Power distribution method of channel sharing for large-scale users in uncertainty condition of channel
An uncertainty and allocation method technology, applied in power management, wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as unknown channel state information, achieve maximum throughput, ensure service quality, and optimize transmit power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
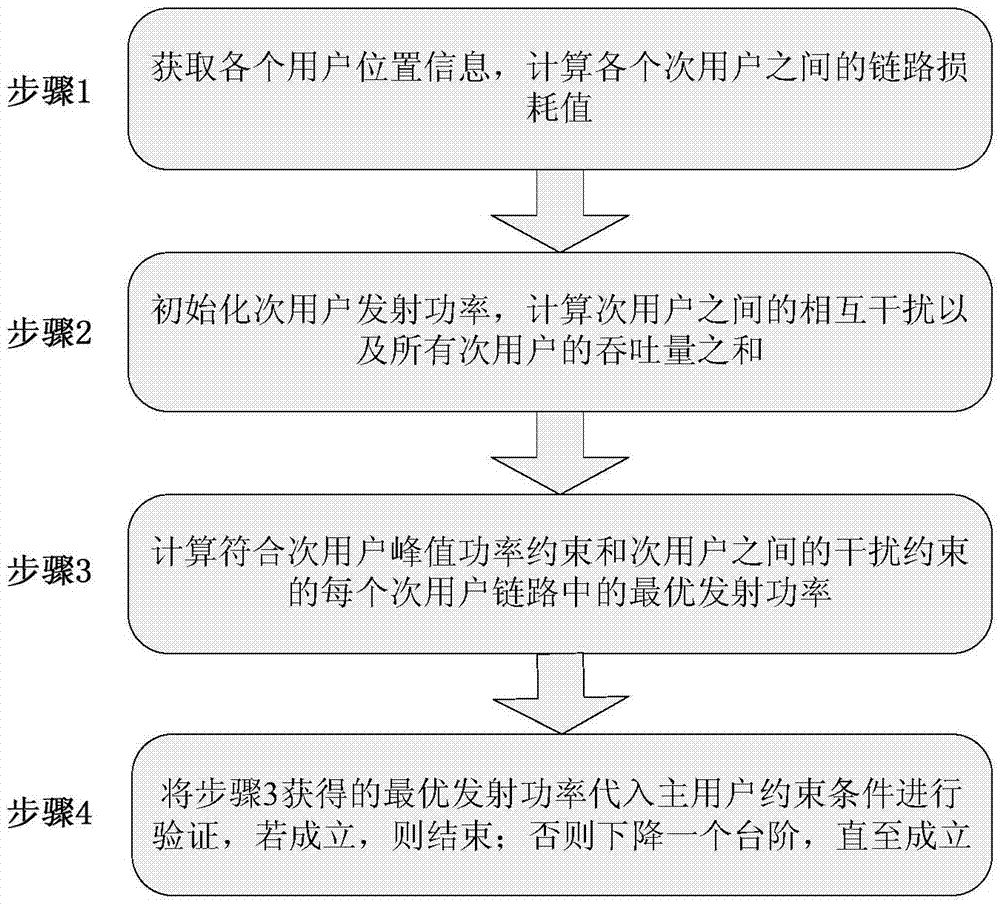
[0114] A specific embodiment of the present invention is described as follows, and the system simulation adopts Matlab software. The following embodiments examine the effectiveness of the method for power allocation of a large-scale user shared channel under the condition of channel uncertainty described in the present invention.
[0115] In this embodiment, the simulation results are obtained through 1000 independent experiments. The scenarios are all cognitive networks of a primary user and a large-scale secondary user. Assume that the center frequency f of the transmitted signal is 700MHz, and the noise power is -130dBm, the path loss index α=4, the antenna height between the transmitter and receiver of the secondary user is l T , l R Both are 2m, the maximum transmit power p of the secondary user transmitter max is 25dBm, the interference threshold I of the secondary user and the primary user max , Respectively -120dBm.
[0116] Such as image 3 As shown, consider ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com