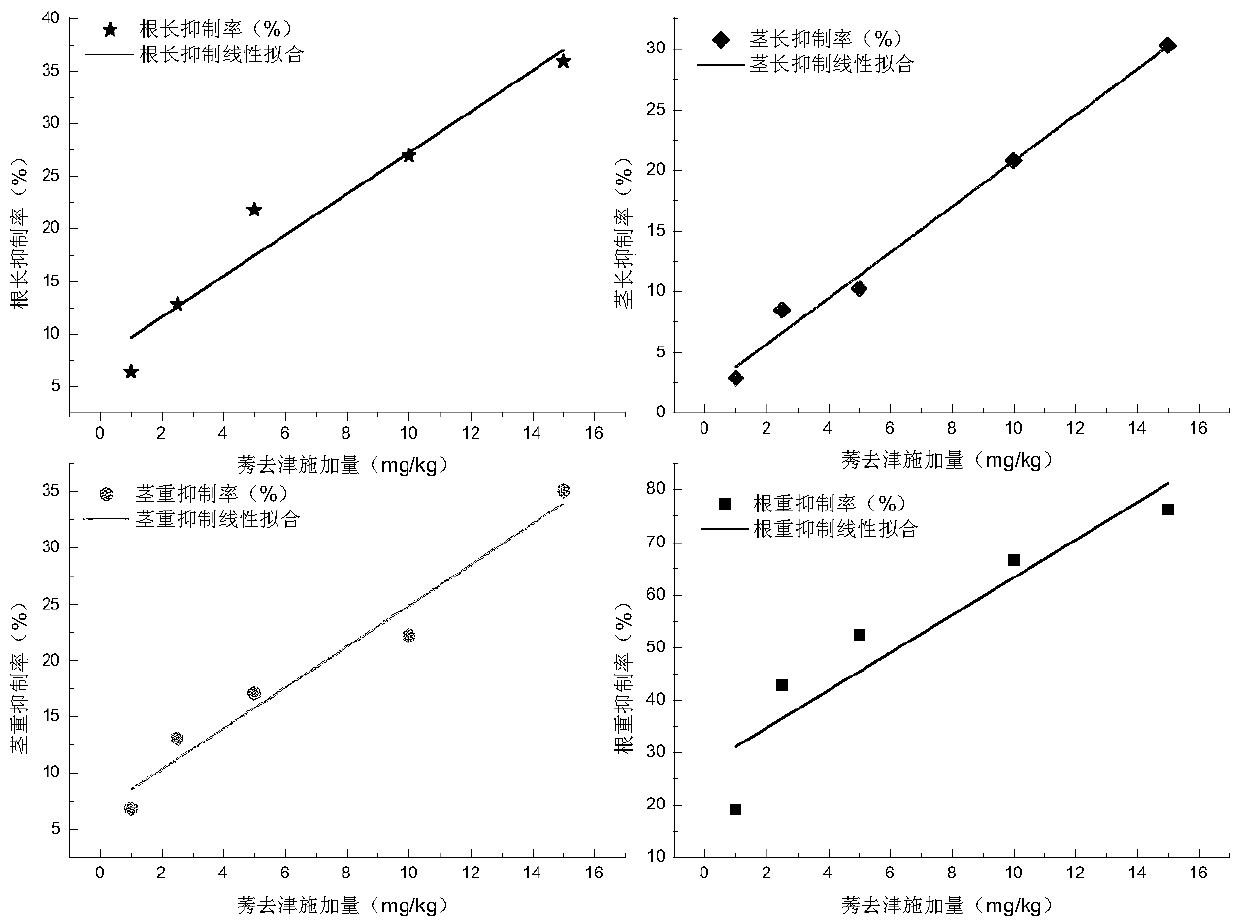
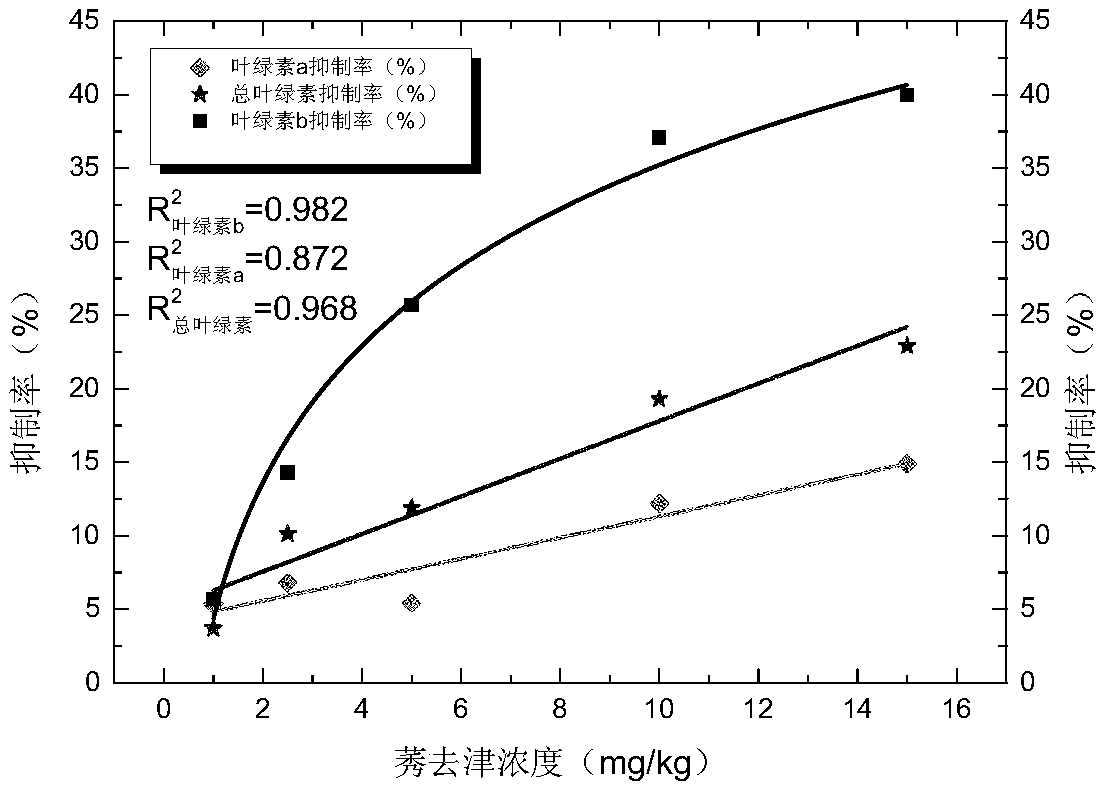
A Method for Evaluating the Ecotoxicity of Soil Residual Atrazine Using Broad Bean
A technology of atrazine and broad bean, applied in the field of soil protection, can solve the problem of less evaluation of soil organic pollutants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: A method for evaluating the ecotoxicity of soil residual atrazine using broad bean
[0023] A method for evaluating the ecotoxicity of soil residual atrazine by applying broad beans, including soil treatment and broad bean pot experiments; the soil treatment refers to adjusting the moisture content of the soil to be tested and the standard soil moisture content to 60wt%, and putting it in 25 ℃ 24 hours in the incubator; Described broad bean pot experiment comprises the following steps:
[0024] The first step: germination
[0025] The broad bean seeds are sterilized with 15% hydrogen peroxide for 20 minutes, then soaked in distilled water, and then transferred to an incubator to cultivate the broad bean seeds to germinate to obtain the seeds after germination;
[0026] Step Two: Germinate
[0027] The seeds after the germination are sown respectively in the second container containing the first container of the soil to be tested and the standard soil, and t...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: A method for evaluating the ecotoxicity of soil residual atrazine by applying broad bean
[0033] A method for evaluating the ecotoxicity of soil residual atrazine by applying broad beans, including soil treatment and broad bean pot experiments; the soil treatment refers to adjusting the moisture content of the soil to be tested and the standard soil moisture content to 60wt%, and putting it in 25 ℃ 24 hours in the incubator; Described broad bean pot experiment comprises the following steps:
[0034] The first step: germination
[0035] The broad bean seeds are sterilized with 15% hydrogen peroxide for 20 minutes, then soaked in distilled water, and then transferred to an incubator to cultivate the broad bean seeds to germinate to obtain the seeds after germination;
[0036] Step Two: Germinate
[0037] The seeds after the germination are sown respectively in the second container containing the first container of the soil to be tested and the standard soil,...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: A method for evaluating the ecotoxicity of soil residual atrazine by applying broad bean
[0043] A method for evaluating the ecotoxicity of soil residual atrazine by applying broad beans, including soil treatment and broad bean pot experiments; the soil treatment refers to adjusting the moisture content of the soil to be tested and the standard soil moisture content to 60wt%, and putting it in 25 ℃ 24 hours in the incubator; Described broad bean pot experiment comprises the following steps:
[0044] The first step: germination
[0045] The broad bean seeds are sterilized with 15% hydrogen peroxide for 20 minutes, then soaked in distilled water, and then transferred to an incubator to cultivate the broad bean seeds to germinate to obtain the seeds after germination;
[0046] Step Two: Germinate
[0047] The seeds after the germination are sown respectively in the second container containing the first container of the soil to be tested and the standard soil,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com