Method for improving transplanting survival rate of big magnoliaceae seedlings
A technology of transplanting survival rate and magnolia, which is applied in the field of landscaping, can solve the problems of high transportation and handling costs, unsatisfactory restoration effect, and poor plant landscape effect, so as to achieve good landscape effect, save the cost of binding materials, and ensure the survival of seedlings rate-enhancing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
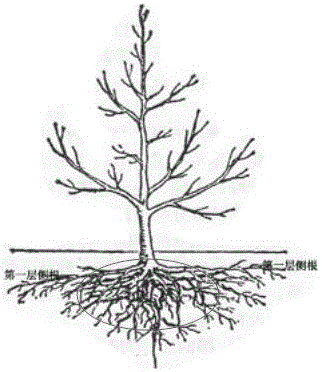
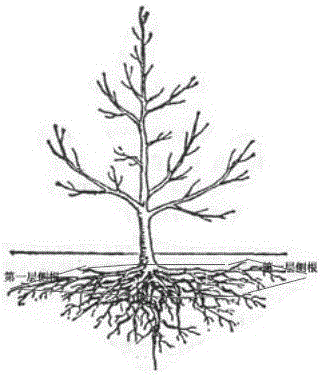
[0031] According to this method, 56 Lechang Michelia seedlings with a DBH of 20 cm were transplanted in Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province in spring. The soil at the excavation site of Lechang Michelia was sandy loam. Digging to 25cm place, its first layer of lateral roots is all dug out, its lower main root and other lateral roots are shoveled off, and the soil on its root system is knocked out to obtain the bare root seedling of Lechang Michelia. After the Lechang Michelia was transported to the transplanting site, it was pruned, with 2 / 3 branches thinned and 4 / 5 leaves removed; planting management was carried out according to other steps of this method. One year after planting, 55 Lechang Michelia trees survived, with a survival rate of 98.2%, and the rate of dead branches of the surviving Lechang Michelia chinensis was 0. The survival rate of ordinary transplanted Lechang Michelia seedlings is less than 60%, and the rate of dead branches after survival is more than 30%. Ado...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Transplant 87 Liriodendron seedlings with a DBH of 15cm in autumn according to this method in Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province. The soil at the excavation site of Liriodendron is sandy loam, and the method of breaking the root soil while excavating is adopted during excavation. Dig out all the lateral roots of its first layer at 30 cm, shovel off its lower main root and other lateral roots, knock out the soil on its root system, and obtain the bare-rooted seedlings of Lechang Michelia. After the Liriodendron is transported to the transplanting point, it is pruned, the amount of thinning is 2 / 3, and all the leaves are removed; planting management is carried out according to other steps of this method. One year after planting, 85 Liriodendron trees survived, with a survival rate of 97.7%, and the rate of dead branches of the surviving Liriodendron was less than 5%. Liriodendron tulipifera seedlings generally have a survival rate of less than 55% after transplanting, and a dead...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com