A method for grafting and rapid propagation of tea tree specific germplasm resources
A specific and germplasm technology, applied in grafting, cultivation, agriculture, etc., can solve the problems of small reproduction coefficient, variation and degradation, and not retaining leaves, etc., and achieve the effect of speeding up propagation and improving survival rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] A total of 10 special tea germplasm resources including Guilu 1, Guilv 2, Guilv 3, Gelu, Gaoyuanlv, Yiwei, Liufang, Qianjiangyue, Hannan 1 and Baihua 1 were grafted and rapidly propagated, including Follow the steps below:
[0035] (1) Treatment of rootstocks: take the 20-year-old clone Fuding Dabai tea as rootstocks, mow in May to June, and form rootstock stumps with a height of 15 to 25 cm from the ground. Select and stay 10-11 strong new shoots in the direction, and cultivate the new shoots into semi-lignified rootstock twigs with a length of 8-10 cm for grafting.
[0036] (2) The processing of scion: with the twig before the semi-lignification of tea tree specific germplasm resource as scion branch, scion branch is cut into partial wedge-shaped short ear with razor, the long 2~3cm of cutting surface, the long 3~3cm of short ear. 4cm, leave a strong and full axillary bud and a leaf, and retain half of the leaf for the large-leaf variety, and ensure that the cut is o...
experiment example 1
[0048] 10 clumps of tea trees grafted in embodiment 1, 50 branches of each clump, establish 3 repetitions, and graft 150 branches altogether; Observe the survival rate after the summer drought at the beginning of September, and observe the tree height, tree height and tree height when the growth stops at the beginning of November for 3 consecutive years. Width and the number of ears that can be cut.
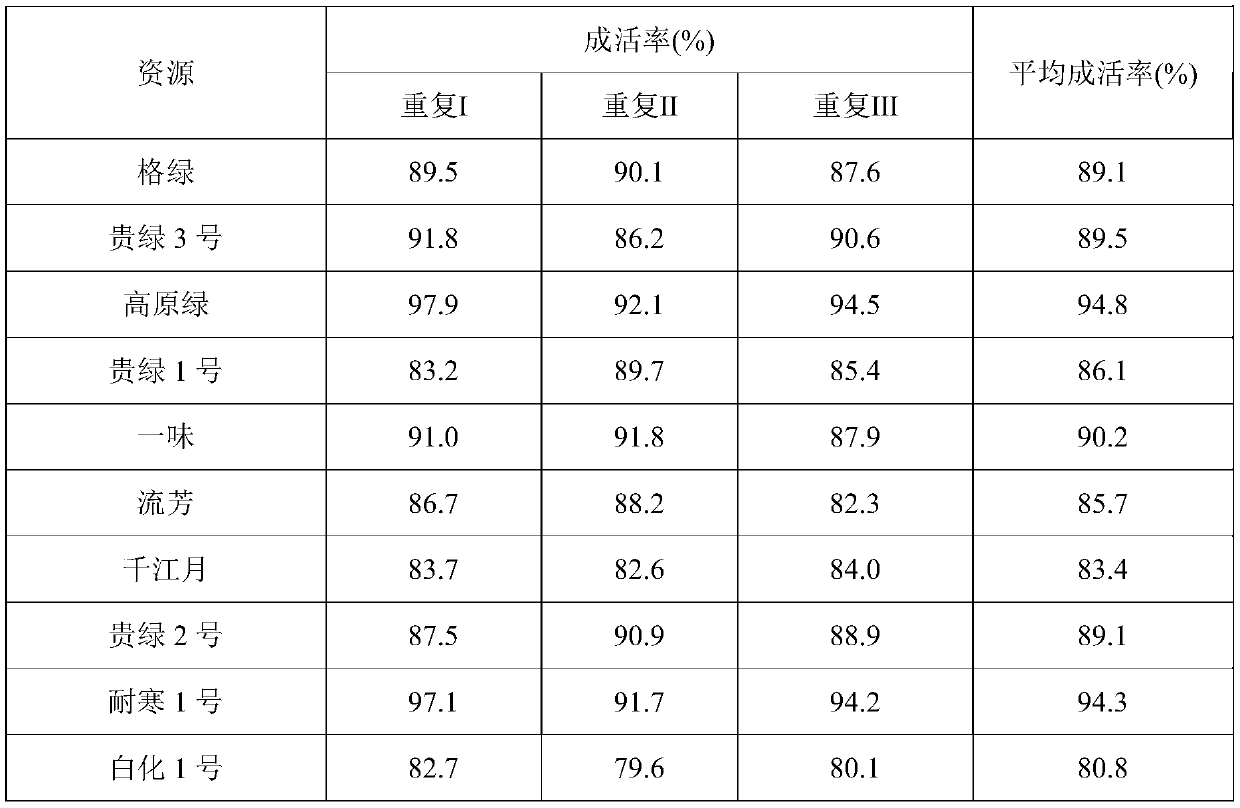
[0049] Table 1. Grafting survival rate of 10 tea tree specific germplasm resources
[0050]
[0051] The results of the grafted survival rates of 10 tea tree specific germplasm resources are shown in Table 1, and the survival rates are all higher than 80%, indicating that the grafting rapid propagation method of the present invention is suitable for tea tree specific germplasm resources.
