Attribute-based data encryption method supporting dynamic user revocation in cloud storage environment
A data encryption and cloud storage technology, which is applied in the field of data encryption in cloud storage environment, can solve data leakage and other problems, and achieve the effect of improving security, high security, and avoiding legal access
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
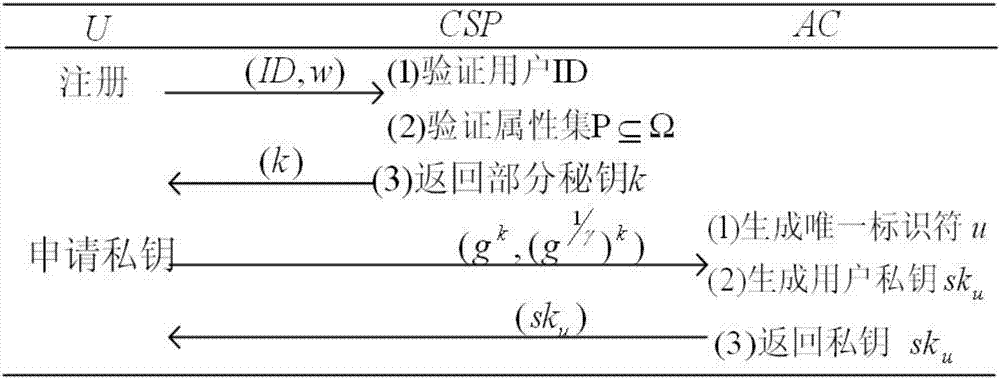
[0044] In order to solve the problem in the existing cloud storage data technology that legitimate users can still access data after logout and easily cause data leakage, this embodiment provides a method such as figure 1 In the shown cloud storage environment, the attribute-based data encryption method that supports dynamic revocation by users firstly uses the partial key generated by CSP and the unique identifier generated by AC for the user to jointly generate U’s private key; then U that satisfies the access structure T uses its own The private key to decrypt encrypted data stored in the cloud. When a registered legal user logs out, the CSP updates some keys and completes the update of the relevant ciphertext, and the unregistered user completes the private key sk u However, users who have logged out cannot decrypt correctly, thereby protecting the confidentiality of shared data. The specific functions of the participants are as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0045] An attr...
Embodiment 2
[0068] User Registration Algorithm
[0069] The above-mentioned D is registered with the CSP: D needs to register before storing data, and the CSP verifies the authenticity of D’s identity ID, and returns k to D through a secure channel for successful registration.
[0070] User U registers in CSP: User U according to CSP attribute set Ω={L 1 , L 2 ,...,L n}, generating its own attribute set in And l j ∈Ω, 1≤j≤n, and submit the identity ID and personal attribute set w to the CSP, and the CSP returns the partial key k to U through a secure channel.
[0071] Encryption Algorithm
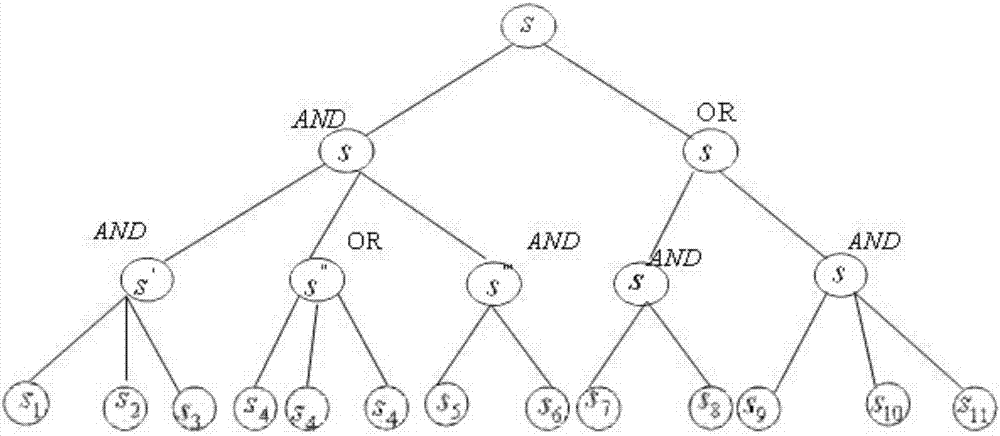
[0072] Before uploading the shared data, D constructs the access structure tree T with attributes in the access structure as leaf nodes and threshold logic symbols (AND, OR) as intermediate nodes. Then D converts the plaintext m ∈ G 1 Encryption is performed under the specified access structure tree T. D randomly selected Assign the value to the root node of the access structure and mark t...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Using the attribute-based data encryption method in the cloud storage environment shown in Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 to support user dynamic revocation and comparing with several existing schemes mainly consider the length of the user’s private key, the storage cost of the ciphertext length, and the user’s The calculation cost of the private key and the calculation cost of the ciphertext. In Table 1, n represents the number of system attributes, n i Indicates the number of values of the i-th attribute, |w|(|w|≤n) indicates the number of attributes of the user's private key, |G| and |G 1 | represent G and G respectively 1 The length of the elements in, t m Indicates the calculation cost of unit power multiplication, t p Indicates the calculation cost of unit dot multiplication. The specific comparison results are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
[0079] Table 1 Storage overhead comparison
[0080]
[0081] Table 2 Computational overhead comparison
[0082] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com