A permanent magnet linear synchronous motor non-uniformly mixed permanent magnet excitation topological structure
A permanent magnet linear synchronization and topology technology, applied in electrical components, electromechanical devices, electric components, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the maximum rated thrust of the motor, damage to the insulation of the motor, and reducing the performance of the motor, and reduce the harmonic content. Fluctuations in electromagnetic thrust, low machining accuracy, and improved sine effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
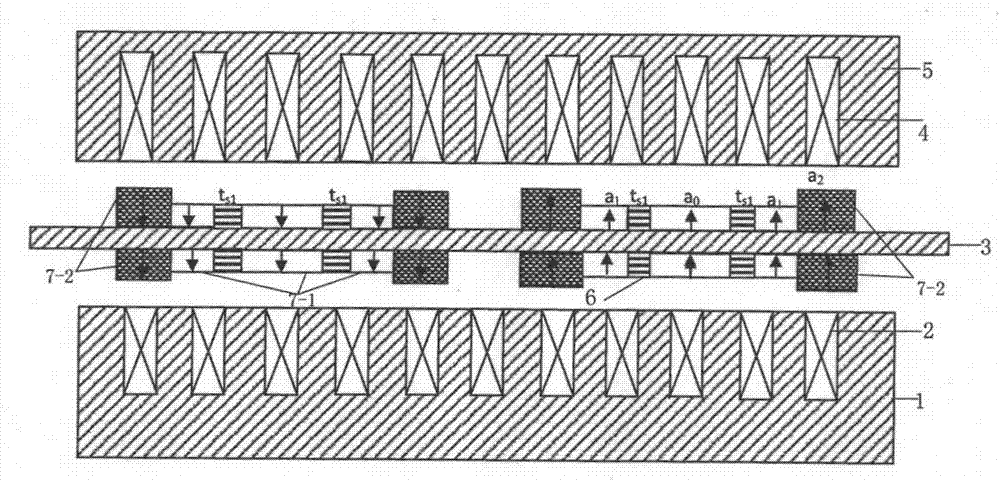
[0027] The motor mainly consists of primary, secondary and air gap.
[0028] Such as figure 1 As shown, the primary side of the bilateral cylindrical permanent magnet linear synchronous motor is divided into inner and outer double-layer structures, consisting of an inner stator and an outer stator.
[0029] The outer stator includes an outer primary core 5 and an outer armature winding 4 . The outer primary iron core 5 is located at the outermost side of the motor and is of tubular structure, and the outer layer armature winding 4 is tightly fixed inside the outer primary iron core 5 .
[0030] The inner stator includes an inner primary core 1 and an inner armature winding 2 . The inner primary iron core 1 is located at the innermost side of the motor and is also of tubular structure, and the inner armature winding 2 is tightly fixed outside the inner primary iron core 1 .
[0031] The inner armature winding 2 and the outer armature winding 4 are connected in series, and bo...
Embodiment 2
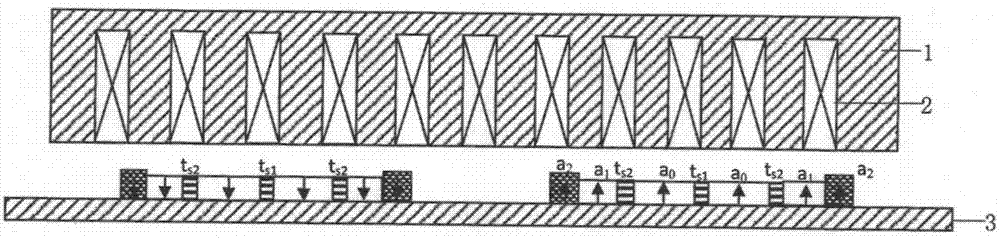
[0047] Such as figure 2 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the unilateral cylindrical permanent magnet linear synchronous motor only includes one layer of iron core and one layer of armature winding, and only the corresponding armature winding on the secondary yoke 3 A permanent magnet is arranged on one side.
[0048] The lower permanent magnet of each pole also adopts the non-uniform block structure described in Embodiment 1. Suppose the width of the two radially magnetized rare earth NdFeB permanent magnets 7-1 in the middle is the same, which is a 0 ; The width of the radially magnetized rare earth NdFeB permanent magnet 7-1 at both ends decreases successively according to the geometric sequence, respectively a 1 、a 2 ,...,a n ; The width of the radially filled ferrite permanent magnet 7-2 is a n+1 , n is a positive integer, and the pole pitch of the cylindrical permanent magnet linear motor is τ P , then a 0 =0.301τ P -0.065...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com