Screening method and application of rapid growth mutants of microalgae
A technology of mutants and microalgae cells, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as unstable genetics, achieve the effect of solving unstable genetics and avoiding blindness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
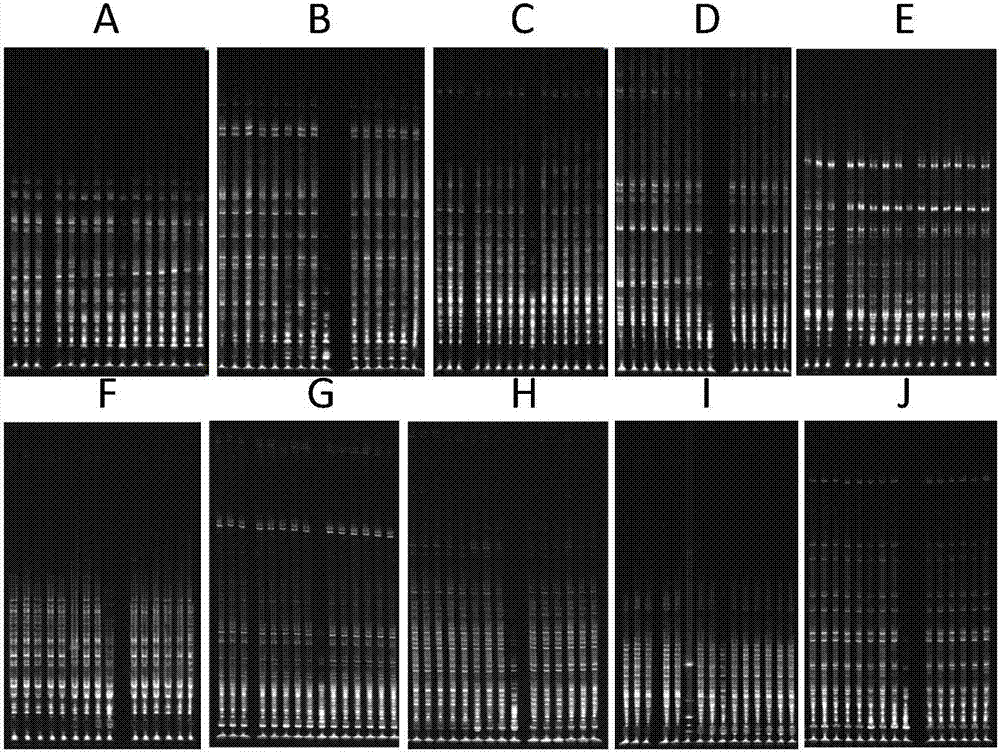
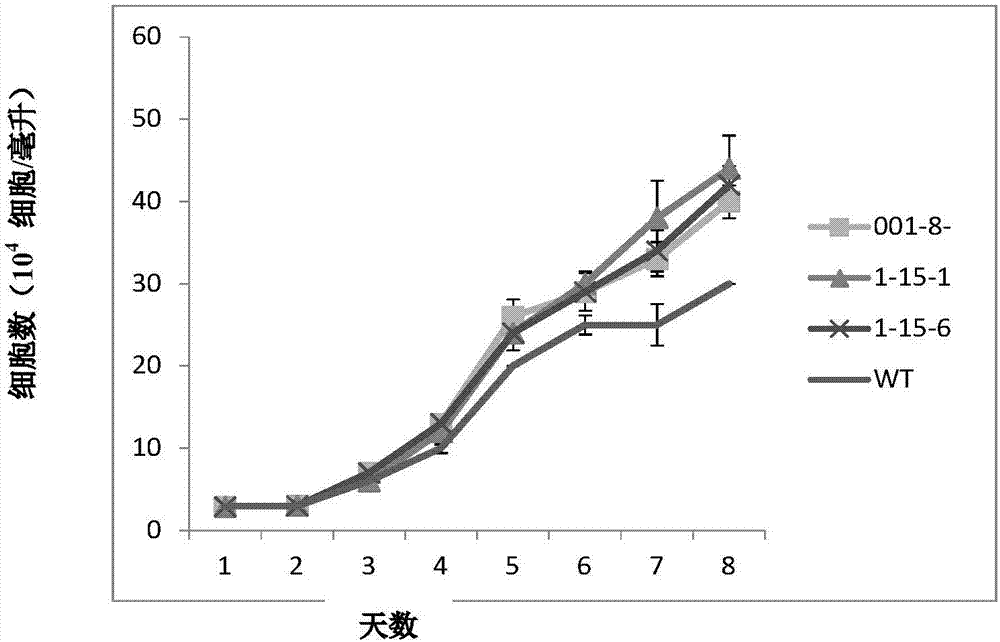
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1, activation and pre-cultivation of Haematococcus:
[0034] Pick the Haematococcus NIES-144 monoclonal algae strain from the solid plate and inoculate it in a 50ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 10ml Basal liquid medium, 15μmol·m -2 ·s -1 , and cultured statically at 20°C for 10 days, then transferred to a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 100 mL of Basal medium and cultured for 4 days under the same conditions. Collect the algae cells by centrifugation at 1500 g for 5 min.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2, EMS chemical mutagenesis algae cell:
[0036] 1. Collect Haematococcus cells in the logarithmic phase by centrifugation at 1500 g for 5 min, and treat with 4% EMS (ethyl methanesulfonate) for 1 h; centrifuge at 1500 g for 5 min to remove the mutagen.
