Method for filling non self-intersecting polygon in FPGA
A filling method and polygonal technology, which is applied in the field of FPGA data processing, can solve problems such as inability to directly fill concave polygons, complex sorting of filling algorithms, and long sorting time, and achieve the effects of reducing sorting calculations, fast filling speed, and reducing time costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
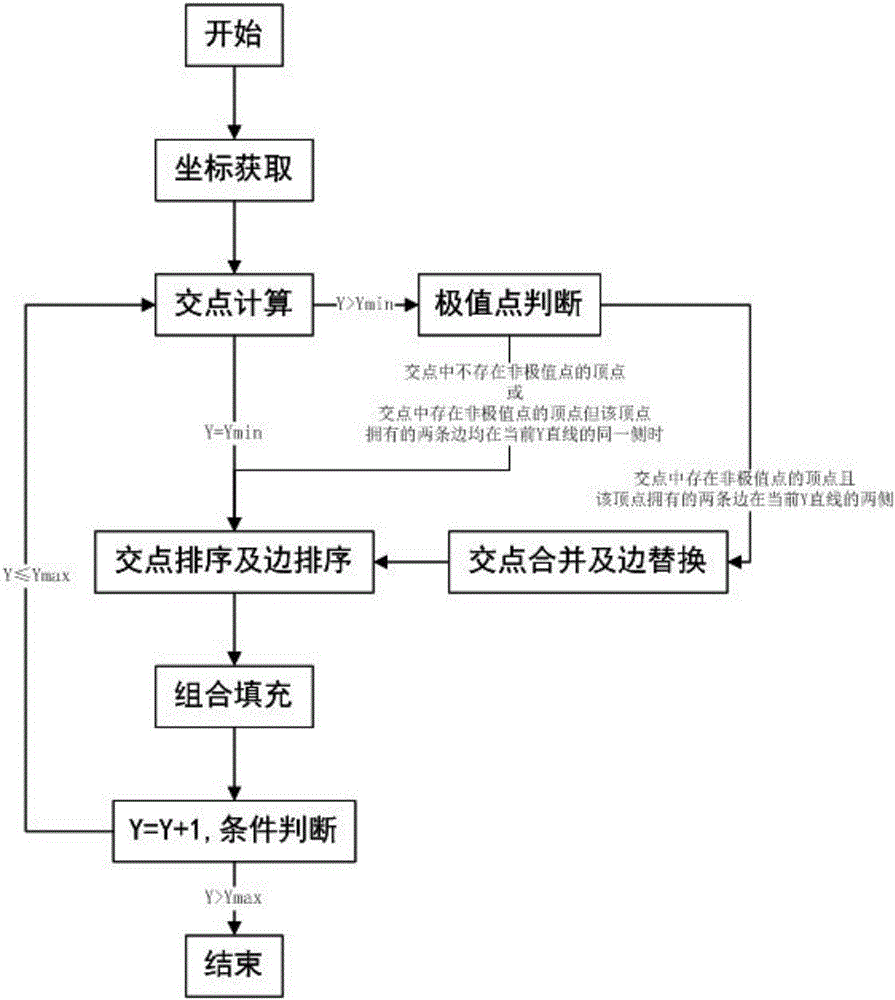
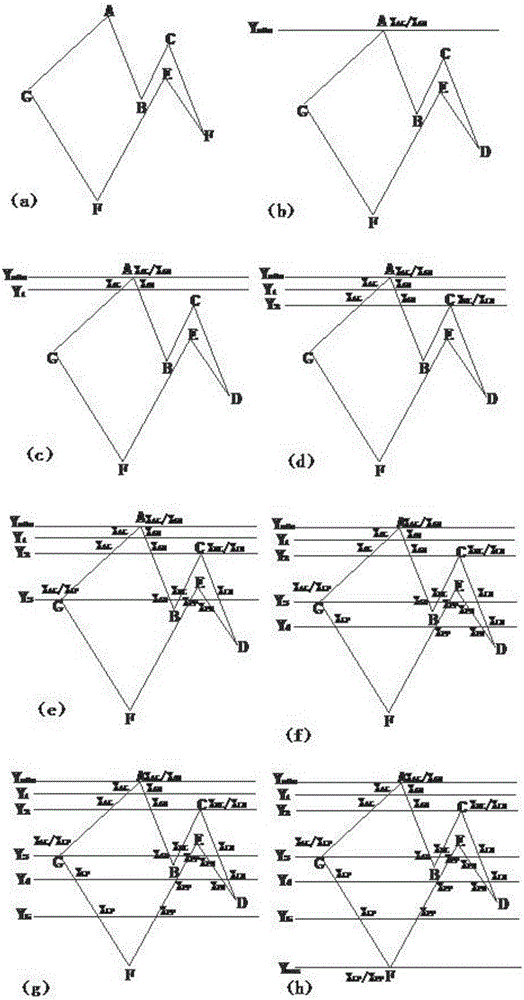
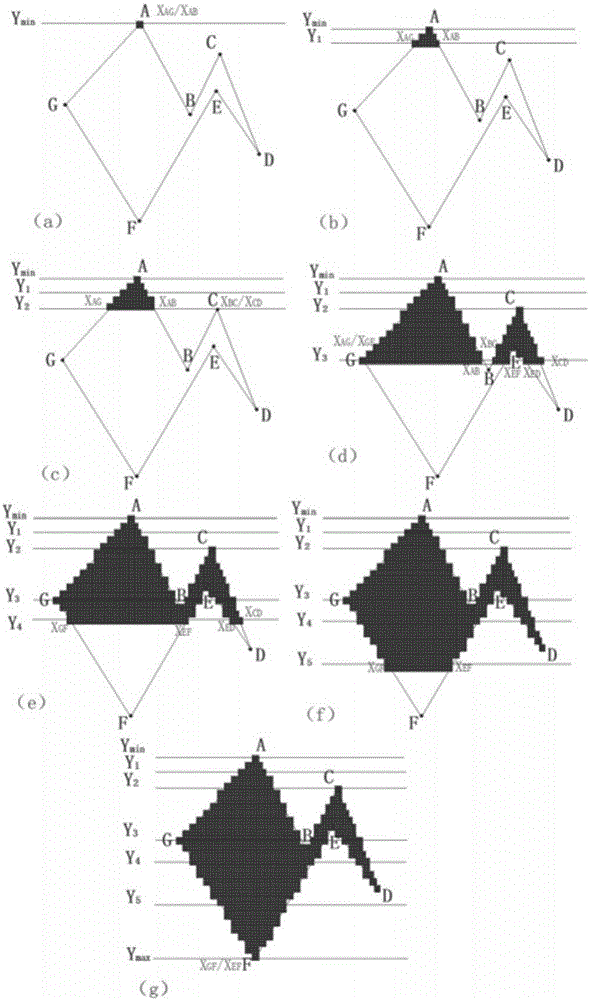
[0044] attached figure 2 (a) is the polygon ABCDEFG to be filled in the present embodiment, and the filling method process of this polygon is as follows:
[0045](1) Coordinate acquisition. Obtain the maximum value, minimum value and non-extreme points of the Y coordinate values of each vertex of the polygon ABCDEFG, such as figure 2 As shown in (a), point A is the minimum value point, namely ; Point F is the maximum value point, namely . Points B, C, D, E, and G are non-extreme points. Number the sides of the polygon ABCDEFG, denoted as AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG, GA.
[0046] (2) Intersection calculation. calculate The intersection of the straight line and the polygon ABCDEFG, such as figure 2 As shown in (b), the intersection points are and , the number of intersection points is 2, and the sides where the intersection points are located are AG and AB.
[0047] (3) Intersection sorting and edge sorting. Compare and the size of the value, , so the orde...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com