A fluorescent probe for selective recognition of ATP based on aggregation-induced fluorescence enhancement properties, synthesis method and application thereof
A technology of fluorescent probe and synthesis method, which is applied in the field of fluorescent probe and synthesis for selectively identifying ATP, can solve the problems of fluorescence quenching, low detection signal-to-noise ratio, and limit the practical application of ATP fluorescent probe, and achieve the synthesis step. Simple, overcoming easy bleaching, easier to mass-produce and apply
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Synthesis of fluorescent probe 1
[0026]
[0027] (1) Synthesis of Compound 2: Add zinc powder (1.56g, 24mmol) and 4,4'-dibromobenzophenone (408mg, 1.2mmol) into anhydrous tetrahydrofuran, and cool the suspension to 0 ℃. Then titanium tetrachloride (2.276g, 12mmol) was slowly dropped into the mixture with a syringe, and the mixture was refluxed for 4h after stirring at 0°C for 30min. Cool and add sodium carbonate solution dropwise with stirring until no bubbles are produced. Dichloromethane and saturated brine were added to separate liquid and extracted, the organic phase was washed three times with saturated brine, the organic phase was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, concentrated, and separated by column chromatography to obtain compound 2 with a yield of 86%.
[0028] (2) Synthesis of Compound 3: Compound 2 (200mg, 0.31mmol), 4-pyridineboronic acid (305mg, 2.48mmol), Pd(dppf)Cl 2 (200mg, 0.245mmol), CH 2 Cl 2 (1mL), Bu 4 NI (25mg, 0.068mmol) and potass...
Embodiment 2
[0031] ATP probe performance test
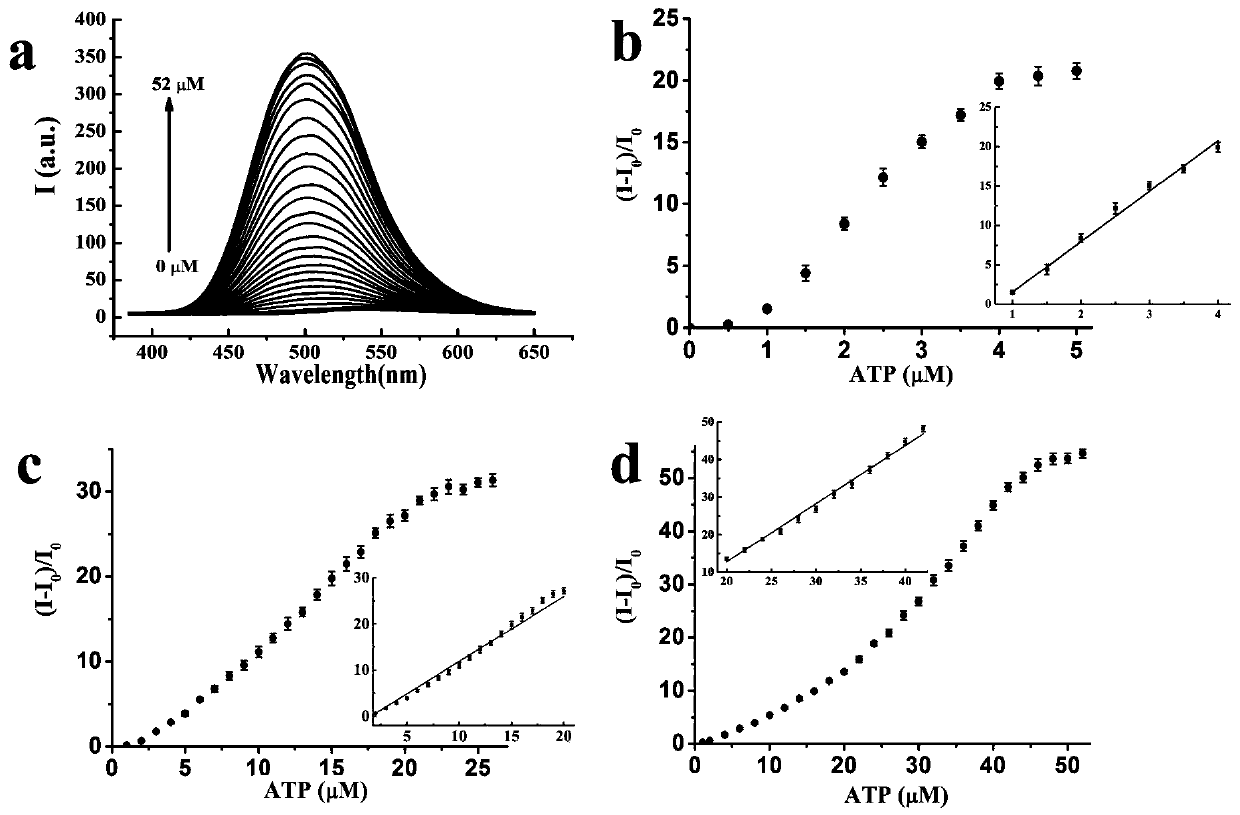
