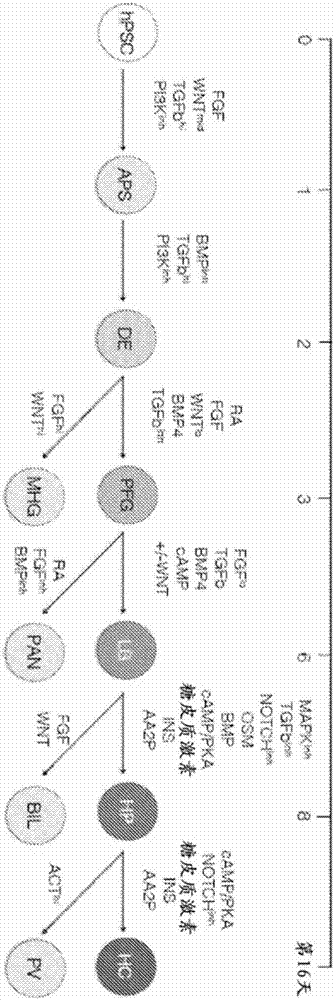
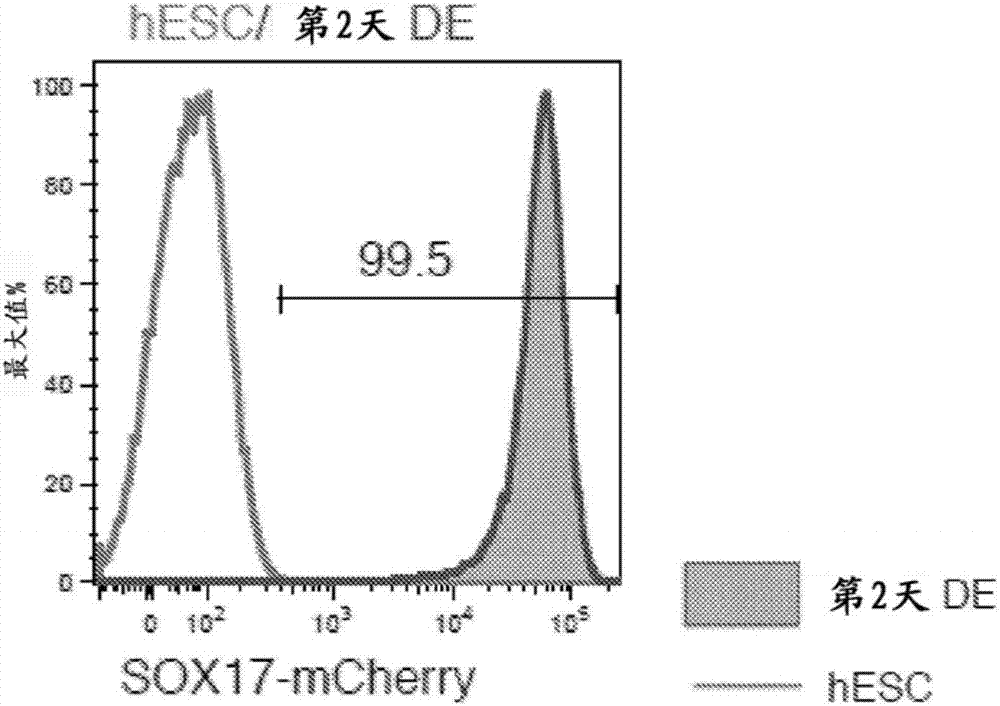
Methods of differentiating stem cells into liver cell lineages
A technology of liver cells and stem cells, applied in the biological field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] definition
[0035] The following words and terms used herein shall have the indicated meanings:
[0036] The term "stem cells" as used herein includes, but is not limited to, undifferentiated cells defined by their ability to self-renew at the single-cell level and differentiate to produce progeny cells, including self-renewing progenitor cells, non-renewing progenitor cells, cells and terminally differentiated cells. For example, "stem cells" can include (1) totipotent stem cells; (2) multipotent stem cells; (3) multipotent stem cells; (4) oligopotent stem cells; and (5) unipotent stem cells.
[0037] As used herein, the term "pluripotent stem cell" (PSC) refers to cells that have the ability to differentiate under different conditions into all three germ cell layers (i.e. endoderm (such as intestinal tissue), mesoderm (including blood, muscle and blood vessels) and outer A cell of developmental potential that is a cell type characteristic of a germ layer (eg, skin ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com