...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com