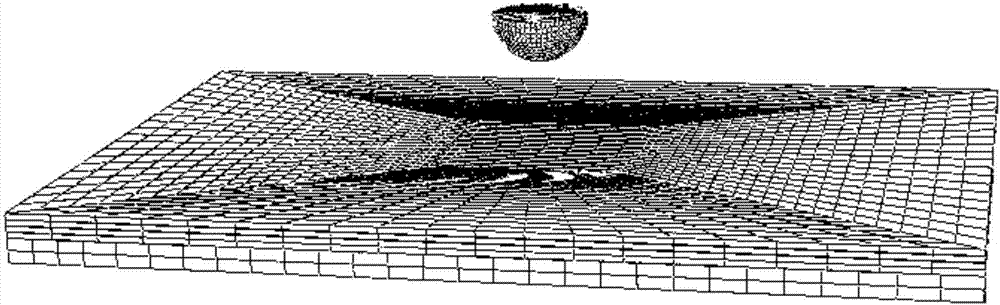
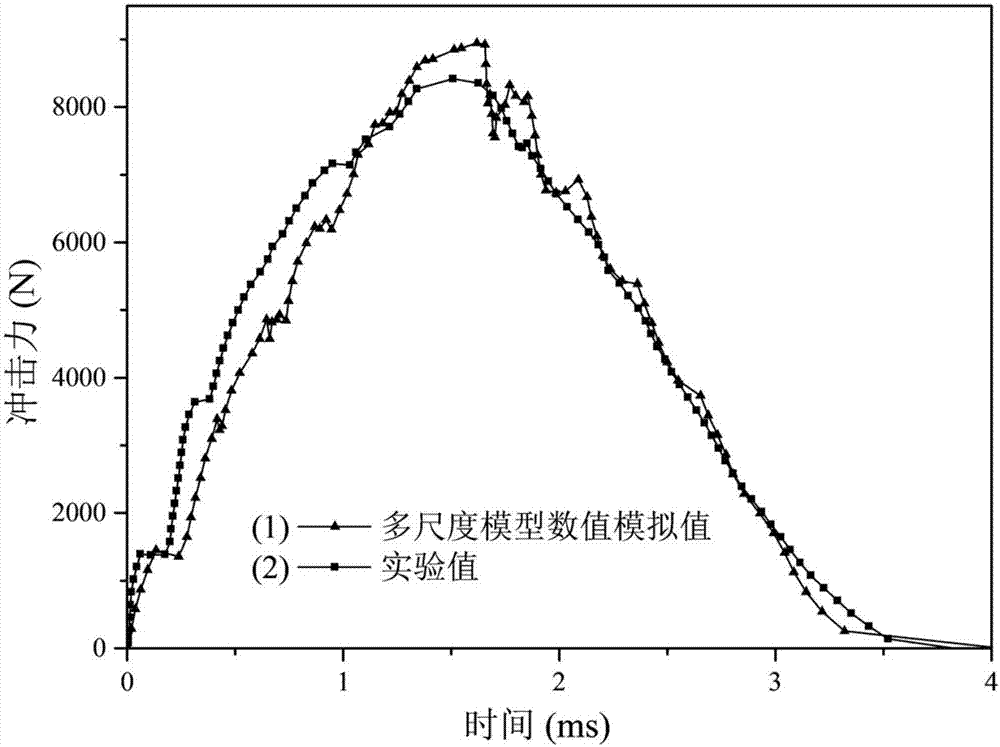
Finite Element Method for Predicting Progressive Failure of Composite Multilayer Thick Plates Under Low Velocity Impact
A composite material and low-velocity impact technology, which is applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to directly apply the three-dimensional PUCK failure criterion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0057] First of all, it needs to be explained that the present invention is an application of computer technology in the field of damage prediction of composite multilayer thick plates. During the implementation of the present invention, the application of multiple software function modules will be involved. The applicant believes that, after carefully reading the application documents and accurately understanding the realization principle and purpose of the present invention, combined with existing known technologies, those skilled in the art can fully implement the present invention by using their software programming skills. Everything mentioned in the application documents of the present invention belongs to this category, and the applicant will not list them one by one.
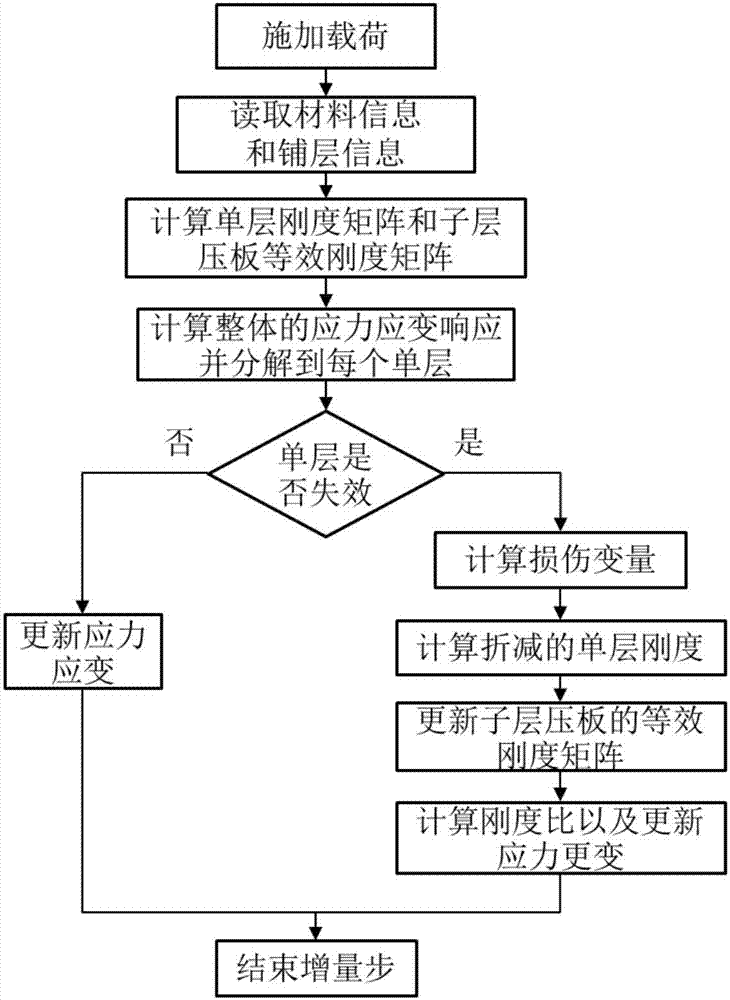
[0058] In the present invention, the finite element method for predicting the progressive failure of composite multilayer thick plates under low-velocity impact includes the following process:
[0059] ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com