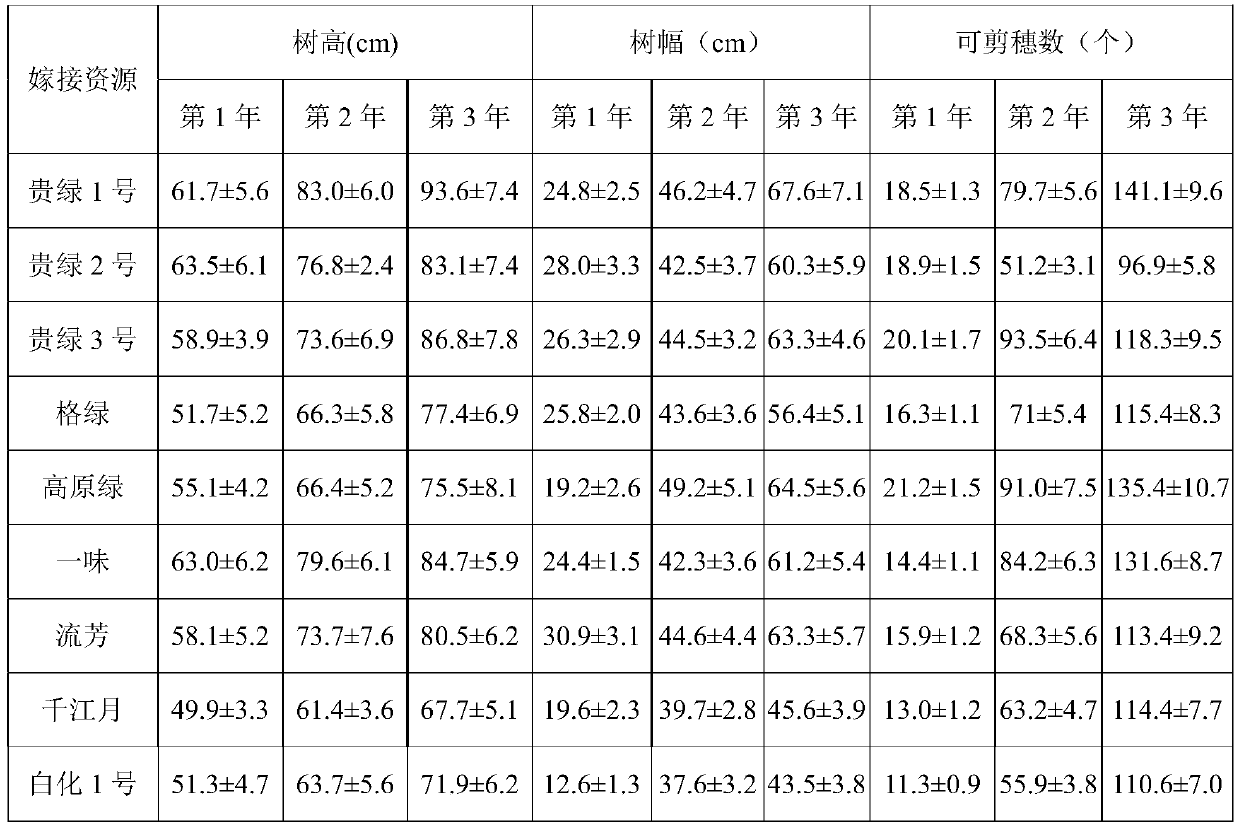
[0052] Table 2. The growth vigor and the number of pruned ears of 10 tea tree specific germplasm resources after grafting
[0053]
[0054]
[0055] As shown in Table 2, after the gra...
experiment example 2
[0057] Using the methods of Example 1 (using the grafting and rapid propagation method of the present invention) and Comparative Example 1 (using the conventional cutting and transplanting method) to propagate a total of 3 tea tree specific germplasm resources of No. 1, No. 2 and No. 3 , and observed the tree height, tree width and the number of pruned ears at the beginning of November when the growth stopped for three consecutive years.
[0058] Table 3. Comparison of the growth vigor and the number of pruned ears of the three tea tree specific germplasm resources under different multiplication methods
[0059]
[0060] As shown in Table 3, the tree height of Guilu No. 1 in the first year of grafting was 61.7cm, which was 2.8cm higher than that in the third year of cutting transplantation, and the number of ears that could be cut in the second year of grafting was 19.1 more than that in the third year of cutting transplantation; Green No. 2 is 63.5cm taller in the first ye...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com