[0032] (1) Fluorescent titration test of fluorescent probe 1 to ATP: Take 5 μL of fluorescent probe 1 in DMSO solution (1 mM) in 2 mL of HEPES buffer solution, and then add different amounts of ATP aqueous solution (1 mM). Fluorescence emission spectra (E x =344nm), the fluorescence intensity of the mixed solution in the concentration range of 1.0 μM to 4.0 μM ATP presents a good linear relationship (such as figure 1 shown in b). When changing the concentration of fluorescent probe 1 to 20.0 μM, the system can show a good linear relationship with the fluorescence intensity of fluorescent probe 1 in the range of 2.0 μM to 20.0 μM ATP concentration (such as figure 1 shown in c). Similarly, when the concentration of fluorescent probe 1 continues to increase to 40.0 μM, the system can present a good linear relationship with the fluorescence intensity of fluorescent probe 1 within the concentration range of 20.0 μM to 40.0 μM ATP (such as fig...
Embodiment 3
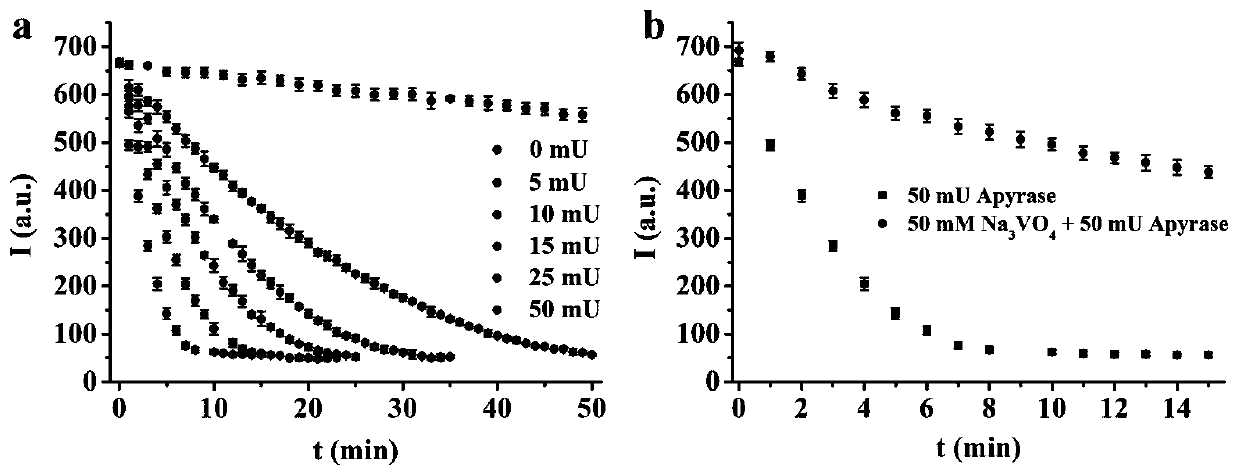
[0035] Monitoring of an ATP hydrolase Apyrase reaction process in the solution: Add different concentrations of ATP hydrolase Apyrase (0,5,10,15,25,50mU) to the HEPES buffer solution containing 20 μM fluorescent probe 1 and 20 μM ATP, respectively, The monitoring system changes the fluorescence intensity with the reaction time at 500nm, and the results show that when there is no Apyrase, the fluorescence intensity of fluorescent probe 1 changes less (3 VO 4 After repeating the above experiments, it was found that due to the activity of the enzyme being controlled by Na 3 VO 4 Inhibition, the decrease rate of the fluorescence intensity of the system with the reaction time is obviously slower (such as image 3 shown in b). It shows that fluorescent probe 1 can be used to monitor the reaction process of ATP hydrolase Apyrase in solution.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com