[0037] 2. 50ml sodium thiosulfate Na 2 S 2 o 3 Resuspend the cells to terminate the mutagenesis reaction.
[0038] 3. Centrifuge to remove sodium thiosulfate, wash algae cells twice with Basal medium, and finally resuspend in Basal medium and keep away from light for 24 hours.
[0039] 4. Inoculate the mutagenized algae cells in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, and record it as the F0 generation, 15μmol·m -2 ·s -1 , static culture at 20°C, after the F0 generation recovers its vitality and grows fresh algae cells, it is successively subcultured and inoculated, which are respectively recorded as F1, F2, F3....
Embodiment 3
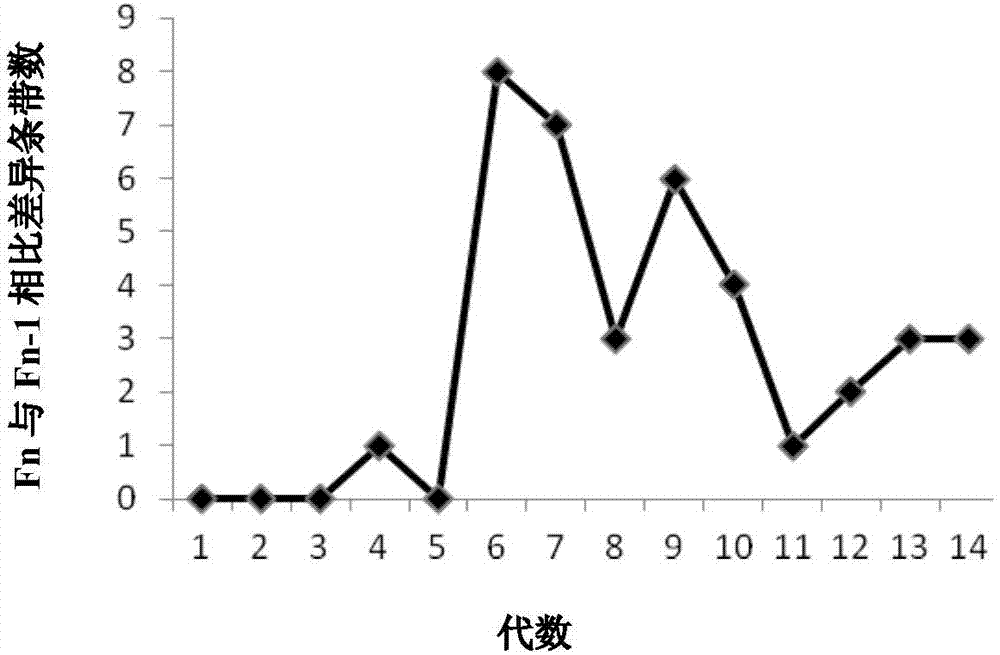
[0040] Embodiment 3, inferring the appropriate number of passages by calculating
[0041] Assume an initial inoculum of N cells containing a fast growing mutant.
[0042] The wild type can grow 10 times in the logarithmic phase, assuming that the fast growing mutant can grow 20 times in the logarithmic phase, then the number of passages required when the proportion of the fast growing mutant increases to 50% can be calculated.
[0043] The proportion of fast-growing mutants (Fn) when each generation grows to the logarithmic phase is as follows
[0044]
[0045] When Fn=50%, if the initial inoculation amount N=4X10 4 , then it can be deduced that the number of passages n=13.7. However, due to the uncertainty of the growth efficiency of the mutants obtained after mutagenesis and the possible differences in the initial inoculum volume, there will be large differences in the number of passages required in practice and in theoretical calculations. There is therefore still a n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com